Have you ever looked up at the night sky and wondered about the stories and mysteries hidden among the stars? One such constellation that has captivated humans for centuries is Ursa Minor, also known as the Little Bear. This small constellation holds great significance in both mythology and ancient civilizations. In this article, we will explore the fascinating legends behind Ursa Minor, learn how to identify it in the night sky, and discover the deep sky objects within it. We will also delve into the astrological and mythological significance of Ursa Minor, as well as its future and the impact of precession. So, grab your telescope or simply step outside on a clear night, and let’s embark on a journey to explore Ursa Minor and the wonders it holds.
Mythology and Significance

In Greek mythology, Ursa Minor is associated with the touching tale of Callisto, a beautiful nymph who caught the attention of Zeus, the king of the gods. Zeus had an affair with Callisto and she became pregnant with his child. However, this angered Zeus’ jealous wife, Hera, who transformed Callisto into a bear in a fit of rage. Despite her new form, Callisto’s son, Arcas, recognized her and almost accidentally killed her while hunting. In a merciful twist, Zeus intervened and placed both Callisto and Arcas in the night sky as the constellations Ursa Major and Ursa Minor, respectively. To this day, their celestial forms serve as a reminder of Zeus’ forbidden love and the consequences it brought upon Callisto and Arcas.
Ursa Minor held significant cultural and navigational importance for ancient civilizations. The North Star, also known as Polaris, resides in Ursa Minor and has played a crucial role in navigation throughout history. Its fixed position relative to the Earth’s rotation makes it a reliable point of reference for determining direction, particularly in the Northern Hemisphere. Ancient seafarers and travelers used Ursa Minor and the North Star to guide their journeys, ensuring they stayed on course and arrived at their destinations safely. Ursa Minor held a symbolic significance in various cultures. It represented guidance, stability, and constancy, serving as a guiding light in both the physical and metaphorical sense. Its presence in the night sky provided reassurance and a sense of direction for those seeking their path in life.
Internal link: To learn more about the celestial twins in another prominent constellation, Gemini, click here.
The Story of Ursa Minor
The story of Ursa Minor is intricately connected to the myth of Callisto, as mentioned earlier. In Greek mythology, Callisto was a companion of the goddess Artemis, known for her beauty and loyalty. However, this caught the attention of Zeus, who disguised himself as Artemis and seduced Callisto. Their union resulted in the birth of a son named Arcas. When Hera, Zeus’ jealous wife, discovered the affair, she transformed Callisto into a bear. Time passed, and one day, Arcas encountered the bear while hunting. Unaware that the bear was his mother, Arcas prepared to strike it. But before he could harm her, Zeus intervened and placed both mother and son in the night sky as Ursa Major and Ursa Minor, respectively.
This tale serves as a cautionary reminder of the consequences of crossing divine boundaries and the mercy of the gods. Ursa Minor’s position as the smaller bear, circling around Ursa Major, reflects the enduring bond between a mother and her child. Their celestial presence serves as a reminder of forbidden love, transformation, and the complexities of relationships. To explore another mythological tale involving constellations, venture into the story of Perseus and Andromeda by clicking here. Or, if you’re curious about another fascinating constellation, learn about the marvels of Boötes, the Herdsman, by clicking here.
The Importance of Ursa Minor in Ancient Civilizations
Ursa Minor, with its prominent North Star Polaris, held immense importance in ancient civilizations. The ancient Egyptians, for example, associated Polaris with the god Osiris, who was believed to be the ruler of the afterlife. The Egyptians believed that the souls of the departed would embark on a journey to the heavens, guided by the North Star. Ursa Minor’s presence in the night sky provided comfort and assurance to the ancient Egyptians, assuring them that Osiris would guide their loved ones to their final resting place.
Similarly, the ancient Greeks revered Ursa Minor and Polaris as essential navigational tools. Greek sailors and explorers heavily relied on the constellation to determine their position and ensure accurate navigation. They recognized the stability of Polaris, which remained stationary while the other stars moved across the sky. This celestial reliability allowed Greek mariners to venture into unknown waters with confidence.
