Nightmares, those unsettling and vividly disturbing dreams that leave us waking up in a cold sweat, have fascinated and perplexed us for centuries. What causes these haunting visions that can leave us feeling terrified and emotionally drained? In this article, we delve into the psychological causes of nightmares, exploring the intricate relationship between our minds and these nocturnal terrors. By understanding the underlying psychological factors that contribute to nightmares, we can gain insights into how to manage and overcome them, ultimately leading to more restful nights and improved mental well-being.
The Nature of Nightmares

Nightmares, those enigmatic and often unsettling experiences that occur during sleep, have intrigued and puzzled humans for centuries. Understanding the nature of nightmares involves exploring their distinctive characteristics and definitions. Nightmares can be defined as intensely distressing dreams that elicit strong negative emotions and often involve vivid and terrifying scenarios. These dreams are often accompanied by physiological responses such as increased heart rate and sweating. Typical characteristics of nightmares include feelings of fear, danger, or helplessness, as well as a sense of realism that can blur the line between dream and reality. While nightmares are a common experience for many individuals, their specific causes and underlying psychological mechanisms remain complex and multifaceted. By exploring the various factors that contribute to nightmares, we can shed light on their nature and gain insights into effective strategies for managing and overcoming them.
Definition of Nightmares
A comprehensive understanding of the
definition of nightmares
is crucial in exploring the psychological causes behind these unsettling dreams. Nightmares can be described as powerful and distressing dreams that evoke intense negative emotions. They often involve vivid and frightening scenarios that may reflect threatening situations or deep-seated fears. These dreams stand out from ordinary dreams due to their ability to elicit strong emotional responses during sleep, and sometimes even upon waking. Nightmares are characterized by their realism and the subjective experience of danger or dread. Physiological responses such as increased heart rate, sweating, and rapid breathing often accompany these dreams, further enhancing the distress individuals feel. While nightmares are a common occurrence, particularly in children, they differ from night terrors which involve sudden episodes of intense fear and panic during sleep. Understanding the intricacies of nightmares’ definition serves as a foundation for exploring the underlying psychological factors contributing to their occurrence and developing effective strategies for managing them. To explore one potential cause, research suggests a strong link between nightmares and stress. To learn more about this connection, you can read our related article on investigating stress and nightmares.
Typical Characteristics of Nightmares
Nightmares exhibit a range of typical characteristics that distinguish them from regular dreams. Understanding these typical characteristics of nightmares can help us identify and differentiate them from other dream experiences. Here are some key aspects:
1. Intense Negative Emotions: Nightmares provoke powerful negative emotions, such as fear, terror, anxiety, and helplessness. These emotions can be so intense that they continue to affect individuals even after waking up.
2. Vivid and Disturbing Content: Nightmares often feature vivid and disturbing content that evokes a sense of danger, threat, or impending doom. Common themes include being chased, attacked, or confronting supernatural entities. The content can be grotesque, surreal, or portray scenarios that violate societal norms.
3. Realistic Sensations and Perception: One of the peculiar aspects of nightmares is the feeling of realism they evoke. While the events may be fantastical or improbable, the sensations and perception within the dream often feel incredibly real to the dreamer.
4. Physical and Psychological Responses: Nightmares can result in physical and psychological responses during sleep. These include increased heart rate, sweating, rapid breathing, and sometimes even sleep disturbances or awakenings.
5. Recollection upon Awakening: Unlike regular dreams that may quickly fade from memory, individuals tend to remember nightmares vividly upon awakening. The emotional intensity and disturbing nature of nightmares make them more memorable than ordinary dreams.
Understanding these typical characteristics can help individuals recognize when they have experienced a nightmare and differentiate it from other dream experiences. The vividness, negative emotions, and realistic sensations associated with nightmares make them stand out in the realm of dream content. By identifying and understanding these traits, individuals can better cope with the impact nightmares may have on their sleep and overall psychological well-being.
