Dreams have long fascinated and mystified human beings across cultures and time periods. They offer a glimpse into the subconscious mind, revealing hidden desires, fears, and emotions. However, dream interpretation is not a universal process. Instead, it is heavily influenced by the cultural background of the dreamer. Culture shapes the way dreams are perceived, understood, and analyzed. From the symbols and taboos embedded in different societies to the language and symbols used, the impact of culture on dream interpretation is profound. In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between culture and dreams, examining how cultural factors shape the interpretation of dreams and the significance they hold for individuals and communities worldwide.
The Role of Culture in Dreams
Culture plays a significant role in shaping dreams and their interpretation. Dreams are not just individual occurrences; they are influenced by the collective experiences, beliefs, and values of a particular culture or society. Dreams can be seen as cultural manifestations, reflecting the norms, customs, and social dynamics of a community.
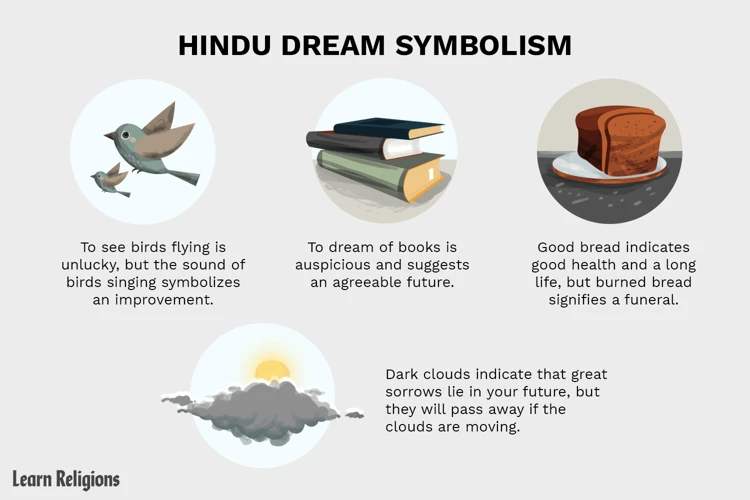
Dreams as Cultural Manifestations: In many cultures, dreams are considered to be messages from the divine or the spiritual realm. For example, in ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Mesopotamia, dreams were often seen as direct communications from the gods. In some indigenous cultures, dreams are regarded as a means of connecting with ancestors or receiving guidance from the spirit world. These cultural beliefs shape the perception of dreams and the significance attributed to them.
Common Cultural Symbols in Dreams: Cultural symbols play a crucial role in dream interpretation. Certain symbols may hold specific meanings within a particular culture. For instance, a lion may symbolize bravery and leadership in Western cultures, while in some African cultures, it could represent royalty or spiritual power. Understanding these cultural symbols is essential to decode the messages hidden in dreams and provide a more accurate interpretation.
Taboos and Superstitions in Dream Interpretation: Culture also influences the taboos and superstitions related to dreams. Some cultures believe that sharing dreams before breakfast can bring bad luck, while others consider dreams of certain animals or natural elements as omens of either good or bad fortune. These cultural taboos and superstitions shape how dreams are perceived and discussed within a society.
Culture plays a foundational role in dreams and their interpretation. By recognizing and understanding these cultural influences, we can gain deeper insight into the rich tapestry of dream symbolism and unlock the hidden messages they hold.
Dreams as Cultural Manifestations
In many cultures, dreams are recognized as powerful cultural manifestations, reflecting the beliefs, traditions, and societal dynamics of a community. These cultures view dreams as a means of communication from the spiritual or divine realm, offering guidance, insights, and messages. For example, in ancient civilizations like Egypt and Mesopotamia, dreams were considered direct messages from the gods or as portals to the supernatural. Aboriginal cultures perceive dreams as a way to connect with ancestors and access ancestral knowledge. Understanding dreams as cultural manifestations allows us to appreciate their significance within a specific cultural context and gain a deeper understanding of the messages they convey. To further explore the role of cultural symbols in dream interpretation, visit our article on the Role of Symbols in Dream Interpretation.
Common Cultural Symbols in Dreams
Common cultural symbols in dreams vary across different societies and carry specific meanings within their respective cultures. These symbols are deeply ingrained in the collective consciousness and can offer valuable insights into the dreamer’s psyche. Here are some examples of common cultural symbols in dreams:
- Animals: Animals often hold symbolic significance in dreams. For instance, in many Native American cultures, the eagle represents spiritual power and wisdom, while the wolf may symbolize intuition and guardianship. Similarly, in Chinese culture, the dragon is associated with strength and good luck.