The importance of Ursa Minor extended to other ancient civilizations as well. In Viking culture, the North Star held great significance as a symbol of guidance and protection. The Norsemen relied on its unwavering presence in the night sky to navigate their longships across treacherous seas, ensuring safe voyages and successful raids.
The Polynesians, famous for their incredible navigational skills, also valued Ursa Minor and Polaris. They used the constellation and its distinguishing star as a navigational reference point during their extensive open-ocean voyages. The Polynesians observed the position of the North Star in relation to other stars and used this knowledge to navigate vast expanses of water, eventually settling on numerous islands across the Pacific.
Ursa Minor’s role in ancient civilizations as a guiding light and navigational aid is a testament to the universal human need for direction and certainty. Its steady presence in the night sky provided a sense of stability and security in an unpredictable world, serving as a celestial beacon for travelers and explorers alike.
Stargazing Guide
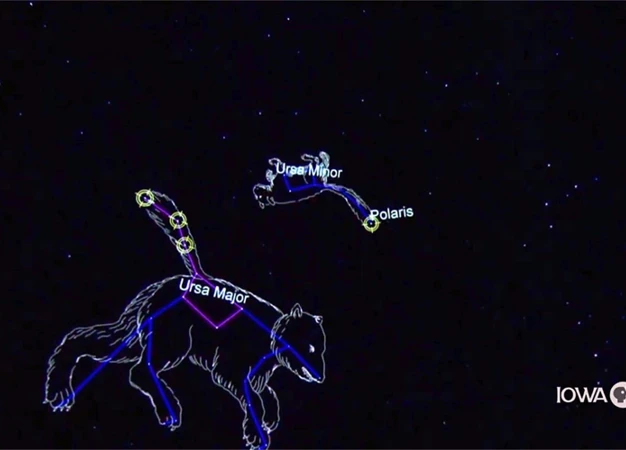
Identifying Ursa Minor in the night sky is a delightfully straightforward task. The constellation, resembling a small bear, can be easily found by locating the iconic Little Dipper asterism. The two outer stars of the Little Dipper’s bowl are the most recognizable ones. Known as Dubhe and Merak, they are often referred to as “The Pointers” since they guide stargazers to Polaris, the North Star. To find Ursa Minor, trace a line from the end of the bowl opposite to the handle through these two stars, leading you directly to Polaris. Once you have located Polaris, you will find Ursa Minor right next to it, resembling a little bear with a long tail.
Within Ursa Minor, there are several notable stars and constellations worth exploring. The brightest star in Ursa Minor is Polaris, which marks the celestial North Pole. Polaris has served as a guiding light for navigators and stargazers alike for centuries. It remains almost motionless in the sky while the other stars appear to rotate around it due to the Earth’s rotation. Another interesting star is Kochab, located at the end of the Little Bear’s tail. Kochab is a giant star with a reddish-orange hue, adding to the allure of the constellation.
Internal link: To discover more about the mythical hero Perseus and his connection to other northern constellations, click here.
Identifying Ursa Minor in the Night Sky
To identify Ursa Minor in the night sky, it is helpful to look for its most recognizable feature, the Little Dipper. The Little Dipper is formed by the seven main stars that make up the shape of a ladle or a small dipper. One of the easiest ways to locate Ursa Minor is by first finding the Big Dipper, another well-known constellation. To do this, look towards the northern horizon in the late evening or early morning hours. The Big Dipper, which is part of Ursa Major, can be identified by its distinct shape of a ladle or plow. The last two stars of the Big Dipper’s ladle point towards the North Star, Polaris, which resides in the handle of the Little Dipper. Once Polaris is located, tracing the curved handle of the Little Dipper and the bowl-shaped arrangement of stars that make up Ursa Minor becomes straightforward. It’s important to find a location with minimal light pollution to observe the fainter stars that form the constellation. Remember, Ursa Minor may not be as prominent or well-known as some other constellations, but once identified, its presence in the night sky is truly captivating.