Common Psychological Causes
Understanding the common psychological causes of nightmares can provide valuable insights into why these unsettling dreams occur. Stress and anxiety are among the primary triggers for nightmares. When we are under significant stress or experiencing heightened anxiety, our minds may manifest these emotions during sleep, leading to frightening dream experiences. Additionally, traumatic experiences, such as physical or emotional abuse, can leave a lasting impact on our subconscious, resulting in recurring nightmares that reflect the unresolved trauma. It is important to note that certain medications, like antidepressants or sleep aids, can also contribute to the occurrence of nightmares as a potential side effect. Psychological disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, or anxiety disorders, may increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. By uncovering the impact of trauma on nightmares and addressing underlying psychological factors, it becomes possible to develop effective strategies for managing and reducing the frequency of these distressing dream experiences.
Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are common psychological factors that can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. When we experience high levels of stress, whether it’s due to work pressures, relationship issues, financial concerns, or other life stressors, our minds can become overloaded. This mental and emotional strain can manifest in nightmares as our subconscious attempts to process and cope with the underlying stress. Anxiety, characterized by persistent worry and fear, can also play a role in nightmares. Individuals who have anxiety disorders or who are prone to excessive worrying may be more susceptible to experiencing nightmares. The heightened emotional state associated with anxiety can intensify the content and intensity of dreams, leading to the occurrence of distressing nightmares. Stress and anxiety can disrupt the quality of sleep, making individuals more prone to experiencing nightmares. It’s important to address and manage stress and anxiety through effective coping mechanisms such as relaxation techniques, therapy, or medication (when prescribed by a healthcare professional). By reducing stress and anxiety levels, individuals may experience a decrease in the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Traumatic Experiences
Traumatic experiences can have a profound impact on our mental and emotional well-being, and they are often connected to the development and recurrence of nightmares. Traumatic experiences can include events such as physical or sexual abuse, accidents, natural disasters, combat exposure, or witnessing violence. These experiences can leave a lasting imprint on our psyche, triggering intense emotions and disturbing imagery that may manifest in our dreams. Nightmares related to trauma often serve as a way for the mind to process and cope with the distressing event. They can be characterized by vivid reenactments of the traumatic event, intense fear, and a recurring sense of helplessness. It is important to note that traumatic nightmares can be indicative of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a psychological disorder that can develop after exposure to a traumatic event. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can be crucial in addressing and working through the psychological aftermath of trauma and its associated nightmares. If you believe your nightmares are related to medication, it is important to consult with a medical professional to discuss potential alternatives or adjustments to your medication plan, as some medications can have an impact on sleep and dream patterns.
Psychological Disorders
Psychological disorders play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. These disorders encompass a range of conditions that affect an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. Conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, depression, and schizophrenia have been linked to an increased likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Individuals with PTSD, for instance, may frequently reexperience traumatic events during their nightmares, which can intensify feelings of fear and distress. Anxiety disorders can also contribute to nightmares, as individuals with anxiety often experience heightened levels of stress and excessive worrying, which can manifest in their dreams. Depression, characterized by persistent feelings of sadness and hopelessness, can lead to nightmares marked by themes of despair and vulnerability. Additionally, individuals with schizophrenia may experience vivid and intense dreams due to the complex interplay of their disturbed thoughts and emotions. It is important for individuals with psychological disorders to seek professional help and explore appropriate treatment options to address their condition and potentially alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms of psychological disorders, but it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before initiating any medication regimen, as certain medications have been associated with an increased risk of nightmares. For more information on the link between medication and nightmares, you can check out our article on medication and nightmares.