- Natural Elements: Elements of nature like water, fire, and trees often carry symbolic meanings. For example, water can represent emotions and the unconscious mind. In Hindu culture, the lotus flower signifies purity and spiritual enlightenment.
- Numbers: Numbers can hold cultural significance in dreams. In Western cultures, the number seven is often associated with spirituality and introspection. In Chinese culture, the number eight symbolizes prosperity and good fortune.
- Colors: Colors can be potent symbols in dreams. Each color carries its own cultural connotations and interpretations. For example, in Western culture, the color red can represent passion or danger, while in Indian culture, it is associated with purity and celebration. [Link to the significance of colors in dream interpretation]
- Objects: Everyday objects can also possess symbolic meanings in dreams. A key, for example, might represent unlocking hidden knowledge or opportunities. These interpretations may vary across cultures and personal experiences.
It is important to remember that while these symbols may have cultural significance, individual experiences and personal symbolism can also influence dream interpretation. Keeping a dream journal can help identify recurring symbolic patterns and provide a deeper understanding of the dreamer’s own cultural symbols and their meanings.
Taboos and Superstitions in Dream Interpretation
Taboos and superstitions play a significant role in dream interpretation within different cultures. These cultural beliefs shape the way dreams are perceived and understood, adding an additional layer of complexity to dream analysis.
Below are some examples of taboos and superstitions commonly associated with dream interpretation:
- Avoiding Sharing Dreams: In some cultures, it is believed that sharing dreams before breakfast can bring bad luck or have negative consequences. This belief stems from the idea that dreams are fragile and discussing them prematurely can cause the dreams to fade or lose their significance.
- Animal Dreams: Animals often carry symbolism in dreams, with different cultures attributing various meanings to specific animals. For instance, dreaming of rats may be seen as a sign of impending danger in some cultures, while in others, it may represent resourcefulness or survival instincts.
- Death Dreams: Dreams involving death can be particularly significant and are often seen as omens in many cultures. While interpretations may vary, some believe that dreaming of a deceased loved one is a message from the spirit world, while others perceive it as a warning sign or a reflection of unresolved emotions.
- Water Dreams: Dreams involving water, such as swimming or drowning, can have diverse interpretations based on cultural beliefs. In some cultures, water is associated with purification and cleansing, while in others, it may symbolize emotions or the subconscious mind.
- Prophetic Dreams: Some cultures believe in the power of prophetic dreams, considering them as an insight into future events or a means of receiving divine messages. Dreamers may be encouraged to keep a dream journal and reflect on their dreams to unravel their hidden meanings or potential predictions.
It is essential to be mindful of these taboos and superstitions when approaching dream interpretation within specific cultural contexts. Recognizing and respecting these beliefs can lead to a more accurate understanding of dreams and their significance within a particular cultural framework.
Cultural Variations in Dream Analysis

Eastern vs. Western Interpretation: One of the significant cultural variations in dream analysis is the difference between Eastern and Western approaches. In Eastern cultures, such as China and India, dreams are often seen as messages from the spiritual realm or as reflections of one’s karma. Eastern interpretations focus on the symbolic meaning of dreams, emphasizing the interplay between the dreamer’s inner self and the external world. On the other hand, Western interpretations tend to rely more on psychological explanations, looking at dreams as manifestations of unconscious desires, fears, or unresolved conflicts.
Indigenous Dream Practices: Indigenous communities around the world have their unique approaches to dream analysis. For example, some Native American tribes believe that dreams are a way of receiving guidance and messages from ancestors or spirit guides. These dreams are considered sacred and play an important role in decision-making and spiritual ceremonies. In contrast, Australian Aboriginal cultures emphasize the connection between dreams, the land, and ancestral spirits, viewing dreams as a means of accessing ancient wisdom and ancestral knowledge.
Religious and Spiritual Influences: Religion and spirituality also heavily influence dream analysis. For instance, in Islamic cultures, dreams are seen as a medium for communication with the divine, and Muslim dream interpreters use religious texts, such as the Quran, to decipher dream symbols. Similarly, in Hinduism, dreams are considered a way for deities to communicate with individuals, and dream analysis is guided by ancient scriptures and texts.
Cultural variations in dream analysis reflect the diverse beliefs, values, and spiritual practices across different societies. By considering these variations, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of dreams and their interpretation within cultural contexts.
Eastern vs. Western Interpretation
Eastern and Western cultures have distinct approaches to dream interpretation, reflecting their unique philosophical and cultural perspectives. In Eastern cultures, such as those influenced by Chinese or Indian traditions, dreams are often seen as a source of spiritual insight and guidance. Eastern interpretation focuses on symbolism, paying close attention to the intricate details and hidden meanings within dreams. In contrast, Western interpretation tends to be more psychological and analytical in nature. Freudian and Jungian theories have greatly influenced Western perspectives on dreams, emphasizing the role of the subconscious mind and the use of dream analysis as a tool for self-reflection and understanding. While both Eastern and Western interpretations offer valuable insights into the significance of dreams, their contrasting approaches highlight the diverse ways in which culture shapes the understanding and exploration of one’s dream world.