Internal link: To read about another fascinating northern constellation, Perseus and Andromeda, known for their tales of heroism and adventure, click here.
Key Stars and Constellations within Ursa Minor
Within the Ursa Minor constellation, there are several key stars and constellations that add to its celestial beauty. The most prominent star in Ursa Minor is Polaris, also known as the North Star. Polaris holds immense navigational significance as it aligns closely with the Earth’s axis of rotation, making it appear almost stationary in the night sky. This characteristic has made it a reliable guiding star for centuries.
Another notable star in Ursa Minor is Kochab, which is the brightest star in the constellation. Kochab, along with Polaris, forms a distinctive pattern that resembles the shape of a ladle or a miniature version of the Big Dipper. This pattern, known as the Little Dipper, is a subset of Ursa Minor and is easier to locate than the entire constellation itself.
As we navigate through Ursa Minor, we encounter other neighboring constellations that enhance its celestial scenery. One such constellation is Draco the Dragon, which intertwines with Ursa Minor and stretches across the northern skies. Draco is a renowned constellation associated with various mythologies and tales, offering stargazers an opportunity to explore multiple stories in the night sky.
Html list:
- Polaris – The North Star
- Kochab – The brightest star in Ursa Minor
- The Little Dipper – A subset of Ursa Minor
- Draco – A neighboring constellation intertwined with Ursa Minor
Exploring the Deep Sky Objects
Within the constellation of Ursa Minor, there are several fascinating deep sky objects that can be explored with a telescope or binoculars. One such object is the Ursa Minoris Cluster, also known as Collinder 399 or the Brocchi’s Cluster. This open cluster is located near the star Kochab, one of the stars that forms the Little Dipper’s bowl. The Ursa Minoris Cluster is a collection of stars that appear close together in the sky, giving the illusion of a tight-knit group. Observing this cluster can be a captivating experience, as its stars vary in brightness and color, creating a visually appealing spectacle.
Another notable deep sky object within Ursa Minor is NGC 3172, a spiral galaxy located approximately 50 million light-years away from Earth. This galaxy showcases beautiful spiral arms, and its bright nucleus is visible with a telescope. Studying NGC 3172 can provide insights into the formation and evolution of galaxies, as well as the intricate structures within them.
Ursa Minor is home to NGC 6217, another captivating spiral galaxy. This galaxy is located approximately 89 million light-years away and is known for its distinctive spiral arms and prominent central bulge. NGC 6217 offers astronomers the opportunity to observe galactic structures and gain a deeper understanding of the vast cosmic tapestry.
By exploring these deep sky objects within Ursa Minor, astronomers can unravel the mysteries of the universe and gain invaluable knowledge about the formation and evolution of galaxies. It is through the study of these distant objects that we come closer to understanding our place in the cosmos and the wonders that lie beyond Earth.
Internal link: To learn more about the heroism depicted in the constellations of Perseus and Andromeda, click here.
Ursa Minoris Cluster
The Ursa Minoris Cluster, also known as NGC 6229, is a fascinating deep sky object located within the constellation of Ursa Minor. This cluster is a tightly packed group of stars that gravitationally interact with each other, forming a visually stunning spectacle. The Ursa Minoris Cluster is classified as a globular cluster, which means it is a spherical collection of stars orbiting around a common center.
With a visual magnitude of 9.29, the Ursa Minoris Cluster can be observed with a medium-sized telescope or a pair of binoculars under optimal viewing conditions. It consists of approximately 150,000 stars densely packed within a diameter of about 90 light-years. These stars are old and have a distinct yellowish hue.
The Ursa Minoris Cluster is estimated to be around 75,000 light-years away from Earth, making it one of the nearest globular clusters to our solar system. Its proximity provides an excellent opportunity for astronomers to study the dynamics and evolution of such star clusters. Studying the Ursa Minoris Cluster offers insights into the formation and structure of globular clusters and contributes to our understanding of stellar populations and galactic evolution.