Childhood Experiences
Childhood experiences play a significant role in the development and manifestation of nightmares later in life. The mind of a child is highly impressionable, and traumatic or distressing events during this formative period can leave lasting imprints on their subconscious. These experiences can include physical or emotional abuse, neglect, witnessing violence, or the loss of a loved one. Such distressing events can disrupt the normal sleep patterns of a child, leading to nightmares as their way of processing and coping with the intense emotions associated with the experience. Additionally, children who have experienced trauma may develop an increased sense of fear and anxiety, making them more susceptible to nightmares. The content of these nightmares may directly reflect the traumatic event or incorporate symbols and imagery related to the experience. It is important for parents, caregivers, and professionals to provide a supportive and nurturing environment for children who have experienced trauma, as addressing and processing these experiences can help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
The Role of Emotions

Emotions play a pivotal role in shaping and influencing the content and intensity of nightmares. The role of emotions in nightmares can be diverse, with different emotions manifesting in different ways during these nocturnal experiences. Fear and anxiety are commonly associated with nightmares, as they often involve scenarios that elicit feelings of terror and apprehension. These nightmares may reflect underlying fears and worries experienced in waking life, allowing the subconscious mind to process and confront these emotions. Additionally, anger and frustration can also be present in nightmares, where individuals may find themselves in conflict or facing obstacles that provoke strong feelings of anger. Similarly, sadness and grief can permeate nightmares, reflecting unresolved emotional pain or loss. Understanding the role of emotions in nightmares can provide valuable insight into our psychological well-being, allowing us to address and process these emotions in a healthy and constructive manner.
Fear and Anxiety
Fear and anxiety are two prominent emotions that play a significant role in the realm of nightmares. When it comes to nightmares, fear often takes center stage, invoking intense feelings of terror and apprehension. Nightmares can tap into our deepest fears, whether they be related to specific phobias, traumatic experiences, or other psychological triggers. The content of nightmares can revolve around scenarios that evoke fear, such as being chased, attacked, or experiencing a life-threatening situation. These fear-based nightmares can leave us feeling shaken and unsettled upon waking, lingering in our minds long after the dream has ended.
Anxiety, on the other hand, can manifest in nightmares through a constant sense of unease and worry. These anxiety-driven nightmares often reflect our subconscious concerns and insecurities, highlighting situations in which we feel overwhelmed, threatened, or unable to cope. Common themes in anxiety-driven nightmares may include being unprepared for an important event, feeling trapped in a stressful situation, or experiencing a loss of control. Such nightmares can heighten our levels of stress and provoke feelings of unrest, impacting our overall well-being and quality of sleep.
Understanding the role of fear and anxiety in nightmares is essential in comprehending their psychological causes. These emotions often indicate underlying psychological issues, such as unresolved trauma, chronic stress, or anxiety disorders. By recognizing the connection between fear, anxiety, and nightmares, individuals may seek appropriate interventions, such as therapy or stress management techniques, to address and mitigate these emotions. Through targeted approaches, it is possible to alleviate the impact of fear and anxiety and reduce the occurrence of distressing nightmares.
Anger and Frustration
Anger and frustration can play a significant role in the occurrence and content of nightmares. When individuals experience intense anger or feel frustrated in their waking lives, these emotions can manifest in their dreams, leading to nightmares with themes related to conflict, aggression, or helplessness. The vividness and emotional intensity of these nightmares can be attributed to the strong emotions associated with anger and frustration. In such dreams, individuals may find themselves in situations where they are fighting, arguing, or being chased, reflecting their inner turmoil and unresolved issues. The content of these nightmares can vary widely, from confrontations with loved ones to encounters with unknown adversaries. It is important to note that nightmares involving anger and frustration may also signal underlying psychological issues, such as repressed anger or unresolved conflicts. Addressing and managing these emotions through therapeutic approaches such as counseling or cognitive-behavioral therapy can help alleviate the occurrence and intensity of nightmares related to anger and frustration.
