Living with narcolepsy can be a challenging journey, affecting various aspects of daily life. From social interactions to work performance, narcolepsy can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being. This article explores the symptoms, prevalence, and causes of narcolepsy. Additionally, it delves into the consequences of narcolepsy on social life, work and education, and relationships. Strategies for coping with narcolepsy, such as maintaining good sleep hygiene, scheduling strategic rest, and managing symptoms, are discussed. The article also provides an overview of treatment options available and highlights the importance of support systems and resources for individuals with narcolepsy. Whether you’re looking for ways to cope with narcolepsy or seeking information to support a loved one, this article aims to provide valuable insights into the impact of narcolepsy on daily life, coping strategies, treatment options, and available support systems.
What is Narcolepsy?

Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. People with narcolepsy often experience excessive daytime sleepiness and may have sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep during the day, known as sleep attacks. These sleep attacks can occur at any time and in various situations, making it challenging for individuals with narcolepsy to stay awake and alert.
Definition and Symptoms
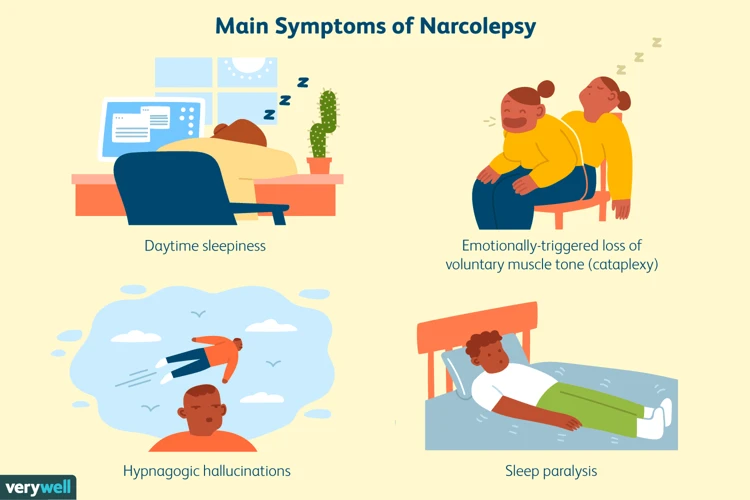
The defining characteristic of narcolepsy is the presence of excessive daytime sleepiness. Individuals with narcolepsy often feel an overwhelming urge to sleep and struggle to maintain wakefulness throughout the day. Other common symptoms include:
- Cataplexy: Sudden loss of muscle tone, usually triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or surprise.
- Sleep paralysis: Temporary inability to move or speak when falling asleep or waking up.
- Hypnagogic hallucinations: Vivid and often terrifying hallucinations that occur when falling asleep or waking up.
- Fragmented nighttime sleep: Individuals with narcolepsy may experience disrupted and restless sleep, leading to frequent awakenings during the night.
Prevalence and Causes
Narcolepsy affects approximately 1 in 2,000 individuals worldwide, with equal prevalence among men and women. While the exact cause of narcolepsy is still not fully understood, researchers believe that it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Studies have shown a strong association between narcolepsy and a specific gene variant called HLA-DQB1*06:02, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Additionally, an autoimmune response may play a role in the destruction of hypocretin-producing cells in the brain, which regulate wakefulness and sleep.
For more information on the science behind narcolepsy, you can refer to this article.
Definition and Symptoms
Narcolepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and a lack of control over sleep-wake cycles. The main symptom of narcolepsy is excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) that is not relieved by sufficient sleep. People with narcolepsy often have an irresistible urge to nap or fall asleep at inappropriate times and may experience sudden and uncontrollable sleep attacks during the day.
In addition to excessive daytime sleepiness, individuals with narcolepsy may also experience other symptoms:
- Cataplexy: This is a sudden loss of muscle tone that can range from a slight weakness in the muscles to a complete collapse. Cataplexy is often triggered by strong emotions such as laughter, surprise, or excitement. It can cause temporary paralysis and hinder a person’s ability to move or speak.
- Sleep paralysis: Sleep paralysis is a state of temporary inability to move or speak that occurs when falling asleep or waking up. It can be a frightening experience as individuals may feel fully conscious but unable to move any part of their body.
- Hypnagogic hallucinations: These are vivid and often terrifying hallucinations that occur while falling asleep or waking up. These hallucinations can be auditory, visual, or tactile and can create a sense of fear or confusion.
