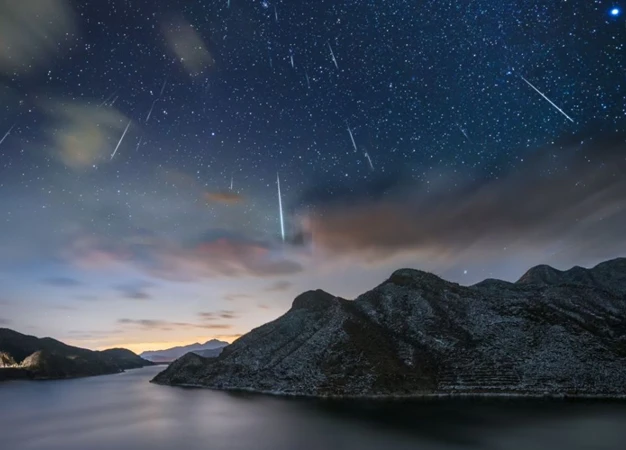
Imagine standing outside on a clear, dark night, gazing up at the vast expanse of the sky. Suddenly, streaks of light start to paint the heavens as dazzling meteors soar across the atmosphere. These spectacular displays, known as meteor showers, have captured the wonder and curiosity of humanity for centuries. But what is the significance of these celestial events? How have they impacted human civilizations and contributed to scientific discoveries? In this article, we will delve into the realm of famous historical meteor showers, their mesmerizing beauty, and the profound insights they have provided to astronomers and scientists throughout history. So, fasten your seatbelts and prepare for an exhilarating journey into the fascinating world of meteor showers.
Impact on Human Civilizations

The impact of meteor showers on human civilizations cannot be underestimated. Throughout history, these celestial events have held great significance in various cultures around the world. They have been revered as omens, symbols of change, and even divine interventions. Ancient civilizations often attributed meteor showers to gods or supernatural forces, associating them with messages or warnings. These awe-inspiring displays have inspired stories, myths, and folklore that have been passed down through generations. Meteor showers have also played a vital role in shaping our understanding of the universe. In recent times, scientists have conducted extensive research to study the composition and trajectory of meteors, uncovering valuable insights about the origins of our solar system and the universe at large. The impact of meteor showers on human imagination, creativity, and scientific inquiry cannot be overstated. They continue to captivate astronomers and amateur stargazers alike, evoking a sense of wonder and curiosity that transcends time and culture. To learn more about capturing the beauty of meteor showers through photography, check out our article on capture meteor shower photography. If you’re interested in observing meteor showers with the naked eye, be sure to read our tips on observing meteor showers with the naked eye. And if you’re curious about the mysteries and unanswered questions surrounding meteor showers, we invite you to explore our article on exploring the mysteries of meteor showers and their unanswered questions.
Scientific Discoveries
Scientific discoveries resulting from the study of meteor showers have significantly expanded our knowledge of the universe. Firstly, meteor showers have made a tremendous contribution to the field of astronomy. By observing the patterns and characteristics of meteor showers, scientists have been able to gather valuable data about the composition and movement of meteors. This data has allowed them to study the origins of these celestial objects and gain a deeper understanding of the formation and evolution of our solar system. Meteor showers have provided vital insights into the evolutionary history of Earth and other celestial bodies. The study of meteors has revealed evidence of ancient impacts, shedding light on past cosmic events that have shaped our planet’s geological and biological history. The analysis of meteorites that have survived their journey through the atmosphere has also offered valuable information about the composition and structure of other planets and asteroids. These scientific discoveries have opened up new avenues for research and continue to fuel our curiosity about the universe we inhabit.
1. Contribution to Astronomy
The contribution of meteor showers to the field of astronomy has been immense. These celestial events have provided astronomers with valuable data and insights into the nature of our solar system and beyond. By studying the patterns and characteristics of meteor showers, scientists have been able to analyze the composition and origin of meteors, shedding light on the mysteries of our universe. Meteor showers offer a unique opportunity to observe and study the debris left behind by comets and asteroids as they intersect Earth’s orbit. The analysis of meteorites, fragments of meteors that survive the journey through Earth’s atmosphere and land on the surface, has provided scientists with important clues about the early formation of our solar system. These extraterrestrial objects carry chemical compositions that differ from those found on Earth, providing a glimpse into the building blocks of planets and their evolution. Additionally, by tracking the paths and trajectories of meteors during meteor showers, astronomers can trace their origins back to specific comets or asteroids, allowing for a better understanding of the dynamics and interactions within our solar system. Meteor showers have therefore played a crucial role in expanding our knowledge of the cosmos and deepening our understanding of our place in the universe.