Sadness and Grief
Sadness and grief can also play a significant role in the occurrence of nightmares. When individuals experience profound feelings of sadness or grief, their emotional state can infiltrate their dreamscape, leading to unsettling and distressing nightmares. The intense emotions associated with sadness and grief, such as loss, longing, or guilt, can manifest in nightmares as vivid scenarios that reflect these deep-seated emotions. These nightmares may involve themes of separation, death, or unresolved issues related to the source of grief. The imagery and content of these dreams can be particularly distressing, as they can trigger painful memories and exacerbate feelings of sadness and grief upon waking. Additionally, the emotional intensity of these dreams can disrupt the quality of sleep, further impacting the individual’s emotional well-being. Seeking support from therapists, grief counselors, or support groups can be beneficial in processing and coping with the emotions tied to sadness and grief, which may ultimately alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares related to these emotions.
The Influence of Personal Beliefs and Culture

Our personal beliefs and cultural backgrounds can significantly influence the content and interpretation of our dreams, including nightmares. The influence of personal beliefs and culture on nightmares is a fascinating area of study, as it highlights how our individual and societal perspectives shape our dream experiences. Religious and spiritual beliefs, for example, can play a significant role in the themes and symbols that appear in nightmares. Cultural and social influences, such as societal norms and values, can also impact the content and emotional tone of nightmares. These influences can range from cultural fears and taboos to collective traumas that have been passed down through generations. By recognizing and understanding the impact of personal beliefs and cultural factors on nightmares, we can gain insight into the deeply rooted psychological processes that contribute to our dreams and work towards effectively managing and interpreting them.
Religious and Spiritual Beliefs
The influence of religious and spiritual beliefs on nightmares is a fascinating aspect to explore. Different belief systems and religious ideologies can shape one’s perception of dreams and their significance. In some religious traditions, dreams are seen as powerful messages from a higher power, conveying divine guidance or warnings. As a result, nightmares may be interpreted as spiritual experiences or symbolic messages. For example, in certain cultures, nightmares can be viewed as a battle between good and evil, with the individual being tested or targeted by malevolent forces. Religious symbols and archetypes may also manifest in nightmares, reflecting the individual’s deep-seated fears and anxieties intertwined with their spiritual journey. On the other hand, individuals who do not adhere to any particular religious beliefs may still experience nightmares that reflect their spiritual or existential concerns, such as the fear of death or unanswered existential questions. Acknowledging and exploring the role of religious and spiritual beliefs can be significant in understanding the personal significance and interpretation of nightmares, providing individuals with a unique lens through which to process and navigate their nocturnal terrors.
Cultural and Social Influences
Cultural and social influences play a significant role in shaping the content and interpretation of nightmares. Our cultural beliefs, values, and social norms can impact our dreams and nightmares. Cultural stories, folklore, and myths often find their way into our subconscious and can manifest in our dreams. For example, individuals from cultures with a strong belief in supernatural entities or spirits may experience nightmares involving encounters with these beings. Additionally, social experiences and interactions can influence the themes and emotions present in our nightmares. Societal issues such as discrimination, social injustice, or violence can infiltrate our dreams and reflect the collective anxieties and concerns of a community or society at large. Shared experiences within a specific cultural or social group can shape the frequency and themes of nightmares. For example, individuals who have experienced a particular traumatic event may share collective nightmares that reflect the impact of that event on their psychological well-being. The power of cultural and social influences on nightmares highlights the interconnectedness between our individual selves and the larger society in which we live. Understanding these influences can provide valuable insights into the complexities of our dream world and facilitate the development of culturally sensitive approaches to managing and interpreting nightmares.