- Fragmented nighttime sleep: People with narcolepsy often have disrupted and fragmented nighttime sleep. They may experience frequent awakenings throughout the night, leading to a feeling of unrested sleep.
For more information on the connection between narcolepsy and mental health, including dreaming and emotional well-being, you can refer to this article.
If you are interested in understanding narcolepsy in children, including signs, diagnosis, and intervention, you may find this article helpful.
Prevalence and Causes
The prevalence of narcolepsy is estimated to be around 1 in 2,000 individuals worldwide. This means that narcolepsy is relatively rare, but it still affects a significant number of people. Men and women are equally likely to develop narcolepsy.
Causes of Narcolepsy
While the exact causes of narcolepsy are not yet fully understood, several factors are believed to contribute to the development of the condition.
Genetics: There is evidence to suggest that narcolepsy may have a genetic component. Research has shown that individuals with certain variants of the HLA-DQB1*06:02 gene are more likely to develop narcolepsy. However, having this gene variant does not guarantee that a person will develop the condition.
Autoimmune Dysfunction: It is thought that narcolepsy may involve an autoimmune response in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the brain that produce hypocretin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate wakefulness and REM sleep. The exact trigger for this autoimmune response is unknown.
Environmental Factors: Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to certain viruses or infections, have been suggested as possible triggers for narcolepsy. However, more research is needed to fully understand the role of these factors in the development of the condition.
To learn more about the link between narcolepsy and mental health, as well as the impact of narcolepsy on children, you can refer to these articles.
The Impact of Narcolepsy on Daily Life
Narcolepsy can have significant social and emotional consequences for individuals affected by the disorder. Excessive daytime sleepiness and unpredictable sleep attacks may lead to feelings of embarrassment, frustration, and isolation. People with narcolepsy often face challenges in maintaining social relationships and participating fully in social activities. They may fear being judged or misunderstood when they suddenly fall asleep or experience other symptoms in public. This can result in a sense of social withdrawal, decreased self-esteem, and even symptoms of depression or anxiety.
The impact of narcolepsy extends to work and education settings as well. Excessive sleepiness can impair an individual’s ability to concentrate, focus, and perform at optimal levels. It may also lead to reduced productivity, frequent absenteeism, and even accidents or errors at work or school. Managing narcolepsy symptoms, such as sleep attacks and difficulty staying awake during long meetings or lectures, can be an ongoing challenge. The need for napping or taking breaks throughout the day to manage fatigue may also be perceived as disruptive or problematic in certain work or educational environments.
Narcolepsy can have a profound impact on personal relationships. Partners, family members, and close friends may struggle to understand the nature and severity of narcolepsy symptoms. The unpredictability of sleep attacks and other symptoms can create strain and frustration in relationships, leading to misunderstandings, feelings of resentment, or a sense of burden for the affected individual and their loved ones. Communication and education about narcolepsy can play a crucial role in fostering understanding, empathy, and support within relationships.
Social and Emotional Consequences
The impact of narcolepsy extends beyond the physical symptoms and can have significant social and emotional consequences. Excessive daytime sleepiness can lead to difficulties in maintaining social interactions and participating in daily activities. People with narcolepsy may constantly struggle to stay awake during meetings, social gatherings, or even while driving, which can result in feelings of embarrassment and isolation.
Additionally, the unpredictable nature of narcolepsy symptoms, such as sudden sleep attacks or cataplexy episodes triggered by emotions, can affect emotional well-being. Individuals with narcolepsy may experience frustration, anxiety, and depression as they navigate the challenges of their condition. The fear of falling asleep or experiencing cataplexy in public settings can lead to social withdrawal and a decreased quality of life.
It is important for individuals with narcolepsy to seek support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals to better manage the social and emotional consequences of the condition. Understanding and education about narcolepsy can also help friends and loved ones provide appropriate support and reduce stigmatization.
For more information on the connection between narcolepsy and mental health, including the impact on dreaming and emotional well-being, you can refer to this article.
Challenges with Work and Education
Narcolepsy can present significant challenges in the workplace and educational settings. The unpredictable nature of narcolepsy symptoms, such as excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks, can interfere with an individual’s ability to perform tasks effectively and maintain productivity. These challenges may lead to difficulties in various aspects:
- Work Performance: The excessive daytime sleepiness experienced by individuals with narcolepsy can impact concentration, memory, and overall cognitive function. This can make it challenging to stay focused and perform tasks efficiently, potentially leading to decreased work performance and productivity.