2. Evolutionary Insights
Evolutionary insights gained from studying meteor showers have provided scientists with valuable information about the development of life on Earth. One significant aspect is the role of meteors in delivering organic molecules, including amino acids, to our planet. The building blocks of life, such as nucleobases and sugars, have been discovered in meteorites that have fallen to Earth. These findings suggest that the ingredients necessary for life may have originated in space and were transported to our planet through meteoric impacts. This concept, known as panspermia, speculates that life on Earth may have been seeded by these extraterrestrial materials. The study of meteor showers has also shed light on the mass extinctions that have occurred throughout Earth’s history. One notable example is the Chicxulub impact, where a massive asteroid collided with Earth approximately 66 million years ago. This catastrophic event is believed to have caused the extinction of the dinosaurs and ushered in a new era for mammalian dominance. By studying the craters left behind by these impacts and the geological records associated with them, scientists have gained insights into the effects of such events on global ecosystems and the subsequent adaptive radiation of species. Meteor showers, with their cosmic origins, have proven to be invaluable in unraveling the mysteries of life’s origins and the evolution of Earth’s biodiversity.
Famous Historical Meteor Showers
Famous historical meteor showers have left an indelible mark on human history and continue to fascinate us with their celestial splendor. Among the most renowned meteor showers is the Leonids, named after the constellation Leo, which produces a breathtaking display of shooting stars. Occurring annually between November 15th and 20th, the Leonids are known for their intense meteor storms, with thousands of meteors streaking across the sky per hour. Another popular meteor shower is the Perseids, which takes place in August each year. With its origins in the debris left by the Swift-Tuttle comet, the Perseids boast a high frequency of meteors and can be easily observed by the naked eye. Lastly, the Geminids shower, which occurs in mid-December, is known for its dazzling display of multicolored meteors. With origins in the asteroid 3200 Phaethon, the Geminids offer a visual treat for stargazers around the world. These famous meteor showers have captivated humanity for centuries and continue to inspire awe and wonder as we gaze up at the night sky.
1. Leonids
The Leonids meteor shower is one of the most famous and captivating celestial events in history. Named after the constellation Leo, from where they appear to radiate, the Leonids have been observed for over a thousand years. Their significance lies not only in their breathtaking beauty but also in their remarkable intensity. The Leonids are known for producing stunning meteor storms, where hundreds or even thousands of meteors can be seen streaking across the night sky every hour. The most notable peak of the Leonids occurred in 1833, when it was described as a rainfall of meteors. This event, often referred to as the “Leonid meteor storm of 1833,” left a lasting impression on those who witnessed it. It was reported that the sky was illuminated with an incredible number of meteors, creating an otherworldly spectacle. The impact of this meteor storm on human civilizations was profound. It sparked widespread awe and wonder, inspiring artists, poets, and writers. The intensity of the Leonids and their periodic outbursts have also provided valuable scientific insights. By studying the Leonids, astronomers have gained a better understanding of meteoroid streams, their origins, and the dynamics of their orbits. The Leonids continue to dazzle observers to this day, although their intensity varies from year to year. Witnessing a Leonid meteor shower is a truly unforgettable experience that reminds us of the immense beauty and mystery of the universe.
2. Perseids
The Perseid meteor shower is one of the most anticipated and widely observed meteor showers in the world. Named after the constellation Perseus, from where they appear to originate, the Perseids grace the night sky every year between July and August. This shower is known for its remarkable display of fast and bright meteors, making it a favorite among stargazers and astrophotographers. The Perseids are associated with the comet Swift-Tuttle, with Earth passing through a cloud of debris left behind by the comet as it orbits the Sun. As a result, the Perseids consist of tiny dust particles and ice fragments that vaporize upon entering Earth’s atmosphere, creating beautiful streaks of light. Peak activity occurs around mid-August, typically offering up to 100 meteors per hour, making it a spectacular celestial event.
The Perseids have a rich historical and cultural significance. Ancient civilizations, like the Greeks and Romans, considered them as messages from the gods. In fact, the Perseids were named after the hero Perseus, who was said to have slayed the Gorgon Medusa. The shower’s peak activity often aligns with the traditional holiday of St. Lawrence’s Day, also known as the “Night of San Lorenzo” in some countries. This day holds cultural and religious importance, where people gather to observe the meteor shower and make wishes upon shooting stars.
In addition to their cultural significance, the Perseids have also contributed to scientific knowledge. Astronomers and scientists have seized the opportunity to study the velocity, composition, and behavior of the meteoroids that make up the Perseids. By analyzing the light emitted by the meteors, researchers can determine their chemical composition and gain insights into the nature of comets. This information helps deepen our understanding of the solar system’s formation and evolution. Studying the Perseids can also shed light on the potential hazards posed by near-Earth objects and aid in the development of strategies for planetary defense.
The Perseids provide an extraordinary opportunity for stargazers and nature enthusiasts to witness the wonders of the universe. Whether you’re an amateur astronomer, a night sky photographer, or simply someone who appreciates the beauty of celestial events, the Perseids offer a captivating and awe-inspiring experience that will leave you in awe of the vastness and mystery of the cosmos.