Effects of Nightmares on Sleep and Mental Health
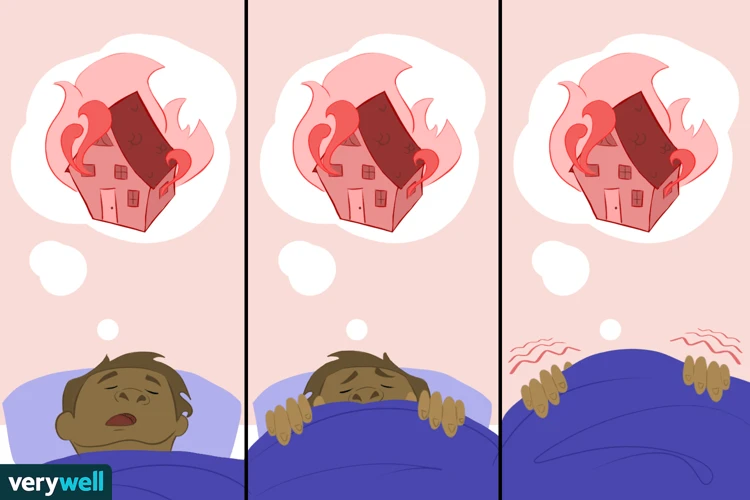

The effects of nightmares extend beyond the realm of sleep, impacting both our physical and mental well-being. Nightmares can disrupt the quality and duration of our sleep, leading to sleep disruptions such as difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and feelings of unrest upon waking. These disruptions can result in daytime fatigue, decreased cognitive functioning, and reduced overall productivity. The negative emotions and distress caused by nightmares can take a toll on our mental health. Persistent nightmares have been linked to an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The relentless loop between nightmares and poor mental health can create a vicious cycle, with nightmares exacerbating psychological distress and vice versa. Recognizing the profound impact of nightmares on sleep and mental well-being underscores the importance of addressing and managing these nocturnal disturbances effectively.
Sleep Disruptions
Sleep disruptions caused by nightmares can have a profound impact on an individual’s overall sleep quality and well-being. When nightmares occur, they can jolt a person awake, interrupting the normal sleep cycle and preventing the individual from experiencing restful and rejuvenating sleep. These disruptions can lead to feelings of fatigue, grogginess, and decreased daytime functioning. Additionally, frequent nightmares can contribute to the development of insomnia, as the fear of experiencing another distressing dream can create anxiety and anticipation around going to sleep. Insufficient sleep caused by nightmares can also impair cognitive function, memory consolidation, and emotional regulation, making it more challenging to navigate daily tasks and responsibilities. Over time, chronic sleep disruptions can have detrimental effects on mental health, exacerbating symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress. It is therefore crucial to address and manage nightmares effectively to promote healthy sleep patterns and overall well-being.
Impact on Mental Well-being
Nightmares can have a significant impact on mental well-being. The distressing nature of these dreams can lead to feelings of fear, anxiety, and even depression. The emotional intensity experienced during nightmares can linger even after waking, affecting a person’s overall mood and emotional stability. Recurring nightmares, in particular, can disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to chronic sleep deprivation and fatigue. This lack of quality sleep further exacerbates the negative impact on mental well-being.
In addition to the emotional toll, nightmares can also affect cognitive functioning. They can impair concentration, memory, and decision-making abilities, making it difficult to perform daily tasks effectively. Persistent nightmares may also contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health disorders such as anxiety disorders and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Individuals who have experienced trauma in their lives may be especially vulnerable to the detrimental effects of nightmares on their mental well-being.
The fear and avoidance associated with nightmares can lead to a decrease in overall quality of life. Individuals may become apprehensive about going to sleep, leading to sleep disturbances and anxiety around bedtime. The fear of experiencing nightmares can result in an increased level of vigilance and hyperarousal, making it challenging to relax and unwind. Over time, this can lead to a cycle of poor sleep, heightened anxiety, and worsening mental well-being.