- Safety Concerns: The sudden onset of sleep attacks can pose safety risks, especially in occupations that require operating machinery or driving vehicles. Individuals with narcolepsy may need to take extra precautions and make accommodations to ensure their safety and the safety of those around them.
- Stigma and Misunderstanding: Unfortunately, narcolepsy is still widely misunderstood, and individuals may face stigmatization or discrimination in the workplace or educational settings. Educating employers, colleagues, and educators about narcolepsy can help create a more supportive and understanding environment.
- Academic Challenges: Students with narcolepsy may experience difficulties in their studies due to excessive daytime sleepiness, fragmented nighttime sleep, and difficulties in maintaining alertness during classes. Teachers and educational institutions can provide accommodations and support to help students manage their condition and excel academically.
It is crucial for individuals with narcolepsy to communicate their needs and seek appropriate accommodations and support to overcome these challenges. Open dialogue with employers, educators, and colleagues can foster a supportive environment that allows individuals with narcolepsy to thrive in their work or educational pursuits.
Effects on Relationships
Living with narcolepsy can have a significant impact on personal relationships. The unpredictable nature of narcolepsy symptoms, such as sudden sleep attacks and cataplexy, can lead to difficulties in maintaining regular social activities and can be misunderstood by others.
1. Strained Intimacy: Narcolepsy can affect intimate relationships, as the symptoms, especially cataplexy, may interfere with physical closeness and intimacy. Fear of triggering cataplexy episodes can create a sense of anxiety and reduce spontaneity in romantic relationships.
2. Social Withdrawal: Excessive daytime sleepiness and the need for frequent napping or rest can lead to individuals with narcolepsy withdrawing from social activities. They may fear embarrassing themselves or experiencing judgment from others. As a result, relationships can suffer as social interactions diminish.
3. Lack of Understanding: Narcolepsy is still widely misunderstood, and individuals with narcolepsy may face skepticism or disbelief from friends, family, and even healthcare providers. This lack of understanding can strain relationships and lead to feelings of isolation and frustration.
4. Communication Challenges: The symptoms of narcolepsy, such as fragmented sleep and cognitive difficulties, can impact communication skills. Individuals with narcolepsy may experience difficulties in expressing themselves, remembering conversations, or staying engaged in social interactions, which can affect the quality of their relationships.
5. Supportive Relationships: Despite the challenges, strong and supportive relationships can make a significant positive impact on the lives of individuals with narcolepsy. Understanding and empathetic partners, family members, and friends can provide a safe and accepting environment, helping individuals with narcolepsy navigate the ups and downs of their condition.
For more information on the connection between narcolepsy and mental health, including the impact on dreaming and emotional well-being, you can refer to this article.
Coping Strategies for Narcolepsy
Sleep Hygiene and Healthy Lifestyle Habits
Establishing good sleep hygiene is crucial for individuals with narcolepsy. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime. It is advisable to limit caffeine and alcohol intake, as these can disrupt sleep patterns. Additionally, engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a healthy diet can contribute to overall better sleep quality.
Nap Scheduling and Strategic Rest
Naps can be an essential tool for managing excessive daytime sleepiness. It is recommended to schedule short, strategic naps throughout the day to help alleviate fatigue. Brief power naps lasting around 15-20 minutes can provide a quick boost of energy. Finding a quiet and comfortable place to rest during the day, such as a designated nap room at work or school, can also be beneficial.
Managing Cataplexy and Other Symptoms
Cataplexy episodes can be disruptive and potentially dangerous. Exploring coping mechanisms such as identifying triggers and learning relaxation techniques can help manage and minimize the impact of cataplexy. It is essential to communicate with healthcare providers and explore medication options to control symptoms. Joining support groups and connecting with individuals who share similar experiences can provide valuable insights and coping strategies.
Sleep Hygiene and Healthy Lifestyle Habits
When managing narcolepsy, implementing good sleep hygiene practices and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits can play a significant role in improving sleep quality and overall well-being. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Consistent sleep schedule: Stick to a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, including weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use blackout curtains or a sleep mask to eliminate external light, and consider using earplugs or white noise machines to minimize noise disruptions.
- Avoid stimulating activities before bedtime: Limit exposure to electronic devices and bright screens at least an hour before bed. Engage in relaxing activities such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing meditation to promote a calm and restful state.
