Have you ever wondered why stress and anxiety seem to invade your dreams, causing vivid and unsettling experiences while you sleep? The impact of stress and anxiety on dreaming is a fascinating and complex topic that many people find themselves curious about. In this article, we will explore the connection between stress, anxiety, and dreaming, delving into the science behind dreams and the ways in which these psychological states can influence our dream experiences. By understanding how stress and anxiety affect our dreams, we can gain insights into the workings of our minds during sleep and find strategies for coping with the often perplexing and disturbing dreams that can arise as a result.
Understanding Stress and Anxiety

Stress and anxiety are two common experiences that most people encounter at some point in their lives. Stress can be defined as the body’s response to a demanding or threatening situation, triggering a range of physical, emotional, and cognitive reactions. On the other hand, anxiety refers to a feeling of unease, worry, or fear about future events or uncertain circumstances. Although stress and anxiety are distinct, they often go hand in hand. Stress can lead to anxiety, and anxiety can exacerbate stress levels, creating a continuous loop of emotional strain. This interplay between stress and anxiety can have a significant impact on various aspects of our lives, including our sleep and dreams. To understand the relationship between stress, anxiety, and dreaming, we need to explore how these psychological states manifest themselves in our dream experiences. Exploring the link between stress, anxiety, and dreaming can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of our minds during sleep.
Definition of Stress
Stress is a natural response that occurs when we face demanding or threatening situations. It is the body’s way of mobilizing resources to deal with perceived challenges. The definition of stress varies across disciplines, but it generally involves a state of physiological and psychological tension. From a psychological perspective, stress can be understood as the subjective experience of feeling overwhelmed, pressured, or unable to cope with the demands placed upon us. This can manifest as feelings of irritability, anxiety, or even a sense of being trapped. Physiologically, stress triggers the release of stress hormones, such as adrenaline and cortisol, which prepare the body for a “fight or flight” response. These hormones increase heart rate, elevate blood pressure, and heighten alertness. Stress can be caused by a variety of factors, including work-related pressures, personal relationships, financial difficulties, or even major life events. It is important to note that stress is not inherently negative and can actually motivate and energize us to perform at our best. However, when stress becomes chronic or overwhelming, it can have detrimental effects on our well-being, including our sleep and dream patterns. Understanding the definition of stress provides a foundation for exploring its impact on our dreams and the strategies we can employ to manage it effectively. To learn more about how stress can influence our dream experiences and the connection between dreams and real-life events, you can refer to the article on dreams and real-life events.
Definition of Anxiety
Anxiety is a multifaceted and complex emotional state that encompasses feelings of worry, fear, and apprehension. It is often characterized by a sense of unease and can manifest in both physical and psychological symptoms. Anxiety can vary in intensity, duration, and triggers from person to person. While it is natural to experience occasional anxiety in response to certain situations, such as speaking in public or going through major life changes, chronic or excessive anxiety can have a debilitating impact on an individual’s daily life. Common symptoms of anxiety include restlessness, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and trouble sleeping. The effects of anxiety can extend beyond the waking hours, infiltrating one’s dreams during sleep. Dream content may be influenced by the themes and emotions associated with anxiety, reflecting the individual’s subconscious concerns and fears. Understanding the definition of anxiety provides a foundation for exploring its influence on dreaming and the potential connections between the mind’s manifestations during sleep and waking life experiences. To learn more about how anxiety influences dreams, refer to our article on the importance of colors in dream analysis. Additionally, gaining insights into the science of dreaming and brain activity can further enhance our understanding of anxiety’s impact on our dream experiences.
The Link between Stress and Anxiety
The link between stress and anxiety is intricate and often intertwined. Both stress and anxiety can have a profound impact on our mental and physical well-being, and they can exacerbate each other’s effects. Here are some key points to understand the connection between stress and anxiety:
1. Physiological response: When we experience stress, our body’s natural fight-or-flight response is triggered, leading to the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. This physiological response can create feelings of anxiety and unease.
2. Psychological impact: Chronic stress can contribute to the development or worsening of anxiety disorders. The constant pressure and strain can overload our coping mechanisms, leading to heightened anxiety levels.
3. Cognitive factors: Stressful situations can alter our thoughts and perceptions, making us more prone to anxious thinking. Negative thought patterns, worry, and rumination can become persistent in the presence of stress.