The Ursa Minoris Cluster is a captivating object to observe, with its dense concentration of stars and its intriguing history dating back billions of years. As you gaze at this beautiful cluster through your telescope, take a moment to appreciate the sheer magnitude and complexity of the universe we are lucky enough to explore.
Internal link: To uncover more deep sky wonders, check out the article on the marvels of another constellation, Bootes, by clicking here.
NGC 3172
NGC 3172 is a fascinating deep sky object located within the constellation of Ursa Minor. It is a small, faint galaxy that belongs to the M81 Group, a collection of galaxies that also includes the well-known Bode’s Galaxy (M81) and the Cigar Galaxy (M82). NGC 3172 is classified as a dwarf elliptical galaxy, meaning it has a spheroidal shape and relatively low luminosity compared to other galaxies. Despite its modest size, NGC 3172 offers a captivating sight through telescopes. With its smooth, uniform appearance, it stands out against the backdrop of darker space. The galaxy’s stars are densely packed, creating a captivating cluster of celestial bodies. NGC 3172 serves as a reminder of the vastness and diversity of the universe, even within the seemingly small constellation of Ursa Minor.
Exploring NGC 3172 and other deep sky objects is a delight for astrophotographers and amateur astronomers. Capturing images of this distant galaxy allows us to marvel at the beauty and intricacy of the cosmos. Whether observing it through a telescope or admiring photographs taken by astrophotographers, NGC 3172 serves as a reminder of the endless wonders that exist beyond our world.
Internal link: If you’re interested in exploring other deep sky objects, you might also enjoy reading about the marvels of the Herdsman constellation in our article “The Marvels of Bootes: Unveiling the Herdsman”.
NGC 6217
NGC 6217 is a mesmerizing spiral galaxy located within the boundaries of the Ursa Minor constellation. This celestial wonder is approximately 67 million light-years away from Earth, making it quite a distant object in the night sky. With its intricate spiral arms and a prominent central bulge, NGC 6217 offers a fascinating spectacle for stargazers and astronomers alike. The galaxy’s structure is adorned with numerous bright clusters of young stars, as well as glowing regions of hydrogen gas that fuel the formation of new stars. NGC 6217 has been a subject of extensive research for astronomers aiming to study the dynamics of spiral galaxies and understand the processes of star formation within them. Its distinctive features make it an exquisite object for astrophotography, capturing the beauty and complexity of our vast universe. So, the next time you’re observing the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the awe-inspiring NGC 6217, a captivating destination in the depths of Ursa Minor’s cosmic realm.
Ursa Minor and Astrology
Ursa Minor holds astrological significance, symbolizing certain qualities and characteristics according to astrological interpretations. Individuals born under the zodiac sign of Ursa Minor are believed to embody the traits of stability, determination, and steadfastness. They are often seen as reliable and consistent, providing a sense of guidance and support for those around them. Ursa Minor’s association with the North Star, Polaris, further emphasizes its symbolism of direction and guidance, which is reflected in the personalities of those born under its influence.
In mythological astrology, Ursa Minor is associated with the story of Callisto and Arcas. This tale is seen as a representation of forbidden love, transformation, and the consequences of one’s actions. Individuals connected to Ursa Minor in mythological astrology may resonate with themes of transformation, hidden potential, and the importance of facing the consequences of their choices. Ursa Minor serves as a reminder to navigate the complexities of life while staying true to oneself and embracing personal growth.
To explore more about the heroism and northern constellations in mythology, including the stories of Perseus and Andromeda, you can click here.
The Astrological Significance of Ursa Minor
The Astrological Significance of Ursa Minor is rooted in the belief that celestial bodies can influence human personality traits and life events. While Ursa Minor is not one of the traditional zodiac constellations, it has a unique role in astrology. Some astrologers associate Ursa Minor with the qualities of steadfastness, adaptability, and resilience. Those born under the influence of Ursa Minor are believed to possess a strong sense of direction and determination, much like the North Star itself. They are often seen as reliable and stable individuals who can navigate through life’s challenges with poise and grace. Ursa Minor’s presence in a birth chart may indicate a resilient personality and a natural inclination to guide and support others. However, it is important to note that the astrological significance of Ursa Minor may vary among different astrological systems and interpretations.