Indigenous Dream Practices
Indigenous Dream Practices:
Indigenous cultures around the world have unique and intricate dream practices that differ from mainstream interpretations. These practices are deeply rooted in their cultural traditions and spiritual beliefs. Here are some examples of indigenous dream practices:
- Dream Incubation: In many indigenous cultures, dream incubation is a common practice. It involves setting an intention before sleep and seeking guidance or answers through dreams. The dreamer may perform certain rituals or engage in specific preparations to enhance the likelihood of receiving insights or visions during sleep.
- Dream Sharing: Indigenous communities often emphasize the importance of sharing dreams within the community. Dreams are seen as a collective experience, and by sharing dreams with others, individuals gain different perspectives and interpretations. This communal approach to dream sharing reinforces social bonds and promotes a sense of interconnectedness.
- Interpretation by Elders or Shamans: Indigenous cultures often have designated individuals, such as elders or shamans, who possess specialized knowledge and skills in dream interpretation. These spiritual leaders serve as bridges between the dreamer and the spiritual realm. They use their wisdom and experience to decipher the symbolism and messages embedded in dreams.
- Rituals and Ceremonies: Indigenous cultures frequently incorporate dreams into their rituals and ceremonies. Dreams are regarded as powerful sources of guidance and inspiration. They may influence decision-making processes, healing practices, and the overall well-being of the community. Rituals and ceremonies are performed to honor and respect the messages received through dreams.
Indigenous dream practices highlight the deep connection between dreams, spirituality, and cultural identity. These practices demonstrate the value placed on dreams as a means of understanding oneself, one’s community, and the wider universe.
Religious and Spiritual Influences
Religion and spirituality are powerful cultural forces that greatly influence the interpretation of dreams. Different religious and spiritual beliefs shape how dreams are perceived and understood within a particular cultural context.
Religious Beliefs:
- In Christianity, dreams are often seen as a means of divine communication. The Bible contains numerous accounts of prophetic dreams, such as Joseph’s dreams in the Old Testament. Christians may interpret dreams as messages or signs from God, providing guidance or revealing hidden truths.
- In Islam, dreams hold a significant place in the faith. Muslims believe that dreams can be a form of divine revelation, especially within the context of prophethood. Dream interpretation is called “ta’bir” and is considered a skill that can be acquired to understand the messages conveyed through dreams.
- In Hinduism, dreams are believed to be influenced by the deities and can offer insights into one’s past, present, or future. Dreams are seen as a reflection of the soul’s journey and can be interpreted based on the Hindu scriptures, such as the Vedas and Upanishads.
Spiritual Influences:
- New Age and spiritual philosophies often incorporate dream analysis as a tool for self-discovery and personal growth. Dreams are seen as a way for the subconscious mind to communicate and provide insights into one’s emotions, desires, and life path.
- Indigenous cultures often view dreams as a bridge between the physical and spiritual realms. Dreams are seen as a means of receiving guidance from ancestors or connecting with spiritual beings. Indigenous dream practices involve rituals and ceremonies to interpret and honor these spiritual messages.
- Additionally, practices such as meditation, mindfulness, and lucid dreaming are influenced by spiritual and philosophical belief systems. These practices aim to enhance dream recall, promote awareness during dreams, and tap into the spiritual dimensions of the dream experience.
Religious and spiritual influences greatly shape the interpretation and significance given to dreams across different cultures. Understanding these influences is essential in comprehending the depth and complexity of dream analysis within specific cultural contexts.
Culture-Specific Dream Themes

Dreams often reflect the cultural values, traditions, and practices of a particular society, giving rise to culture-specific dream themes. These themes can vary widely across different cultures, offering a unique lens into the collective consciousness and aspirations of the people.
Traditional Wedding Dreams: In many cultures, dreams of weddings are prevalent and hold significant meaning. In Western cultures, wedding dreams are often associated with notions of love, commitment, and partnerships. They may symbolize the desire for a romantic relationship or signify upcoming nuptials. In contrast, in some Asian cultures, wedding dreams can represent familial expectations, societal pressures, or even the notion of arranged marriages. Understanding the cultural context is crucial in interpreting these dream themes accurately.