- Regular exercise: Engaging in physical activity regularly can help regulate sleep patterns. Incorporate moderate exercise into your daily routine, but avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it may interfere with sleep.
- Healthy eating habits: Maintain a balanced diet and avoid consuming large meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Opt for lighter, sleep-friendly snacks if needed.
- Reduce stress: Implement stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness practices, to promote relaxation and better sleep quality.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can create an environment that supports better sleep and helps manage the symptoms of narcolepsy.
Nap Scheduling and Strategic Rest
Nap scheduling and strategic rest are essential components for managing narcolepsy and minimizing excessive daytime sleepiness. By incorporating planned naps into their daily routine, individuals with narcolepsy can improve alertness and reduce the frequency of sleep attacks. Here are some strategies for effective nap scheduling:
- Short, regular naps: Taking short naps of around 15-20 minutes can help alleviate sleepiness without interfering with nighttime sleep. It’s advisable to schedule these naps strategically, ideally during periods when sleepiness is most pronounced.
- Avoiding long naps: Although long naps can provide temporary relief from sleepiness, they can disrupt nighttime sleep and lead to grogginess upon waking. It’s best to limit nap duration to prevent interference with nighttime rest.
- Creating a comfortable nap environment: Selecting a quiet, darkened, and comfortable space for napping can enhance the quality of rest and promote relaxation. Earplugs, eye masks, and comfortable bedding can contribute to a more peaceful nap experience.
- Strategic rest breaks: In addition to planned naps, individuals with narcolepsy can benefit from frequent rest breaks during the day. These short breaks can be used to relax, engage in calming activities, or simply close the eyes and rest, helping to combat daytime sleepiness.
By implementing these nap scheduling and strategic rest strategies, individuals with narcolepsy can better manage their symptoms and maintain optimal daytime functioning.
Managing Cataplexy and Other Symptoms
One of the most challenging symptoms associated with narcolepsy is cataplexy, which is the sudden loss of muscle tone and control. While there is no cure for cataplexy, there are strategies and medications available to help manage its impact on daily life. Here are some approaches that can be effective in managing cataplexy and other symptoms:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants, can help reduce the frequency and severity of cataplexy episodes. These medications function by stabilizing and regulating the neurotransmitters in the brain that are involved in controlling muscle tone.
- Lifestyle modifications: Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage cataplexy and narcolepsy symptoms. These include practicing good sleep hygiene, maintaining a regular sleep schedule, and avoiding triggers that may induce cataplexy, such as strong emotions or excessive alcohol consumption. A healthy lifestyle, incorporating regular exercise and a balanced diet, can also contribute to overall well-being and help minimize symptom severity.
- Regular napping: Strategic napping can be a useful coping mechanism for individuals with narcolepsy. Scheduled short naps throughout the day can help alleviate excessive daytime sleepiness and reduce the likelihood of sudden sleep attacks. It is important to create a comfortable and conducive environment for napping, such as a quiet and dark room.
- Social support: Building a strong support system and educating family, friends, and coworkers about narcolepsy can greatly contribute to managing its impact. By understanding the condition and its symptoms, loved ones can provide support and assistance during episodes of cataplexy or excessive daytime sleepiness. Open communication can help alleviate feelings of embarrassment or isolation and foster a supportive environment for individuals with narcolepsy.
It is essential for individuals with narcolepsy to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific symptoms and needs. By implementing a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, and support systems, individuals with narcolepsy can effectively manage cataplexy and other symptoms, allowing for a better quality of life.
Treatment Options for Narcolepsy

While there is currently no cure for narcolepsy, there are several treatment options available to manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with the condition.
Stimulant Medications and Wake-Promoting Agents
Stimulant medications, such as amphetamines and methylphenidate, are commonly prescribed to combat excessive daytime sleepiness in individuals with narcolepsy. These medications help promote wakefulness and increase alertness. Modafinil and armodafinil, wake-promoting agents, are also used to alleviate symptoms of daytime sleepiness without the stimulant effects associated with traditional medications.
Antidepressants and Sodium Oxybate
In cases where cataplexy is a prominent symptom, antidepressant medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may be prescribed. These medications help control cataplexy episodes by regulating neurotransmitters in the brain.