4. Behavioral changes: Stress can lead to changes in behavior, such as avoidance or withdrawal from certain activities or situations. These behavioral changes can increase feelings of anxiety and perpetuate a cycle of stress and anxiety.
5. Impact on sleep: Stress and anxiety can disrupt our sleep patterns, leading to difficulties falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing restful sleep. The resulting sleep disturbances can further contribute to stress and anxiety.
It is important to recognize the link between stress and anxiety and take proactive steps to manage and reduce both. By addressing the underlying causes of stress and implementing stress-management techniques, we can alleviate anxiety symptoms and improve overall well-being.
The Science of Dreaming

Dreaming is a mysterious and captivating phenomenon that has intrigued scientists and researchers for centuries. At the core of dreaming lies the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep stage, which is often referred to as the dream stage. During REM sleep, our brain becomes remarkably active, and our eyes move rapidly beneath our eyelids. This stage is characterized by heightened brain activity, resembling that of waking consciousness, despite being in a state of deep sleep. Dreams can be vivid, fantastical, and sometimes even surreal, often involving a mix of familiar and unfamiliar elements. While the exact function of dreams is still not fully understood, several theories suggest that dreaming may serve a variety of purposes, including memory consolidation, problem-solving, emotional processing, and simulation of real-life events. By studying the science behind dreaming and delving into the intricacies of REM sleep, researchers have made significant progress in unraveling the mysteries of our dream world.
REM Sleep: The Dream Stage
REM sleep, also known as Rapid Eye Movement sleep, is a fascinating stage of the sleep cycle that is closely associated with dreaming. During this stage, our brain activity becomes more intense, and our eyes move rapidly under our closed eyelids. REM sleep typically occurs multiple times throughout the night, with each REM period gradually increasing in duration. This sleep stage is characterized by a state of heightened brain activity, similar to when we are awake. In fact, research has shown that the brain regions responsible for memory, problem-solving, and emotional processing are particularly active during REM sleep. This increased brain activity, combined with the temporary paralysis of our muscles, allows us to experience vivid and immersive dreams. During REM sleep, our dreams can be filled with a diverse range of emotions, sensations, and narrative structures. Dreams experienced during this stage commonly involve intense visual imagery, intricate storylines, and a strong sense of presence and realism. While the exact function and purpose of dreaming are still being studied, it is believed that REM sleep and the accompanying dream experiences play a crucial role in processing emotions, consolidating memories, and promoting overall psychological well-being. Understanding the significance of REM sleep and its connection to dreaming gives us valuable insight into how stress and anxiety can impact the content and intensity of our dreams.
The Function of Dreams
The Function of Dreams:
– Dreams play a crucial role in the overall functioning of the human mind and have been the subject of intrigue and speculation for centuries. While their exact purpose is still debated among researchers and experts, several theories attempt to explain the function of dreams.
– One common belief is that dreams serve as a way for the brain to process and consolidate information gathered throughout the day. During sleep, our brain organizes and integrates memories, experiences, and emotions, helping us make sense of our waking lives.
– Dreams also provide a platform for problem-solving and creativity. The relaxed state of sleep allows our mind to explore alternative routes and solutions, unconstrained by the limitations of reality. Many inventors, artists, and scientists have drawn inspiration from vivid dreams that have led to groundbreaking ideas and discoveries.
– Another function of dreams is emotional regulation. Dreams can provide a safe outlet for the expression of repressed emotions, allowing the psyche to release and process these feelings. In this way, dreams can act as a form of therapy, helping individuals cope with unresolved conflicts or traumas.
– Additionally, some experts suggest that dreams serve as a simulation for potential real-life events. By simulating threatening situations or practicing new skills during dreams, our subconscious mind prepares us for similar experiences in the waking world, promoting survival instincts and enhancing learning abilities.
Understanding the various functions of dreams gives us a glimpse into the intricate workings of the human mind during sleep. While the exact purpose of dreams may remain elusive, their significance in cognitive and emotional processing is widely recognized.