3. Geminids
The Geminids is one of the most spectacular meteor showers to grace the night sky. It occurs annually in mid-December when the Earth passes through the debris field of an asteroid called 3200 Phaethon. Named after the constellation Gemini, the Geminids are known for their abundance and vibrant colors. Unlike other meteor showers that are caused by comets, the Geminids originate from an asteroid, making them unique and intriguing to astronomers.
The Geminids have a rich history and have been observed for centuries. The first recorded observation of this meteor shower dates back to the early 1800s. However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that the Geminids gained widespread attention and recognition as a major annual meteor shower. Since then, their popularity and intensity have only grown.
What sets the Geminids apart is the sheer number of meteors that can be seen during their peak. On a clear night away from light pollution, skywatchers can witness up to 120 meteors per hour, making it one of the most prolific meteor showers of the year. The Geminids are also known for their slow-moving meteors, which create long-lasting trails across the sky, adding to the mesmerizing spectacle.
Interestingly, the Geminids have gradually become more prominent over time. While most meteor showers diminish in intensity as centuries pass due to the gravitational disruptions caused by nearby planets, the Geminids have been steadily increasing in strength. This phenomenon has puzzled scientists, who are still trying to unravel the reasons behind this unusual behavior.
The Geminids have not only captivated skywatchers and scientists but have also yielded important insights into the composition and characteristics of asteroids. As the parent asteroid, 3200 Phaethon, sheds debris when it gets close to the Sun, the Earth’s atmosphere collides with these small particles, resulting in the stunning display we observe as the Geminids. By studying the properties of the meteors and their trajectories, scientists have been able to learn more about the nature of asteroids and their potential threat to Earth.
So, mark your calendars for mid-December and prepare to witness the breathtaking Geminids meteor shower. Find a comfortable spot under the night sky, away from city lights, and allow yourself to be immersed in this celestial spectacle. It’s an experience like no other, reminding us of the vastness and wonder of our universe.
Conclusion
In conclusion, meteor showers have left an indelible mark on human civilizations throughout history. These captivating celestial events have not only fascinated and inspired people but have also contributed to significant scientific discoveries. Meteor showers have served as a source of artistic inspiration, fueled myths and folklore, and triggered scientific curiosity. They have provided invaluable insights into the origins of our universe and the evolution of our solar system. From the ancient civilizations that saw them as divine omens to the modern-day scientific community studying their composition and trajectory, meteor showers continue to captivate and intrigue. As we gaze up at the night sky, let us marvel at the beauty and significance of meteor showers, appreciating the wonder and connection they bring to humanity’s relationship with the cosmos.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How often do meteor showers occur?
Meteor showers occur regularly throughout the year, although some are more prominent than others. Major showers, such as the Perseids and Leonids, can be seen annually during specific periods when the Earth passes through the debris left by comets or asteroids.
2. Can meteor showers be seen from anywhere on Earth?
Yes, meteor showers can be observed from all parts of the Earth as long as the sky is clear and free from light pollution. However, the visibility and intensity of the meteor shower may vary depending on the observer’s location and the time of year.
3. What causes a meteor shower?
Meteor showers occur when the Earth intercepts the path of a comet or asteroid in its orbit. As these celestial bodies travel through space, they leave behind a trail of debris. When the Earth passes through this debris field, the particles burn up upon entering the atmosphere, creating a beautiful display of shooting stars.
4. Can meteor showers be dangerous?
Meteor showers are generally not dangerous. The meteors burn up high in the Earth’s atmosphere and pose no threat to people on the ground. However, it is always important to find a safe location away from any potential hazards and to follow proper observation guidelines.
5. Do all meteor showers have names?
No, not all meteor showers have names. Only the most significant and well-known showers are named after the constellation from which they appear to originate.
6. How long do meteor showers last?
Meteor showers can last from a few hours to several days, with the peak activity typically occurring during a specific window of time. It is during this peak period that observers can witness the highest concentration of meteors.
7. Can you predict when a meteor shower will occur?
Yes, astronomers can predict when meteor showers will occur with a fair amount of accuracy. These predictions are based on the orbits of comets or asteroids and the history of past observations. However, the intensity and visibility of a meteor shower can still vary from year to year.
8. Are all meteor showers visible to the naked eye?
Most meteor showers are indeed visible to the naked eye. However, the brightness and number of meteors visible may vary. Some may produce only a few meteors per hour, while others, like the Perseids, can produce dozens or even hundreds of meteors per hour during their peak.
9. Can meteor showers be heard?
No, meteor showers cannot be heard. The meteors burn up high in the Earth’s atmosphere, far above the point where sound can be heard. However, on rare occasions, exceptionally large meteors can produce sonic booms that can be heard on the ground.
10. Can I make a wish on a shooting star during a meteor shower?
Making a wish on a shooting star is a popular tradition. While it may not have any scientific or supernatural significance, it can be a fun and whimsical activity enjoyed by people during meteor showers. So, feel free to make a wish and see what the universe has in store for you!