Death and Afterlife Beliefs: Death is a universal theme that carries diverse cultural interpretations and beliefs. Dreaming about death can be seen as a reflection of one’s attitudes towards mortality in a specific cultural context. For instance, in some cultures, death dreams may signify rebirth, renewal, or the continuity of life after death. In other cultures, they may represent anxieties about mortality or serve as a reminder to cherish and appreciate life. The symbolism and interpretation of death-related dreams are deeply rooted in cultural beliefs and traditions.
Ambition and Success in Modern Society: Dreams often reflect the aspirations and values of the society in which they occur. In modern cultures that emphasize individualism and achievement, dreams related to success, fame, and ambition are common. These dreams may involve scenarios such as receiving accolades, achieving career milestones, or gaining financial wealth. They reflect the cultural emphasis on personal accomplishment and the pursuit of individual goals.
By understanding the culture-specific dream themes, we can gain insights into the shared hopes, fears, and aspirations of different societies. These themes provide a window into the cultural psyche and offer valuable clues for interpreting dreams within their specific cultural contexts.
Traditional Wedding Dreams
Traditionally, weddings hold profound cultural significance and are often associated with dreams of love, commitment, and union. In many cultures, dreaming about weddings is believed to symbolize a joyous union, not only between two individuals but also between families and communities. These dreams may feature elements such as wedding dresses, ceremonies, or wedding rings, each carrying its own cultural symbolism. For example, in Western cultures, a white wedding dress often symbolizes purity and innocence, while in some Asian cultures, the color red is associated with luck and prosperity. Dreaming of a traditional wedding can represent cultural norms and expectations surrounding marriage, family, and societal values. It is important to consider the cultural context when interpreting these dreams, as they can provide insights into the dreamer’s desires for partnership and their relationship with their cultural identity.
Death and Afterlife Beliefs
Cultural beliefs about death and the afterlife have a profound impact on how dreams related to these topics are interpreted. Different cultures hold diverse perspectives on what happens after death, and these beliefs shape the symbolism and meaning attributed to dreams about death and the afterlife.
1. Reincarnation: Some cultures, such as Hinduism and Buddhism, believe in the concept of reincarnation. Dreams about deceased loved ones may be seen as messages that the person has been reborn or is trying to communicate from another realm. These dreams may carry a sense of continuity and offer comfort to those who believe in the cycle of life and death.
2. Ancestral Spirits: In many indigenous cultures, dreams about deceased ancestors are considered significant. These dreams are often seen as a form of communication or visitation from the spirit realm. They may provide guidance, warnings, or blessings and are regarded as an important way to stay connected with one’s lineage and heritage.
3. Judgment and Afterlife: Religions like Christianity and Islam have beliefs in a judgment day and an afterlife. Dreams related to these concepts may be interpreted as symbolic representations of the soul’s journey to heaven, hell, or purgatory. These dreams could involve encounters with divine beings, visions of heavenly landscapes, or symbolic representations of celestial realms.
4. Symbolism of Death: Culture also influences the symbolism associated with death. In some cultures, death is viewed as a transition or a natural part of the life cycle. Dreams about death may be seen as symbolic representations of change, transformation, or endings. Conversely, cultures with strong beliefs in the afterlife may interpret these dreams as messages from the deceased or encounters with spirits.
The interpretation of dreams related to death and the afterlife is deeply influenced by cultural beliefs and religious teachings. Understanding these cultural nuances allows for a more accurate and sensitive interpretation of the symbolism and messages embedded within these dreams.
Ambition and Success in Modern Society
In modern society, ambition and success are highly valued, and these cultural values often find their way into our dreams. Ambition is a driving force for many individuals, and it is not unusual for ambitions and aspirations to manifest in dreams. People may dream about achieving their career goals, gaining recognition, or attaining financial success. These dreams reflect the cultural emphasis placed on ambition and success in contemporary society.
The Pursuit of Success: Dreams about success often symbolize the desire for personal fulfillment and achievement. They may manifest as scenarios where the dreamer is excelling in their chosen field, receiving accolades, or reaching significant milestones. These dreams can provide insight into the dreamer’s goals, motivations, and aspirations.
Societal Pressure and Expectations: The influence of culture on dreams can also be seen in the pressure and expectations placed on individuals to succeed. In societies that value achievement and social status, individuals may experience dreams that reflect the fear of failure, the stress of competition, or the anxiety of not meeting societal expectations. These dreams serve as a reflection of the cultural context in which the dreamer exists.
Perceptions of Success: Culture plays a role in shaping our perceptions of success. In some societies, success may be equated with material wealth and professional accomplishments. In others, success may be associated with personal relationships, spiritual growth, or contributions to the community. These cultural perceptions influence the interpretation of dreams related to success and the specific goals and ideals that are deemed worthy of pursuit.