Sodium oxybate, also known as gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), is another medication that can be prescribed for the treatment of cataplexy. It is taken at night to improve nighttime sleep quality and reduce daytime sleepiness and cataplexy episodes.
Behavioral Therapies and Sleep Medications
In addition to medication, behavioral therapies can be helpful in managing narcolepsy symptoms. Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can address any psychological factors contributing to sleep disturbances and provide strategies for improving sleep hygiene. Sleep medications, such as sedatives or hypnotics, may also be prescribed to help regulate sleep patterns and improve the quality of nighttime sleep.
It is important for individuals with narcolepsy to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific symptoms and needs.
Stimulant Medications and Wake-Promoting Agents
Stimulant medications and wake-promoting agents are commonly used in the treatment of narcolepsy to combat excessive daytime sleepiness and improve wakefulness. These medications work by stimulating the central nervous system, increasing alertness, and reducing the frequency of sleep attacks. Here are some commonly prescribed stimulant medications and wake-promoting agents for narcolepsy:
- Methylphenidate: This stimulant medication is often prescribed to promote wakefulness and reduce daytime sleepiness. Methylphenidate works by increasing the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, which enhances alertness and attention.
- Amphetamines: Drugs such as dextroamphetamine and modafinil are commonly used to treat narcolepsy. These medications stimulate the release of certain neurotransmitters, promoting wakefulness and reducing excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Sodium oxybate: Also known as gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), sodium oxybate is a central nervous system depressant that is used to treat both excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy in individuals with narcolepsy. It helps promote more restful nighttime sleep and reduces the occurrence of cataplexy attacks.
- Pitolisant: Pitolisant is a newer medication that acts as a selective histamine 3 (H3) receptor antagonist. By blocking these receptors, pitolisant increases the release of histamine, which promotes wakefulness and reduces daytime sleepiness.
It’s important to note that these medications should only be prescribed and taken under the supervision of a healthcare provider with experience in treating narcolepsy. The specific medication and dosage will vary depending on individual needs and may require adjustments over time.
Antidepressants and Sodium Oxybate
Antidepressants and sodium oxybate are two commonly used medications in the treatment of narcolepsy.
Antidepressants:
Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are sometimes prescribed to manage narcolepsy symptoms. While these medications are primarily used to treat depression, they can also help reduce excessive daytime sleepiness and improve overall alertness in individuals with narcolepsy. Antidepressants work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, promoting wakefulness and mood stabilization.
Sodium Oxybate:
Sodium oxybate, also known as gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), is a central nervous system depressant that is used in the treatment of narcolepsy with cataplexy. It is typically taken at night and works by promoting deep sleep and reducing the frequency and intensity of cataplexy episodes. Sodium oxybate helps improve nighttime sleep quality and can also help reduce excessive daytime sleepiness. It is a controlled substance due to its potential for abuse and is tightly regulated.
It’s important to note that these medications should only be used under the guidance and prescription of a healthcare professional, as they may have potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Behavioral Therapies and Sleep Medications
Behavioral therapies and sleep medications are commonly used to help manage the symptoms of narcolepsy and improve overall sleep quality. These treatment approaches aim to regulate sleep-wake patterns, promote restful sleep, and reduce daytime sleepiness.
Behavioral Therapies:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT helps individuals with narcolepsy develop strategies to modify negative thought patterns and behaviors that may contribute to sleep disturbances. It can also address any underlying sleep-related anxiety or insomnia.
- Sleep Hygiene Education: Sleep hygiene practices involve adopting healthy sleep habits and creating a conducive sleep environment. This may include maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding stimulants close to bedtime, and incorporating relaxation techniques before sleep.
- Nap Management: Strategic nap scheduling can help individuals with narcolepsy combat excessive daytime sleepiness. Short, intentional naps taken at regular intervals during the day can provide necessary rest and help mitigate sleep attacks.
- Stimulus Control: Stimulus control therapy involves establishing a strong association between the bed and sleep. This includes using the bed only for sleep, eliminating other stimulating activities, and maintaining a consistent bedtime routine.
Sleep Medications:
Sleep medications may be prescribed to individuals with narcolepsy to help regulate sleep patterns and reduce daytime sleepiness. These medications are typically prescribed on an individual basis, taking into account factors such as symptom severity and overall health. Common sleep medications used in the management of narcolepsy include:
- Modafinil and Armodafinil: These FDA-approved wake-promoting agents help promote wakefulness during the day and can improve alertness and reduce excessive daytime sleepiness.