- Steadfastness: Individuals influenced by Ursa Minor are known for their unwavering commitment and loyalty. They possess a strong sense of perseverance and can weather any storm that comes their way.
- Adaptability: Similar to Ursa Minor’s position in the sky, these individuals have a remarkable ability to adapt and navigate through different circumstances. They possess a flexible nature that allows them to handle change and uncertain situations with ease.
- Resilience: Ursa Minor represents the ability to stay strong even in the face of adversity. People influenced by this constellation are believed to possess inner strength and the capacity to bounce back from setbacks and challenges.
- Guiding Light: Much like the North Star, those influenced by Ursa Minor often serve as a guiding light for others. They have a natural inclination to offer support, wisdom, and guidance to those around them.
The astrological significance of Ursa Minor adds an intriguing layer of interpretation to the influence of the celestial world on our lives. However, it is important to remember that astrology is subjective and can vary based on individual beliefs and perspectives.
Ursa Minor in Mythological Astrology
Ursa Minor holds a special place in mythological astrology due to its connection with the Greek myth of Callisto. The constellation is believed to symbolize endurance, resilience, and transformation. People born under the influence of Ursa Minor are often seen as steadfast and reliable, able to navigate through life’s challenges with grace and patience. They possess a strong sense of direction and purpose, much like the North Star that guides them. The tale of Callisto’s transformation into a bear also highlights the theme of personal growth and evolution. Individuals associated with Ursa Minor in mythological astrology are believed to undergo transformative experiences in their lives, emerging stronger and wiser. The constellation’s presence in astrological charts is often interpreted as a reminder to trust the journey, embrace change, and find stability and guidance within oneself. It serves as a celestial guardian, encouraging individuals to persevere and follow their true path in life.
Ursa Minor’s Future
Ursa Minor’s future holds intriguing changes due to the astronomical phenomenon known as precession. Precession is the gradual shift in the Earth’s rotational axis, causing the celestial poles to change over time. Currently, Polaris sits very close to the North Celestial Pole, making it the North Star. However, in approximately 26,000 years, Vega from the neighboring constellation Lyra will take over as the North Star, while Polaris will move away from its current position. This means that Ursa Minor will no longer be directly associated with the North Star. Instead, it will become a much more inconspicuous constellation, blending in with the rest of the stars in the night sky. The shifting position of Ursa Minor and the North Star adds a temporal aspect to the constellation’s significance, reminding us of the transient nature of celestial objects and the ever-changing cosmos.
Internal link: To understand more about the impact of precession on celestial objects, you can read about the marvels of another constellation, Boötes, unveiling the herdsman, by clicking here.
Ursa Minor’s Motion Over Time
Ursa Minor, like all celestial objects, undergoes motion over time due to various astronomical phenomena. One such phenomenon is known as precession, which causes the slow wobbling of Earth’s axis. As a result of precession, the position of Ursa Minor and other constellations change relative to our planet. Over a period of approximately 26,000 years, the North Star shifts due to this wobble. Currently, Polaris, the brightest star in Ursa Minor, serves as the North Star. However, in the future, this will not always be the case. This motion means that the North Star position will gradually move away from Polaris and start nearing other stars in the Northern Hemisphere. Eventually, around 14,000 years from now, the star Vega in the constellation Lyra will take over as the North Star. This celestial dance adds a dynamic element to Ursa Minor and reminds us of the continuous motion and change within the cosmos.
Internal link: To explore another constellation affected by precession, read about the heroism of Perseus and Andromeda and their connection to the northern constellations here.