The Impact of Stress on Dreaming
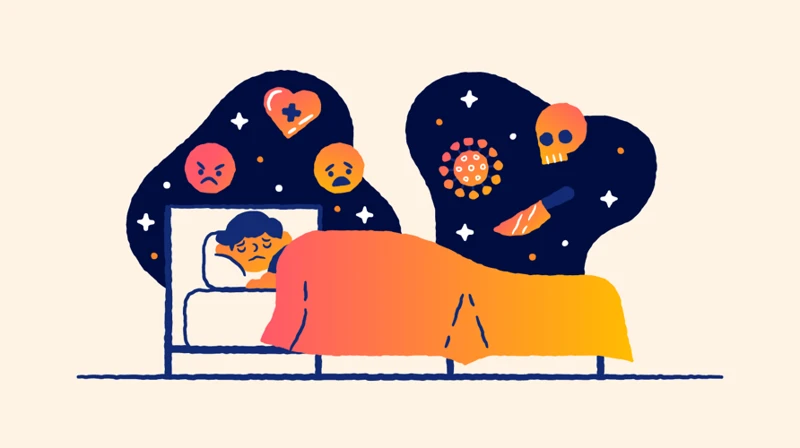
Stress can have a profound impact on our dreaming experiences, altering the frequency, content, and emotional tone of our dreams. One common effect of stress on dreaming is increased dream frequencies. When we are stressed, our minds often remain highly active even during sleep, causing an uptick in dream recall and the number of dreams we experience per night. This may be attributed to the hyperarousal of the brain and heightened cognitive processes triggered by stress. Additionally, stress can give rise to nightmares and disturbing dreams. Nightmares are intense, distressing dreams that can leave us feeling anxious, fearful, or unsettled upon waking. They often contain vivid and realistic scenarios related to the sources of our stress. Lastly, stress can influence the emotional aspect of our dreams, leading to emotional dreams and symbolism. Stressful experiences during waking life can manifest in our dreams as exaggerated or heightened emotions, symbolically representing our inner turmoil. These dreams may serve as a means for our minds to process and cope with the stress we experience in our everyday lives. So, the impact of stress on dreaming goes beyond simple sleep disruptions, shaping the very content and emotional landscape of our dreams.
Increased Dream Frequencies
Increased dream frequencies are a common manifestation of the impact of stress on dreaming. When stress levels are elevated, it can lead to a disruption in sleep patterns, including more frequent awakenings throughout the night. These awakenings can occur during REM sleep, the stage of sleep where dreaming occurs most vividly. As a result, individuals may find themselves waking up multiple times during the night, more aware of their dreams than usual. This heightened dream frequency can be attributed to the hyperarousal state that stress creates in the body. Stress activates the sympathetic nervous system, triggering a heightened state of alertness that can intrude upon the sleep cycle and increase dream recall. Additionally, the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol, can also contribute to increased dream activity. The combination of disrupted sleep patterns and physiological changes during times of stress can lead to a greater number of dreams in a single night. These dreams may vary in content and intensity, reflecting the underlying stressors and emotional experiences that an individual is grappling with.
Nightmares and Disturbing Dreams
Nightmares and disturbing dreams are common manifestations of the impact of stress on dreaming. When experiencing heightened levels of stress, individuals may be more prone to having nightmares, which are intensely distressing dreams that often awaken the dreamer during the night. These nightmares can be vivid, filled with feelings of fear, terror, or unease, and may involve themes of danger, harm, or helplessness. The content of nightmares can vary widely, ranging from realistic scenarios to surreal or fantastical situations. Some individuals may also experience recurring nightmares, where the same disturbing themes or events replay in their dreams on multiple occasions.
Apart from nightmares, stress can also contribute to the occurrence of overall disturbing dreams. These dreams may not qualify as nightmares, but they still evoke negative emotions and leave a lasting impact on the dreamer upon waking. Disturbing dreams can involve a range of unsettling scenarios, such as conflict, loss, failure, or anxiety-inducing situations. These dreams may reflect the individual’s underlying stressors, fears, or unresolved psychological conflicts.
It is important to note that the frequency and intensity of nightmares and disturbing dreams can vary among individuals. Some people may have occasional unsettling dreams during periods of heightened stress, while others may experience more frequent and intense episodes. The exact mechanisms behind why stress gives rise to nightmares and disturbing dreams are not fully understood, but researchers suggest that stress-related hormones and neurotransmitters may play a role.