- Sodium Oxybate: Sodium oxybate, also known as gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), is a medication that helps regulate sleep patterns and reduce cataplexy. It is usually taken in divided doses before bedtime and during the night.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), may be prescribed to manage symptoms of cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations.
In some cases, a combination of behavioral therapies and sleep medications may be recommended to achieve optimal management of narcolepsy symptoms.
Support Systems and Resources for Narcolepsy
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with narcolepsy can be immensely helpful. Support groups and online communities provide a safe space for individuals to share their experiences, ask questions, and receive support from others who can relate. These groups often offer valuable insights, coping strategies, and emotional support. Popular online communities for narcolepsy include forums, social media groups, and dedicated websites where individuals can engage in discussions, share resources, and build meaningful connections with others in similar situations.
Advocacy organizations play a crucial role in raising awareness about narcolepsy and advocating for the needs of individuals affected by this condition. These organizations provide valuable resources, educational materials, and support networks. They aim to empower individuals with narcolepsy by providing information about the latest research, treatment options, and coping strategies. Many advocacy organizations also organize educational events, conferences, and webinars where individuals can learn from experts in the field and connect with others in the narcolepsy community.
By accessing support groups, online communities, and resources provided by advocacy organizations, individuals with narcolepsy can find comfort, guidance, and a sense of belonging. These support systems can help individuals better navigate the challenges of daily life with narcolepsy and offer a space for sharing triumphs, challenges, and personal stories.
Support Groups and Online Communities
Being diagnosed with narcolepsy can feel overwhelming, but finding support from others who understand can make a significant difference. Support groups and online communities provide valuable resources and a sense of belonging for individuals with narcolepsy. These platforms offer a safe space to share experiences, ask questions, and receive support from others who are going through similar challenges.
Support Groups
Support groups for narcolepsy are typically formed locally and meet regularly, either in person or virtually. These gatherings provide an opportunity for individuals with narcolepsy to connect face-to-face, share their stories, and offer mutual support. Support groups may be organized by healthcare providers, narcolepsy advocacy organizations, or community centers.
In these groups, participants can find comfort in knowing they are not alone and gain insights from others who have learned to navigate living with narcolepsy. Sharing tips, discussing coping strategies, and hearing success stories can provide encouragement and motivation for managing the challenges presented by narcolepsy.
Online Communities
Online communities offer a convenient and accessible way for individuals with narcolepsy to connect with others from all over the world. These communities exist in the form of forums, social media groups, and dedicated websites. They provide a platform for individuals to seek advice, share their experiences, and find emotional support.
Within these communities, individuals can engage in discussions, ask questions, and learn from the experiences of others. The anonymity of online platforms can make it easier for individuals to open up about their struggles and seek guidance without fear of judgment.
Some online communities also provide access to educational materials, resources, and updates on narcolepsy research. These platforms can be especially helpful for individuals who may not have access to local support groups or prefer to connect with a larger community.
For individuals seeking more information on the mental health aspects of narcolepsy and its impact on emotional well-being, this article offers in-depth insights.
Advocacy Organizations and Educational Materials
For individuals with narcolepsy, finding support and reliable information is crucial. There are several advocacy organizations and educational resources available that can provide valuable assistance and guidance.
1. Narcolepsy Network: Narcolepsy Network is a non-profit organization dedicated to providing education, support, and advocacy for individuals with narcolepsy and their families. They offer a variety of resources, including online forums, educational materials, and support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges.
2. American Sleep Association: The American Sleep Association is a trusted source for comprehensive information on sleep disorders, including narcolepsy. They provide educational materials, articles, and resources to help individuals understand their condition and explore available treatment options.
3. National Sleep Foundation: The National Sleep Foundation is committed to improving sleep health for all individuals. They offer educational materials, webinars, and informational resources that cover various sleep disorders, including narcolepsy.
4. The Hypersomnia Foundation: The Hypersomnia Foundation aims to raise awareness and support research efforts for rare sleep disorders, including narcolepsy. They provide educational materials, webinars, support groups, and opportunities for individuals to contribute to research studies.
By accessing these advocacy organizations and educational materials, individuals with narcolepsy and their loved ones can gain knowledge, connect with supportive communities, and stay informed about the latest advancements in narcolepsy research and treatment.