In modern society, ambition and success are culturally significant, and they can impact our dreams and how we interpret them. Understanding these cultural influences allows us to delve deeper into the meanings behind dreams and gain a broader understanding of the human experience in relation to ambition and success.
The Influence of Language and Symbols

The Influence of Language and Symbols: Language plays a vital role in dream interpretation, as it shapes how individuals perceive and express their dreams. The linguistic diversity across different cultures can lead to variations in dream experiences and interpretations.
The Impact of Linguistic Diversity on Dream Interpretation: Each language has its own set of words, phrases, and idioms that capture specific concepts and emotions. These linguistic nuances can impact how dreams are described and understood. For example, a dream that evokes a feeling of nostalgia may be more explicitly expressed in languages that have specific terms for this sentiment. Conversely, dreams that require elaborate and nuanced descriptions may be more challenging to convey in languages with limited vocabulary.
Symbolism and Cultural Context: Symbols play a significant role in dream interpretation, and their meanings are often shaped by cultural context. A symbol that holds a particular significance in one culture may have a completely different meaning in another. For instance, the color white commonly symbolizes purity and innocence in Western cultures, while in some Eastern cultures, it may symbolize mourning or death. Understanding the cultural connotations and associations can help decipher the symbolism embedded in dreams.
Language and symbols are deeply intertwined, influencing how dreams are communicated and interpreted. Considering both the linguistic and cultural aspects is essential for accurate and comprehensive dream analysis.
The Impact of Linguistic Diversity on Dream Interpretation
Linguistic diversity has a profound impact on dream interpretation. The language we speak frames our thoughts and perceptions, and this extends to our dreams as well. Different cultures and languages assign unique meanings to words and symbols, which can significantly influence the interpretation of dreams. For example, a dream about a “snake” may be seen as a symbol of evil or danger in one culture, while in another, it could represent transformation or healing. The intricacies of language also play a role in how dreams are communicated and understood. Translation challenges may arise when trying to articulate the nuances of a dream, as certain words or expressions may not have direct equivalents in other languages. The linguistic context in which a dream is expressed and interpreted is crucial in capturing its true essence.
Symbolism and Cultural Context
Symbolism and Cultural Context:
When it comes to dream interpretation, symbolism plays a pivotal role. However, the meanings assigned to symbols can vary greatly depending on the cultural context in which they are interpreted. Symbols carry cultural significance and can differ from one culture to another.
Here are a few examples of how symbolism can be influenced by cultural context:
- Animals: Animals hold symbolic value in dreams and can represent different qualities or concepts. For instance, in Western cultures, a snake might symbolize deceit or danger. However, in some indigenous cultures, it may represent wisdom and transformation. Similarly, a crow may be associated with death in some cultures, but it can symbolize intelligence and resourcefulness in others.
- Colors: Colors can have diverse meanings in different cultures. For example, in Western cultures, white is often associated with purity and innocence. However, in some Eastern cultures, white is the color of mourning and death. Similarly, the color red might symbolize passion and love in one culture, while it can represent luck and celebration in another.
- Numbers: Numbers can also carry cultural symbolism. In some cultures, the number seven is considered lucky, while in others it may have spiritual or religious connotations. Similarly, the number four may be seen as unlucky in many East Asian cultures due to its association with death.
Cultural context provides the framework for understanding the symbolism present in dreams. It is important to consider the cultural background of the dreamer and their associated cultural symbols when interpreting dreams. By doing so, we can gain a more nuanced understanding of the messages conveyed through dream symbolism and avoid misinterpretation.
Cultural Factors in Dream Recall and Perception
There are several cultural factors that influence dream recall and perception. These factors shape how individuals within a culture remember and interpret their dreams, contributing to the overall understanding and significance given to these nocturnal experiences.
One cultural factor that impacts dream recall is the sleep environment. Different cultures have varying sleep practices and habits that can influence dream recall. For example, cultures that prioritize uninterrupted sleep may have individuals who experience longer and more detailed dreams due to longer periods of REM sleep. Additionally, cultural beliefs and practices related to dream rituals may also affect dream recall. Some cultures encourage individuals to keep dream journals or engage in specific morning rituals to enhance dream recall. These practices demonstrate the importance placed on dreams within a particular culture.
Another cultural factor is the distinction between collective and individualistic cultures. In collective cultures, such as many Asian cultures, dreams may be seen as shared experiences or as messages from the collective unconscious. Dream interpretation in these cultures often considers the collective, societal implications of dreams rather than focusing solely on the individual dreamer. On the other hand, individualistic cultures, like those in Western societies, tend to prioritize individual experiences and personal interpretations of dreams.