It is worth mentioning that experiencing nightmares and disturbing dreams can further exacerbate stress and anxiety, creating a vicious cycle. These intense dream experiences can leave individuals feeling anxious, unsettled, and fatigued upon waking, making it more challenging to manage stress levels during waking hours. Understanding the impact of stress on nightmares and disturbing dreams can help individuals develop strategies to promote better sleep and alleviate the burden of these unsettling dream experiences.
| Nightmares and Disturbing Dreams: |
|---|
| – Intensely distressing dreams – Themes of danger, harm, or helplessness – Realistic or surreal scenarios – Recurring nightmares – Negative emotions in disturbing dreams – Reflection of stressors, fears, or conflicts – Frequency and intensity vary among individuals – Role of stress-related hormones and neurotransmitters – Vicious cycle of stress, nightmares, and anxiety |
Emotional Dreams and Symbolism
Emotional dreams and symbolism play a significant role in understanding the impact of stress and anxiety on our dream experiences. Dreams are known to be laden with emotions, and during times of stress and anxiety, these emotions can become intensified. Emotional dreams often reflect the underlying psychological states we are experiencing, serving as a reflection of our fears, worries, and unresolved conflicts. In these dreams, we may encounter familiar individuals, places, or objects that hold emotional significance in our waking life. These symbols and images can represent deeper meanings and serve as metaphors for the stress and anxiety we are grappling with. For example, dreaming of being chased by an unknown assailant may symbolize the feeling of being pursued or overwhelmed by stressors in our waking life. Similarly, dreams of being trapped or unable to escape may reflect the sense of being trapped or overwhelmed by anxiety. By paying attention to these emotional dreams and analyzing the symbolism within them, we can gain insight into our subconscious mind and the emotional impact of stress and anxiety on our dream world. This awareness can be empowering and help us navigate the challenges we face in our waking lives.
The Influence of Anxiety on Dreaming
Anxiety has a profound influence on our dreaming experiences, often intensifying the emotions and sensations we feel during sleep. When we experience heightened levels of anxiety, our dreams may become more intense, vivid, and emotionally charged. These dreams can be characterized by a sense of unease, restlessness, or fear, reflecting the underlying anxiety we are experiencing in our waking lives. Anxiety-induced nightmares are a common phenomenon, causing distress and disrupting our sleep patterns. These nightmares often involve themes of being chased, falling, or being trapped, mirroring the sense of danger or helplessness associated with anxiety. Additionally, anxiety dreams may follow certain patterns, such as recurring themes or situations, which can provide valuable insights into our subconscious fears and concerns. Understanding the influence of anxiety on dreaming can help us navigate and process our emotions more effectively, ultimately leading to a greater sense of inner peace and well-being.
Heightened Dream Intensity
Heightened Dream Intensity refers to the increased vividness, clarity, and emotional depth of dreams that can be experienced when one is dealing with anxiety. When anxiety levels are high, dreams may become more intense and realistic, almost as if they are playing out in real life. This heightened intensity can be attributed to the way anxiety affects the brain and emotional processing. During anxious periods, the amygdala, the part of the brain responsible for emotional responses, becomes hyperactive, leading to heightened emotional experiences in both waking life and dreams. As a result, dreams may feel more emotionally charged, with intense feelings of fear, panic, or unease. Additionally, the heightened activation of the brain during anxiety can lead to increased sensory details in dreams. Colors may appear more vibrant, sounds may be more vivid, and textures may feel more tactile. These heightened sensory experiences can make dreams feel incredibly lifelike and immersive. It is important to note that the intensity of dreams during anxiety can vary from person to person and may also fluctuate based on individual circumstances and stress levels.
Anxiety-Induced Nightmares
Anxiety-induced nightmares are a specific type of dream that occurs as a result of heightened anxiety levels. When we experience anxiety, our minds can become preoccupied with worry, fear, and negative thoughts, which can spill over into our dream states. These nightmares are often characterized by intense and distressing imagery, vivid emotions, and a sense of helplessness or impending danger. Anxiety-induced nightmares can be recurrent, causing significant distress and impacting the quality of sleep. These nightmares may involve themes related to personal fears, phobias, or traumatic experiences. For instance, someone with a fear of flying may have recurring nightmares about being in a plane crash. Similarly, individuals who have experienced a traumatic event may have nightmares that replay the traumatic experience or incorporate elements associated with it. These dreams can be highly realistic and may cause the individual to wake up feeling anxious, frightened, and even physically aroused. The impact of anxiety-induced nightmares extends beyond the duration of sleep, as they can lead to daytime distress, impaired mood, and heightened anxiety levels. Managing anxiety through stress reduction techniques, therapy, and addressing underlying issues is crucial in minimizing the occurrence and impact of anxiety-induced nightmares.