The Impact of Precession on Ursa Minor
The impact of precession on Ursa Minor is a fascinating phenomenon that has significant implications for the position and visibility of the constellation over time. Precession refers to the slow shift in the Earth’s axis of rotation, causing the orientation of the celestial poles to change gradually. As a result of precession, the North Star or Polaris, which is currently located in Ursa Minor, will not always remain the North Star. Over a 26,000-year cycle, the North Celestial Pole migrates in a circular motion, causing different stars to take on the role of the North Star.
This means that in the future, Ursa Minor may no longer be the go-to constellation for navigation. Other stars, such as Vega in the constellation Lyra or Deneb in the constellation Cygnus, will eventually take their turn as the North Star due to the Earth’s axial movement. Although Polaris has served as a reliable guiding light for centuries, explorers and navigators of the future will need to adjust their navigational methods to account for this shift. The impact of precession on Ursa Minor reminds us of the dynamic nature of our universe and the need to adapt to changes over time.
To envision the impact of precession on Ursa Minor, imagine the slow circular motion of the Earth’s axis as it traces a path through the sky. This gradual shift alters the positions of the stars and constellations, including Ursa Minor, over thousands of years. As a result, future generations may witness different constellations occupying the once-familiar regions of the night sky. The impact of precession highlights the ever-changing nature of our celestial environment and encourages us to appreciate and study the night sky as a dynamic entity.
Internal link: If you’re interested in exploring another constellation impacted by precession, check out our article on Bootes: Unveiling the Herdsman.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of Ursa Minor, we have delved into its mythology, significance in ancient civilizations, and its astrological and navigational importance. The story of Callisto and her transformation into Ursa Minor serves as a poignant reminder of the consequences of forbidden love. Throughout history, Ursa Minor and its prominent star, Polaris, have guided sailors, travelers, and dreamers alike, providing a sense of stability and direction. Even in the ever-changing cosmos, Ursa Minor remains a steadfast presence in the night sky. Its deep sky objects offer further glimpses into the vast wonders of the universe. Whether you observe Ursa Minor for its enchanting mythology, its practical navigational significance, or for its celestial beauty, one thing is certain: this little bear constellation continues to captivate and inspire us, reminding us of the enduring mysteries and tales that lie among the stars.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQs About Ursa Minor
1. How can I locate Ursa Minor in the night sky?
To locate Ursa Minor, look for the North Star, Polaris, which is found at the end of the Little Bear’s handle.
2. Can Ursa Minor be seen from the Southern Hemisphere?
Ursa Minor is primarily visible from the Northern Hemisphere. However, in the Southern Hemisphere, it can be seen low on the northern horizon.
3. What are the major stars within Ursa Minor?
The major stars within Ursa Minor include Polaris (the North Star), Kochab, and Pherkad.
4. Are there any deep sky objects within Ursa Minor?
Yes, there are several deep sky objects within Ursa Minor, such as the Ursa Minoris Cluster, NGC 3172, and NGC 6217.
5. Is Ursa Minor associated with any specific zodiac signs?
No, Ursa Minor is not associated with any specific zodiac signs. It holds its own mythological and navigational significance.
6. Is Ursa Minor visible year-round?
Yes, Ursa Minor is visible year-round in the Northern Hemisphere. Its position near the North Pole means it is circumpolar and does not dip below the horizon.
7. Is Ursa Minor a prominent constellation in ancient mythology?
While Ursa Minor is not as well-known as some other constellations, it does hold significance in Greek mythology as the transformed nymph, Callisto.
8. Can Ursa Minor be viewed with the naked eye?
Yes, Ursa Minor can be viewed with the naked eye, especially in areas with low light pollution. Binoculars or a telescope can enhance the viewing experience.
9. Is Ursa Minor part of a larger constellation family?
Ursa Minor is part of the larger Ursa constellation family, which includes Ursa Major, the Great Bear.
10. Does Ursa Minor change position over time due to precession?
Yes, like all celestial objects, Ursa Minor experiences a slight shift in position over time due to the Earth’s precession.