Recognizing the impact of nightmares on mental well-being is crucial for individuals seeking to address and manage their experiences. Seeking professional help, such as therapy or counseling, can provide valuable support and guidance in overcoming the negative effects of nightmares. Additionally, adopting healthy sleep habits, practicing relaxation techniques, and implementing stress-management strategies can contribute to improved mental well-being and a reduction in the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
Techniques for Managing Nightmares
Nightmares can be incredibly distressing, but there are techniques that can help manage and alleviate their impact. One effective approach is keeping a dream journal. By recording and analyzing recurring themes or patterns in nightmares, individuals can gain a better understanding of the underlying emotions and triggers. This awareness can serve as a foundation for exploring and addressing the root causes of these nightmares. Another technique is to seek therapeutic approaches. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be beneficial in helping individuals develop coping strategies and challenge negative thought patterns associated with nightmares. Additionally, making certain lifestyle changes can contribute to improved sleep and reduced likelihood of nightmares. These changes may include establishing a consistent sleep routine, engaging in relaxation techniques before bed, and creating a comfortable sleep environment. By implementing these techniques, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing nightmares and promoting better sleep and overall well-being.
Keeping a Dream Journal
Keeping a Dream Journal is a valuable technique for managing and gaining insights into one’s nightmares. By documenting dreams in a journal, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of the themes, images, and emotions that emerge during their nightmares. Here are some key considerations and benefits of keeping a dream journal:
1. Consistency: It is essential to make journaling a regular habit. Set aside a few minutes each morning to write down all the details you can remember from your dreams, including any specific elements that stood out, emotions experienced, and any recurring themes.
2. Detail: Be as detailed as possible when describing your dreams. Include sensory experiences, such as sights, sounds, smells, and textures. These small details can provide valuable clues about the underlying meanings and triggers of your nightmares.
3. Patterns and Triggers: Over time, as you review your dream journal, you may start to identify patterns or common triggers that precede your nightmares. By recognizing these patterns, you can become more aware of the factors that contribute to your nightmares and take steps to mitigate them.
4. Symbolism: Dreams often communicate through symbols and metaphors. Keeping a dream journal allows you to explore and interpret the symbolism within your nightmares. Note down any recurring symbols or themes and reflect on their personal significance.
5. Emotional Healing: Writing about your dreams can serve as a therapeutic outlet for processing difficult emotions associated with nightmares. It provides an opportunity to express and release negative feelings, promoting emotional healing and potentially reducing the frequency or intensity of nightmares.
6. Discussion and Analysis: Consider sharing your dream journal entries with a therapist or support group. Engaging in discussions about your dreams can offer fresh perspectives and insights that you may not have considered on your own.
7. Tracking Progress: A dream journal enables you to track your progress over time. You can observe any changes in the frequency or content of your nightmares, as well as the effectiveness of any interventions or coping strategies you may be implementing.
Remember, the goal of keeping a dream journal is not only to document your nightmares but also to gain a deeper understanding of your subconscious mind and work towards resolving the underlying psychological causes. Embrace the process of self-discovery and exploration as you embark on your journaling journey.
Therapeutic Approaches
Therapeutic approaches play a crucial role in managing and addressing nightmares. There are several effective techniques and therapies that can help individuals reduce the frequency and intensity of their nightmares. Here are some key therapeutic approaches to consider:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely used therapeutic approach that can be beneficial for individuals experiencing nightmares. This therapy focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to distressing dreams. By learning to reframe negative thoughts and develop more adaptive coping strategies, individuals can gain control over their nightmares and reduce their impact.
2. Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing individuals to the content of their nightmares in a controlled and safe environment. This approach aims to desensitize individuals to the distressing elements of their dreams, helping them develop a sense of mastery and control. Over time, exposure therapy can lead to a reduction in the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
3. Imagery Rehearsal Therapy (IRT): IRT focuses on altering the content of nightmares by rehearsing alternative, positive endings to the dreams. Individuals are encouraged to vividly imagine a new version of the nightmare that is less distressing or more empowering. By repeatedly practicing this revised dream scenario during waking hours, the individual can potentially influence their dream content and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
4. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage nightmares, particularly if they are linked to underlying mental health conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Medications like prazosin or antidepressants may be used to reduce the intensity and frequency of nightmares and promote better sleep.
5. Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery can help alleviate stress and anxiety, which are common triggers for nightmares. These techniques promote relaxation and improve overall sleep quality.