Anxiety Dreams and Patterns
Anxiety dreams are a specific type of dream that is characterized by feelings of unease, worry, or fear. These dreams often reflect the individual’s underlying anxiety and can manifest in different patterns. One common pattern seen in anxiety dreams is the recurrence of specific themes or situations that evoke feelings of anxiety. It could be recurring dreams about being chased, falling, or being unprepared for an important event. These repetitive themes serve as psychological signals, highlighting the areas of stress and anxiety that are most prominent in the individual’s waking life.
Another pattern observed in anxiety dreams is the presence of heightened intensity and vividness. These dreams tend to be more emotionally charged and may involve detailed scenarios that evoke strong feelings of fear or panic. The intense emotions experienced during anxiety dreams can sometimes be so overwhelming that they wake the individual up from sleep, leaving them feeling shaken and anxious upon waking.
In addition to recurring themes and heightened intensity, anxiety dreams can also exhibit symbolic elements. Symbols in dreams serve as representations of subconscious thoughts and emotions. Anxiety dreams often incorporate symbols that reflect the individual’s specific anxieties or fears. For example, a dream about being trapped in a confined space may symbolize a feeling of being trapped in a stressful situation or a sense of suffocation due to anxiety.
It is important to note that anxiety dreams can vary greatly from person to person. While some individuals may experience vivid and intense dreams filled with specific fears and recurring themes, others may have more abstract or symbolic anxiety dreams. The interpretation of these dreams requires a deep understanding of the individual’s personal experiences, fears, and anxieties.
Understanding anxiety dreams and recognizing the patterns within them can provide valuable insights into the individual’s subconscious mind and the underlying sources of their anxiety. By identifying recurring themes, analyzing vividness and intensity, and decoding symbols, individuals can gain a better understanding of their fears and anxieties. This awareness can serve as a starting point for addressing and managing anxiety in their waking life.
Coping with Stress and Anxiety Dreams

Coping with stress and anxiety dreams can be challenging, but there are effective strategies to minimize their impact on our well-being. Stress reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help alleviate overall stress levels, leading to more peaceful and less disruptive dreams. Additionally, incorporating anxiety management strategies into our daily routine can promote a sense of calmness and relaxation before bedtime. This may include practicing mindfulness, engaging in relaxation exercises, or utilizing techniques like progressive muscle relaxation. Journaling and dream interpretation can also be valuable tools for coping with stress and anxiety dreams. By documenting and analyzing our dreams, we can gain insight into their underlying meanings and emotions, helping us address the root causes of our stress and anxiety. Seeking support from friends, family, or a mental health professional can be immensely beneficial in navigating these challenging dreams. By implementing these coping mechanisms, we can work towards reducing the frequency and intensity of stress and anxiety dreams, promoting a better quality of sleep and overall psychological well-being.
Stress Reduction Techniques
One effective way to manage stress and reduce its impact on dreaming is by incorporating stress reduction techniques into your daily routine. These techniques can help calm the mind and body, promoting a sense of relaxation and well-being. One popular technique is deep breathing exercises, which involve taking slow, deep breaths to activate the body’s relaxation response. Another technique is progressive muscle relaxation, where you systematically tense and relax different muscle groups to release tension and promote relaxation. Engaging in mindfulness meditation can also be beneficial, as it allows you to focus on the present moment and let go of stress and anxiety. Additionally, regular physical exercise can help reduce stress by releasing endorphins, improving mood, and promoting better sleep. Journaling can serve as a therapeutic outlet, helping you process stressful emotions and identify patterns or triggers. Lastly, engaging in self-care activities such as taking relaxing baths, practicing yoga, or enjoying hobbies can provide a much-needed break from stress and promote better sleep. Remember, finding the right stress reduction techniques may require some experimentation, so be open to trying various methods until you find what works best for you.
Anxiety Management Strategies
When it comes to managing anxiety, there are various strategies that can be effective in reducing its impact on our daily lives. Here are some approaches that can help alleviate anxiety symptoms and promote a sense of calm and well-being:
1. Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing, can activate the body’s relaxation response and help to reduce anxiety. Focus on slow, deep breaths, inhaling through the nose and exhaling through the mouth.
2. Exercise Regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity can help to release endorphins, improve mood, and reduce anxiety levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking, jogging, or yoga, on most days of the week.