Family and community influence is another cultural factor that affects dream recall and perception. In some cultures, dreams are often discussed and shared within the family or community setting. This communal sharing of dreams can provide additional perspectives for interpretation and validation of dream experiences. In contrast, cultures that discourage open discussion of dreams may lead to individuals having a more private and individualized approach to dream recall and interpretation.
Cultural factors significantly influence how individuals remember and perceive their dreams. By understanding these factors, we can gain insight into the diverse interpretations and significance that dreams hold across various cultures. These cultural influences highlight the complex interplay between society, belief systems, and the world of dreams.
Sleep Environment and Dream Experience
The sleep environment is a crucial factor that can influence the dream experience. Different cultures have varying sleep practices and environments that impact the way dreams are perceived and interpreted. For example, in Western cultures, it is common for individuals to sleep in separate bedrooms, which may result in more individualistic dream experiences. In contrast, in collectivist cultures where co-sleeping is prevalent, dreams may be more influenced by shared experiences and communal values. Additionally, the physical environment, such as the presence of noise, temperature, or lighting, can affect the content and emotional tone of dreams. These cultural variations in sleep environment contribute to the diversity and uniqueness of dream experiences across different societies.
Collective vs. Individualistic Cultures
Collective vs. Individualistic Cultures:
One of the key aspects of culture that influences dream recall and perception is the distinction between collective and individualistic cultures.
| Collective Cultures: | Individualistic Cultures: |
| In collective cultures, such as those found in many Asian, African, and Latin American societies, the emphasis is on the interconnectedness of individuals within a community. Dreams are often seen as part of a collective experience, and the meaning and interpretation of dreams are often sought within the context of the community. Dream symbols and themes are shared and discussed among community members, and collective dream interpretation can involve the input of elders, spiritual leaders, or shamans. | In contrast, individualistic cultures, such as those prevalent in Western societies, prioritize personal autonomy and individual achievement. Dreams are often viewed as a reflection of one’s personal thoughts, desires, and experiences. Dream interpretation in individualistic cultures tends to focus on the individual’s unique perspective and experiences, and the meaning of dreams is often sought through self-reflection and personal introspection. The individual is seen as the authority on their own dreams, and personal journals or dream diaries are commonly used tools for recording and analyzing dreams. |
The cultural distinction between collective and individualistic orientations significantly impacts the way dreams are understood and discussed. While collective cultures emphasize community input and shared interpretation, individualistic cultures emphasize personal autonomy and self-reflection in dream analysis.
Family and Community Influence
Family and community exert a significant influence on the interpretation and perception of dreams. Cultural values and familial beliefs shape how dreams are understood and discussed within these social units.
- Cultural Values: Different cultures place varying emphasis on the importance of dreams within the family and community context. In collectivist cultures, such as many Asian cultures, dreams are often seen as a collective experience that reflects the well-being of the family or community as a whole. This communal perspective influences how dreams are interpreted and shared within these cultures.
- Interpretation Practices: Families and communities often have established methods or rituals for interpreting dreams. These practices may involve seeking guidance from elders, consulting religious or spiritual leaders, or utilizing traditional methods of dream analysis. For example, some indigenous communities have specific individuals, like shamans or tribal healers, who are regarded as experts in dream interpretation.
- Shared Dream Experiences: In some cultures, dreams are seen as a shared experience that can connect loved ones or community members. For example, in certain African tribes, dreams are believed to enable communication between ancestors and the living, creating a sense of interconnectedness and unity. The sharing and discussion of dreams within families and communities reinforce the cultural significance of dreams.
- Family Dream Journals: Keeping dream journals within the family unit is a practice observed in some cultures. This allows family members to document and share their dreams, creating a collective repository of dream experiences. These dream journals can serve as valuable references for future dream interpretations and provide insights into recurring themes or symbols within the family.
The influence of family and community on dream interpretation highlights the social nature of dreams. By examining dreams within the context of familial and communal beliefs, we can gain a deeper understanding of the cultural significance of dreams and their role in connecting individuals to their social networks.
The Role of Cultural Experts
When it comes to interpreting dreams within a cultural context, cultural experts play a vital role. These individuals, often well-versed in the traditions and beliefs of a specific culture, possess the knowledge and understanding needed to provide insightful interpretations.
Shamans, Psychics, and Dream Interpretation: In many indigenous cultures, shamans or spiritual leaders are the primary experts in dream interpretation. They are believed to have a connection with the spiritual realm and possess the ability to communicate with the divine. Shamans may interpret dreams as messages from ancestors or spirits, providing guidance and insight for individuals within the community. Similarly, psychics or clairvoyants in other cultures may specialize in dream interpretation, using their intuitive abilities to decipher the hidden meanings behind dreams.