Each individual is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. It is important to work closely with a qualified therapist or healthcare professional to find the most suitable therapeutic approach for managing nightmares. Combining different approaches or tailoring interventions to specific needs can increase the likelihood of success in reducing the impact of nightmares and improving sleep quality.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can be an effective approach in managing nightmares and improving overall sleep quality. Lifestyle changes involve modifications to daily habits and routines that can positively impact sleep patterns and reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares. One important aspect to consider is maintaining a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at consistent times. This helps regulate the body’s internal clock and promotes more restful sleep. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine can also be beneficial, such as engaging in calming activities like reading a book or taking a warm bath before sleep. Reducing exposure to potential triggers before bedtime is also crucial, such as avoiding stimulating activities, heavy meals, caffeine, and electronic devices. Establishing a comfortable sleep environment, including a cool and quiet bedroom with proper lighting, can contribute to better sleep quality. Engaging in regular physical activity and managing stress through techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises can also minimize the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. It is important to note that lifestyle changes may take time to show their full effect, so consistency and patience are key in implementing and maintaining these adjustments to promote healthier sleep and reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the psychological causes of nightmares is crucial in effectively managing and addressing these unsettling dreams. Nightmares can arise from a variety of sources, including stress, trauma, psychological disorders, and childhood experiences. The emotions associated with nightmares, such as fear, anxiety, anger, and sadness, play a significant role in their manifestation. Additionally, personal beliefs and cultural influences can shape the content and interpretation of nightmares. The impact of nightmares extends beyond sleep disturbances, often leading to negative effects on mental well-being. However, there are techniques available for managing nightmares, such as keeping a dream journal, seeking therapeutic approaches, and making lifestyle changes. By implementing these strategies, individuals can gain a better understanding of their nightmares and work towards improving their sleep quality and overall mental health. Ultimately, conquering nightmares can lead to a more peaceful and restorative sleep experience, fostering a sense of well-being and vitality.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary purpose of dreams?
The primary purpose of dreams is not fully understood, but they are believed to serve various functions, including processing emotions, consolidating memories, and aiding in problem-solving and creativity.
Are nightmares more common in children or adults?
Nightmares are more common in children than in adults. It is estimated that up to 50% of children between the ages of 3 and 5 experience nightmares, while the prevalence decreases with age.
Can certain medications cause nightmares?
Yes, some medications, such as antidepressants, beta-blockers, and drugs that affect the central nervous system, have been associated with an increased risk of nightmares.
How can stress and anxiety contribute to nightmares?
Stress and anxiety can disrupt the normal sleep cycle and lead to increased emotional arousal during sleep, making individuals more prone to experiencing nightmares. Additionally, unresolved stress and anxiety during wakefulness can manifest in nightmares during sleep.
Can traumatic experiences contribute to recurring nightmares?
Yes, traumatic experiences can contribute to recurring nightmares. The mind often uses dreams as a way to process and attempt to make sense of traumatic events, which can result in repetitive nightmares related to the trauma.
Which psychological disorders are commonly associated with nightmares?
Psychological disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, depression, and sleep disorders like insomnia are often associated with an increased frequency of nightmares.
Do cultural and social factors influence the content of nightmares?
Yes, cultural and social factors can influence the content of nightmares. Beliefs, values, and societal norms can shape the themes and symbols present in nightmares experienced by individuals.
How can nightmares affect sleep quality?
Nightmares can disrupt the sleep cycle by causing awakenings throughout the night. These disruptions can lead to fragmented sleep, insomnia, and a decreased overall quality of sleep.
What impact can nightmares have on mental well-being?
Nightmares can contribute to increased stress, anxiety, and emotional distress. They may also have a negative impact on mental well-being by exacerbating existing psychological conditions and interfering with daily functioning.
What strategies can help manage nightmares?
Strategies for managing nightmares include keeping a dream journal to identify patterns, seeking therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, and making lifestyle changes like improving sleep hygiene and reducing stress levels.