3. Practice Mindfulness: Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation or body scans, can help to calm an anxious mind and bring attention to the present moment. Set aside dedicated time each day to engage in mindfulness practices and cultivate a sense of inner peace.
4. Establish a Routine: Creating structure and consistency in your daily life can help to reduce anxiety and provide a sense of stability. Establish a regular sleep schedule, meal times, and designated periods for work, relaxation, and self-care.
5. Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Both caffeine and alcohol can increase feelings of anxiety and disrupt sleep patterns. Limit your consumption of these substances, particularly in the evening, to promote better sleep and overall well-being.
6. Seek Support: Don’t hesitate to reach out for support from friends, family, or a mental health professional. Talking to someone about your anxiety can provide validation and guidance, and therapy can offer coping strategies tailored to your individual needs.
Remember, it’s important to find the strategies that work best for you and to be patient with yourself as you navigate the process of managing anxiety. Implementing these anxiety management strategies can help reduce the impact of anxiety on your daily life and, ultimately, contribute to more peaceful and restful nights of sleep.
Journaling and Dream Interpretation
Journaling and dream interpretation can be incredibly useful tools for coping with stress and anxiety dreams. Keeping a dream journal allows you to capture the details and emotions of your dreams, providing a valuable outlet for expressing and processing your experiences. When you wake up from a stressful or anxiety-inducing dream, take a few moments to jot down any vivid imagery, themes, or emotions that stood out to you. This practice can help you gain a better understanding of the underlying stress or anxiety triggers that may be present in your subconscious mind. As you continue to journal your dreams over time, you may begin to notice patterns or recurring symbols that can offer insights into your psychological state. Dream interpretation involves analyzing these symbols and themes to uncover deeper meanings and connections to your waking life. It’s important to note that dream interpretation is subjective and personal, and there is no one-size-fits-all approach. However, exploring the symbolism and themes in your dreams can be a powerful tool for self-reflection and gaining a greater understanding of your subconscious thoughts and emotions. You can also seek the guidance of a therapist or dream expert to help you navigate the interpretation process.
The Role of Therapy and Support
When dealing with the impact of stress and anxiety on dreaming, seeking therapy and support can be incredibly valuable. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a common therapeutic approach that can help individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors, ultimately reducing stress and anxiety levels. Through CBT, individuals can learn effective coping mechanisms and stress management techniques that can positively impact their sleep and dreaming patterns. Another beneficial avenue is joining stress and anxiety support groups, where individuals can share their experiences, gain support from others facing similar challenges, and learn from one another’s coping strategies. Additionally, engaging in journaling and dream interpretation can provide insights into the underlying causes of stress and anxiety dreams. By recording and interpreting our dreams, we can gain a deeper understanding of our subconscious thoughts and emotions, facilitating self-reflection and personal growth. It is important to remember that seeking professional help and support from others can offer valuable tools and resources to navigate the challenging impact of stress and anxiety on our dreams and overall well-being.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a widely recognized and effective therapeutic approach for managing stress and anxiety. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to these psychological states. When it comes to coping with stress and anxiety dreams, CBT can be an invaluable tool.
Here are some key aspects of CBT that can help individuals in managing stress and anxiety dreams:
1. Identifying and challenging negative thoughts: CBT helps individuals become aware of their negative thought patterns and teaches them techniques to challenge and reframe these thoughts. By recognizing and disputing irrational or distorted thinking, individuals can reduce the emotional impact of stress and anxiety dreams.
2. Behavioral interventions: CBT encourages individuals to engage in activities that promote relaxation and reduce stress. This may include practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or engaging in regular exercise. By incorporating these behaviors into their daily routine, individuals can create a more relaxed and conducive environment for sleep, thereby minimizing the occurrence of stress and anxiety dreams.
3. Developing coping strategies: CBT equips individuals with practical tools and techniques to manage stress and anxiety in both waking life and within dreams. This may involve learning stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness or meditation, to regulate emotions and promote a sense of calm. Additionally, individuals may learn specific strategies to address anxiety dreams, such as imagery rehearsal therapy, where they practice mentally rehearsing more positive dream scenarios.