Conclusion
Narcolepsy can have a profound impact on an individual’s daily life, affecting not only their sleep patterns but also their social, emotional, and professional well-being. Understanding the symptoms, prevalence, and causes of narcolepsy is crucial in providing appropriate support and resources for individuals living with this condition.
While there is no cure for narcolepsy, there are various coping strategies and treatment options available to manage its symptoms. Maintaining good sleep hygiene, scheduling strategic rest periods, and managing symptoms like cataplexy can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with narcolepsy.
Treatment options for narcolepsy include the use of stimulant medications, wake-promoting agents, antidepressants, and sodium oxybate. Behavioral therapies and sleep medications can also be effective in reducing symptoms and improving overall sleep quality. It is important for individuals with narcolepsy to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans.
Support systems and resources, such as support groups and online communities, play a crucial role in providing emotional support and information-sharing for individuals with narcolepsy. Advocacy organizations and educational materials can also help raise awareness and provide valuable resources for individuals with narcolepsy and their loved ones.
In conclusion, narcolepsy is a complex neurological disorder that requires comprehensive management, ranging from lifestyle adjustments to medical interventions. By utilizing coping strategies, exploring treatment options, and accessing support systems, individuals with narcolepsy can lead fulfilling lives and navigate the challenges associated with this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the risk factors for developing narcolepsy?
The primary risk factor for developing narcolepsy is believed to be genetics. It is more common in individuals who have a family history of the condition. Certain genetic variations, such as the HLA-DQB1*06:02 gene variant, are strongly associated with narcolepsy.
Can narcolepsy be diagnosed in children?
Yes, narcolepsy can occur in children, although it is less common compared to adults. Diagnosing narcolepsy in children can be challenging as the symptoms may be initially attributed to other conditions. Identifying signs of narcolepsy in children and seeking early intervention is crucial for managing the condition effectively. You can learn more about narcolepsy in children in this article.
Are there any lifestyle factors that worsen narcolepsy symptoms?
Yes, certain lifestyle factors can exacerbate narcolepsy symptoms. Irregular sleep patterns, a lack of quality sleep, and excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption can all contribute to increased daytime sleepiness and reduced alertness in individuals with narcolepsy.
Is narcolepsy associated with other mental health conditions?
There is a connection between narcolepsy and mental health. Studies have shown a higher prevalence of conditions such as depression and anxiety among individuals with narcolepsy. The impact of narcolepsy on emotional well-being and the relationship between narcolepsy and mental health are explored in this article.
Are there any natural remedies or alternative treatments for narcolepsy?
While there is no cure for narcolepsy, various strategies and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms. These include maintaining good sleep hygiene, establishing regular sleep schedules, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in regular exercise. It’s important to note, however, that alternative treatments should be discussed with a healthcare professional and used in conjunction with traditional medical approaches.
Can narcolepsy be treated with medication?
Yes, medication is a common treatment approach for narcolepsy. Stimulant medications, such as modafinil and methylphenidate, are often prescribed to promote wakefulness and reduce daytime sleepiness. Sodium oxybate, an FDA-approved medication, is also used to manage symptoms of narcolepsy, particularly cataplexy. Antidepressant medications can be prescribed to manage symptoms like cataplexy and improve sleep quality.
What are some coping strategies for managing narcolepsy at work or school?
Coping with narcolepsy at work or school involves implementing practical strategies. Taking regular short naps during breaks, creating a comfortable and sleep-friendly work or study environment, and practicing good time management can help individuals with narcolepsy stay productive and alert. Implementing strategies for managing cataplexy, such as avoiding emotional triggers, can also be beneficial.
Can narcolepsy affect an individual’s driving ability?
Yes, narcolepsy can impact an individual’s driving ability due to excessive daytime sleepiness and potential sleep attacks. It is important for individuals with narcolepsy to assess their driving abilities and, if necessary, make accommodations, such as avoiding long drives or taking regular breaks to rest during journeys.
What support systems are available for individuals with narcolepsy?
Individuals with narcolepsy can benefit from support systems such as support groups and online communities. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and valuable insights into managing narcolepsy. Additionally, advocacy organizations and educational materials offer resources and information to help individuals navigate their condition.
Is narcolepsy a progressive condition?
Narcolepsy is not considered a progressive condition, meaning that the symptoms do not worsen over time. With proper management, individuals with narcolepsy can lead fulfilling lives, although symptoms may vary in severity and require ongoing treatment and lifestyle adjustments.