Traditional Cultural Healing Practices: Dream interpretation is often integrated into traditional healing practices of various cultures. In some cultures, dreams are seen as a means of diagnosing illness or imbalance within the body. Traditional healers may use dreams as a source of insight to guide their treatment methods. For example, in the Aboriginal cultures of Australia, dreams are believed to provide guidance for healing and are an essential aspect of the holistic approach to health and well-being.
Modern Approaches to Cultural Dream Analysis: In contemporary society, there are individuals specializing in cultural dream analysis. These experts have studied and gained knowledge of various cultural symbols, beliefs, and practices from around the world. They utilize this knowledge to provide interpretations that take into account cultural nuances and significance. These modern approaches to cultural dream analysis aim to bridge the gap between ancient traditions and contemporary understanding, helping individuals navigate the complexities of their dreams within their cultural framework.
Consulting cultural experts can provide valuable insights into dream interpretation, as they possess the cultural knowledge necessary to decode the symbols and messages embedded within dreams. Their expertise allows for a deeper understanding of dreams and their significance within specific cultural contexts.
Shamans, Psychics, and Dream Interpretation
Shamans, psychics, and other spiritual practitioners have long played a crucial role in dream interpretation within various cultures. They possess specialized knowledge and skills to interpret dreams in a cultural context, often serving as intermediaries between the dreamer and the spiritual realm. Shamans, for example, are believed to have the ability to communicate with spirits and access hidden knowledge. They can provide guidance and insight into the meaning and significance of dreams, offering a spiritual perspective that goes beyond the traditional psychological interpretations. Psychics, on the other hand, may use their intuitive abilities to tap into the energies surrounding the dreamer and provide interpretations based on their unique spiritual gifts. These cultural experts provide a valuable lens through which dreams can be analyzed, offering individuals a deeper understanding of themselves, their experiences, and their connection to the spiritual world.
Traditional Cultural Healing Practices
Traditional Cultural Healing Practices:
1. Shamanic Healing: Shamanic healing is a traditional cultural practice found in various indigenous communities around the world. Shamans, as spiritual leaders and healers, often incorporate dream interpretation as a tool for healing. They believe that dreams provide insights into the spiritual realm and can guide individuals towards physical and emotional well-being. In shamanic traditions, dreams are viewed as messages from the spirit world and are analyzed to identify the root causes of ailments or imbalances.
2. Rituals and Ceremonies: Many cultures have specific rituals and ceremonies centered around dream interpretation and healing. These rituals often involve gathering community members together to share and interpret dreams. The collective interpretation process allows for a deeper understanding of the dreams and can provide communal support in addressing individual or shared challenges. The rituals may include elements such as chanting, drumming, or the use of sacred objects to enhance the dream interpretation process.
3. Herbal and Medicinal Remedies: Traditional cultural healing practices often incorporate the use of herbal and medicinal remedies alongside dream interpretation. In many indigenous cultures, plants and herbs are believed to possess healing properties and are used to enhance the dream state. Certain plants or herbal preparations may be taken before sleep to induce vivid or prophetic dreams, which are then interpreted to provide insights into a person’s health or well-being.
4. Ancestral Guidance: In some cultures, dreams are seen as a means of receiving guidance from ancestors or deceased loved ones. Dreamers may seek connection and guidance in their dreams by inviting the presence of ancestors through rituals or prayers. The dreams are then interpreted in the context of ancestral wisdom, providing comfort, advice, or warnings to the dreamer.
5. Energy Healing: Traditional cultural healing practices often recognize the role of energy in dreams and overall well-being. Practitioners may work with energy healing techniques such as Reiki or acupuncture to address imbalances or blockages revealed through dream interpretation. These practices aim to restore harmony and balance within the individual’s energy system, promoting healing on physical, emotional, and spiritual levels.
Traditional cultural healing practices encompass a holistic approach to dream interpretation and healing. They recognize the interconnectedness of the mind, body, and spirit, and offer unique insights and methodologies to promote well-being and personal transformation.
Modern Approaches to Cultural Dream Analysis
Modern Approaches to Cultural Dream Analysis: With the evolving understanding of culture and its impact on dream interpretation, modern approaches to dream analysis have emerged. These approaches aim to integrate cultural sensitivity and awareness into the interpretation process, recognizing that dreams cannot be completely detached from their cultural context.
One such approach is cross-cultural dream analysis, which seeks to compare and contrast dream symbols and themes across different cultures. By examining the similarities and differences in dream experiences and interpretations between cultures, researchers and psychologists can gain a broader understanding of the universal aspects of dreams as well as the cultural variations.