4. Managing sleep hygiene: CBT emphasizes the importance of maintaining healthy sleep habits, known as sleep hygiene. This includes establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing the sleep environment for optimal rest. By improving sleep quality and quantity, individuals can potentially reduce the frequency and intensity of stress and anxiety dreams.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy offers a comprehensive and evidence-based approach for individuals struggling with stress and anxiety dreams. Working with a trained therapist can provide personalized guidance and support to help individuals effectively manage their emotions, thoughts, and behaviors, both during sleep and in waking life.
Stress and Anxiety Support Groups
Stress and anxiety support groups are valuable resources for individuals who are looking for a supportive community to help them manage and cope with their mental health challenges. These groups bring together individuals who are experiencing similar struggles with stress and anxiety, providing a safe and non-judgmental space for sharing experiences, seeking guidance, and offering emotional support. Participating in a stress and anxiety support group can help individuals realize that they are not alone in their struggles and can provide a sense of belonging and validation. These groups often follow a structured format, allowing participants to discuss their challenges, share coping strategies, and learn from one another’s experiences. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques are often incorporated into these support groups, helping individuals develop effective tools for managing stress and anxiety. Group members can receive valuable feedback, encouragement, and insights from others who have faced similar difficulties, fostering a sense of community and solidarity. Stress and anxiety support groups can be either in-person or online, providing flexibility for individuals to connect with others based on their preferences and needs. These groups are facilitated by trained professionals or peers who have expertise in managing stress and anxiety. Attending a stress and anxiety support group can be an empowering step towards healing and personal growth, providing individuals with a network of support to navigate their journey towards emotional well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the impact of stress and anxiety on dreaming is undeniable. As we have explored throughout this article, stress and anxiety can significantly influence the frequency, intensity, and content of our dreams. Increased dream frequencies, disturbing nightmares, emotional symbolism, heightened dream intensity, anxiety-induced nightmares, and recurring anxiety dream patterns are all common experiences that can arise due to stress and anxiety. However, it is important to remember that stress and anxiety dreams are a natural part of the human experience and can serve as a reflection of our inner thoughts, emotions, and concerns. Managing stress and anxiety through various techniques like stress reduction, anxiety management, journaling, and therapy can help alleviate the impact of these psychological states on our dreams and overall well-being. By acknowledging and understanding the relationship between stress, anxiety, and dreaming, we can gain valuable insights into our own mental and emotional state. Ultimately, finding effective coping strategies and seeking support when needed can help us navigate the intricacies of our dream world and achieve a sense of balance and tranquility in our waking lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between stress and anxiety?
While stress is a response to external pressures or demands, anxiety is a feeling of worry or unease about future events or uncertain circumstances.
How do stress and anxiety affect our sleep patterns?
Stress and anxiety can disrupt our sleep patterns by making it difficult to fall asleep, causing frequent awakenings during the night, and leading to restless or restless sleep.
Do stress and anxiety impact our dreams?
Yes, stress and anxiety can impact our dreams by increasing dream frequencies, causing nightmares, and influencing the content and emotions experienced in our dreams.
What is REM sleep?
REM sleep, or rapid eye movement sleep, is the stage of sleep during which most dreaming occurs. It is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreams.
Why do we dream?
The function of dreams is not fully understood, but theories suggest that dreaming helps consolidate memories, process emotions, and problem-solve. Dreams may also serve as a way for the brain to simulate and prepare for future events.
Can stress increase the frequency of our dreams?
Yes, stress can increase the frequency of our dreams. When we are under stress, our brain remains more active during sleep, resulting in a higher occurrence of dream experiences.
Why do nightmares and disturbing dreams occur?
Nightmares and disturbing dreams often occur as a result of elevated stress and anxiety levels. These dreams can be the mind’s way of processing negative emotions, fears, and traumatic experiences.
What are anxiety-induced nightmares?
Anxiety-induced nightmares are vivid and intense dreams that are directly influenced by anxiety. These nightmares often feature scenarios related to the person’s specific anxieties or fears.
Is dream interpretation useful in understanding stress and anxiety?
Yes, dream interpretation can be an effective tool for understanding and processing stress and anxiety. Analyzing dream symbolism and themes can provide insights into the underlying emotions and issues that contribute to these psychological states.
How can journaling help with stress and anxiety dreams?
Journaling can help with stress and anxiety dreams by providing an outlet for expressing and reflecting on the emotions and experiences encountered in dreams. It allows individuals to gain a deeper understanding of their dreams and identify patterns or triggers that contribute to stress and anxiety.