Cultural psychologists and anthropologists contribute to the modern approaches to cultural dream analysis by studying dreams within their cultural contexts. They explore how dreams are shaped by cultural experiences, beliefs, and values, and how they can serve as a window into the collective psyche of a society.
Another modern approach is the integration of technology in dream analysis. The use of digital tools and platforms allows individuals from diverse cultural backgrounds to share and analyze their dreams. Online dream forums, social media groups, and dream journaling apps provide spaces for individuals to document their dreams, seek interpretations, and engage in cross-cultural discussions around dream experiences.
Cultural dream workshops and retreats have also gained popularity in recent years. These events bring together people from different cultures and provide a platform for sharing and exploring the cultural aspects of dreams. Participants learn from each other’s experiences, gain insight into the diverse interpretations of dream symbols, and cultivate a deeper understanding of how culture influences dreams.
Modern approaches to cultural dream analysis strive to honor and embrace the cultural diversity present in dream experiences. By recognizing the cultural nuances and unique perspectives, these approaches contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of dreams and their significance in different cultural contexts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, culture has a profound influence on dream interpretation. Dreams are not isolated occurrences but are deeply embedded in the cultural fabric of a society. Cultural beliefs, symbols, and taboos shape the way dreams are perceived, understood, and analyzed. From the spiritual and religious influences to the significance placed on certain symbols, culture plays a pivotal role in decoding the messages hidden within dreams.
Furthermore, cultural variations in dream analysis are evident, as different cultures have unique approaches to interpreting dreams. Eastern and Western cultures, for example, have contrasting interpretations and understandings of dreams. Indigenous cultures often have their own traditional practices for dream analysis, connecting dreams to ancestors and the spirit world. Religious and spiritual influences also play a significant role in how dreams are interpreted within specific cultures.
Language and symbols are additional cultural factors that contribute to dream interpretation. Linguistic diversity can impact dream analysis, as different languages may have different meanings attached to specific words or symbols. Moreover, symbols in dreams are often deeply rooted in cultural contexts. Understanding the cultural connotations of symbols is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Cultural factors also influence dream recall and perception. Sleep environment, collective versus individualistic cultures, and family and community influence can all shape the way dreams are experienced and remembered. Furthermore, cultural experts such as shamans, psychics, and traditional healers play a significant role in interpreting dreams within their respective cultures.
In the realm of dream interpretation, it is essential to recognize and appreciate the diversity of cultural influences. By understanding the role of culture in dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of ourselves, our communities, and the rich tapestry of human experiences reflected in our dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can dreams be influenced by cultural beliefs and practices?
Yes, cultural beliefs and practices have a strong influence on dreams. Different cultures have unique interpretations and meanings attributed to specific symbols, events, or themes in dreams.
2. Are there any universal dream symbols that transcend cultural boundaries?
While some symbols may have universal meanings, many symbols are culture-specific. However, certain symbols like water, fire, and flying tend to have commonly shared interpretations across different cultures.
3. How do cultural taboos affect dream interpretation?
Cultural taboos shape how dreams are perceived and discussed. For example, in some cultures, dreaming about certain animals or objects may be considered taboo or bring about negative associations, influencing the interpretation of the dream.
4. Do different cultures have different approaches to recording and analyzing dreams?
Yes, cultures vary in their practices of recording and analyzing dreams. Some cultures encourage keeping dream journals, while others emphasize oral traditions or communal interpretations within a social setting.
5. Is dream interpretation influenced by religious beliefs?
Religious beliefs can heavily influence dream interpretation. For example, a person’s religious background may shape their interpretation of dreams involving symbols related to their faith or spiritual beliefs.
6. Are dreams affected by language barriers?
Language can impact dream interpretation, as different languages may have unique words or concepts that are difficult to translate. This can influence the accuracy and depth of understanding when interpreting dreams across cultural and linguistic boundaries.
7. How do cultural differences in communication styles affect dream interpretation?
Cultural differences in communication styles can impact the way dreams are expressed and understood. Some cultures may have more indirect or symbolic communication patterns, requiring a deeper understanding of cultural nuances when interpreting dreams.
8. Are dreams influenced by cultural rites and rituals?
Absolutely. Cultural rites and rituals can influence the content and symbolism present in dreams. For example, participating in a traditional ceremony may lead to dreams containing elements or symbols related to the ritual.
9. Can individuals from different cultures have shared dream experiences?
While cultural influences shape dreams, there can still be shared experiences across cultures. For example, dreams related to love, fear, or basic human emotions can be experienced by individuals from different cultural backgrounds.
10. Are there cultural variations in the importance placed on dream interpretation?
Yes, the importance placed on dream interpretation can vary across cultures. Some cultures may view dreams as valuable sources of information and guidance, while others may consider them less significant in daily life.