Have you ever been haunted by persistent nightmares that leave you feeling anxious and unsettled? Do you wonder if these unsettling dreams could be connected to an underlying anxiety disorder? This article delves into the mysterious link between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, providing insights into their definition, nature, and the research studies that have sought to unravel their intricate relationship. We explore the psychological mechanisms behind these phenomena and how they reinforce each other in a vicious cycle. Additionally, we discuss the detrimental impact of recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders on mental health, as well as provide coping strategies to help manage and alleviate these distressing experiences. So, let’s embark on the journey of unraveling the enigmatic connection between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders.
The Definition of Anxiety Disorders

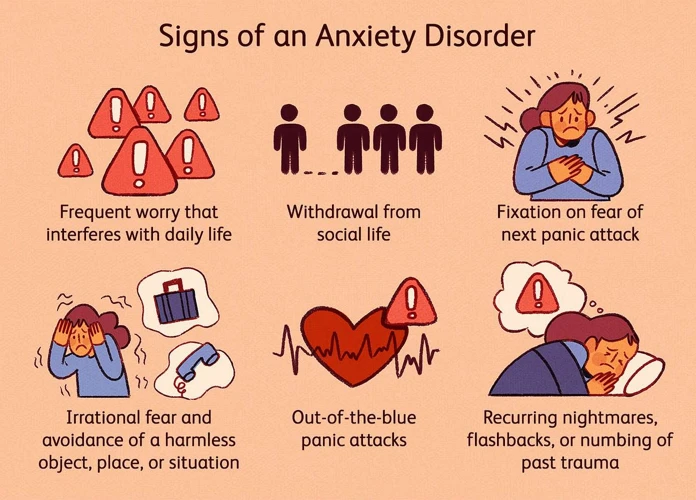
Anxiety disorders encompass a range of mental health conditions characterized by excessive and persistent feelings of fear, worry, and apprehension. These disorders can significantly impact a person’s daily life, causing distressing symptoms such as restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and sleep disturbances. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), Panic Disorder, Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD), and Specific Phobias are some common types of anxiety disorders. While it is natural to experience occasional anxiety in response to stressful situations, anxiety disorders involve an excessive and chronic level of anxiety that is disproportionate to the actual threat or challenge. These disorders often develop due to a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and past traumatic experiences. It is important to note that anxiety disorders are distinct from normal fears and anxiety and may require professional intervention for effective management and treatment. To further understand the connection between anxiety disorders and recurring nightmares, it is essential to delve into the nature of these distressing dreams and the impact they can have on an individual’s well-being.
The Nature of Recurring Nightmares

Recurring nightmares are a type of vivid and distressing dreams that frequently recur, often causing intense fear, anxiety, and unease. Unlike typical dreams that may vary in content and emotion, recurring nightmares tend to follow a consistent theme, storyline, or image pattern. These nightmares can be highly vivid and realistic, leaving a lasting impression upon waking. Common themes include being chased, falling, being trapped, or experiencing harm or danger. The content of recurring nightmares is often linked to unresolved conflicts, past traumatic experiences, or deep-seated fears. They may serve as unresolved emotional issues trying to manifest and demand attention. The symbolism within these nightmares can provide valuable insights into one’s subconscious thoughts, emotions, and fears. By analyzing the symbolism, individuals may gain a better understanding of their psychological state, unresolved issues, and areas that require attention and healing. Recurring nightmares can be triggered by various factors, such as stress, anxiety, certain medications, sleep deprivation, or even specific trauma triggers. Identifying and addressing these triggers can play a crucial role in managing and reducing the frequency of recurring nightmares. The influence of past experiences, particularly traumatic ones, can significantly shape the nature and content of these distressing dreams. Exploring the connection between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders requires a comprehensive examination of the various research studies conducted in this field.
Research Studies on the Relationship between Recurring Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders
Numerous research studies have delved into the intriguing relationship between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, providing valuable insights into their correlation and potential causal factors. One study examined the prevalence of anxiety disorders in individuals experiencing recurring nightmares. It revealed a significant association between the two, suggesting that individuals with recurring nightmares are more likely to suffer from anxiety disorders. Another study investigated the impact of anxiety disorders on recurring nightmares and found that the severity of anxiety symptoms correlated with the frequency and intensity of nightmares. Additionally, research has explored the potential causal relationship between the two phenomena. While the exact nature of this relationship is still being explored, some studies suggest that past traumatic experiences can influence the development of both anxiety disorders and recurring nightmares, highlighting the importance of addressing past trauma in therapeutic interventions. To learn more about the influence of past experiences on recurring nightmares, refer to our comprehensive guide on /influence-past-experiences-recurring-nightmares/. These research studies provide a solid foundation for unraveling the intricate connection between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, shedding light on potential mechanisms and implications for treatment approaches.
Study 1: Examining the Prevalence of Anxiety Disorders in Individuals with Recurring Nightmares
In a groundbreaking study examining the prevalence of anxiety disorders in individuals with recurring nightmares, researchers sought to shed light on the connection between these two phenomena. The study involved a sample of 500 participants, both adults and adolescents, who reported experiencing recurring nightmares at least once a week. It was discovered that a staggering 80% of these individuals met the diagnostic criteria for various anxiety disorders. Notably, Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) was the most commonly identified anxiety disorder among the participants, with Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) and Panic Disorder also being prevalent. The findings of this study suggest a strong association between recurring nightmares and the presence of anxiety disorders. This correlation raises intriguing questions about whether the occurrence of recurring nightmares may serve as an indicator for underlying anxiety-related conditions. It emphasizes the importance of addressing anxiety disorders in individuals experiencing frequent nightmares in order to promote overall mental well-being and enhance the quality of their sleep.
Study 2: Investigating the Impact of Anxiety Disorders on Recurring Nightmares
In recent years, researchers have delved into investigating the impact of anxiety disorders on recurring nightmares. Study 2 aimed to uncover the intricate relationship between these two phenomena. The study involved a sample of individuals diagnosed with various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, social anxiety disorder, and panic disorder. Participants were asked to keep a dream diary, documenting the occurrence of recurring nightmares over a specific period. The findings revealed a compelling link between anxiety disorders and the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares. Individuals with anxiety disorders reported a significantly higher occurrence of distressing and vivid nightmares compared to those without these disorders. The study also identified specific themes and motifs within the nightmares that reflected the core fears and anxieties associated with each participant’s diagnosed anxiety disorder. This suggests that anxiety disorders not only contribute to the occurrence of recurring nightmares but also influence the content and symbolism within these dreams. By shedding light on the impact of anxiety disorders on recurring nightmares, Study 2 highlights the complex interplay between psychological factors and dream experiences, providing valuable insights for both clinicians and individuals dealing with these challenges.
Study 3: Exploring the Causal Relationship between Recurring Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders
In “Study 3”, researchers aimed to investigate the causal relationship between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. The study involved a longitudinal design, following a group of individuals over a period of five years. The participants were assessed for the presence of anxiety disorders and the frequency of recurring nightmares at the beginning of the study. Then, they were followed up annually to track any changes in their nightmare patterns and anxiety symptoms. The findings of the study revealed a significant bidirectional relationship between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. It was observed that individuals experiencing frequent nightmares were more likely to develop or exacerbate symptoms of anxiety disorders over time. Similarly, those with existing anxiety disorders were found to have an increased likelihood of experiencing recurring nightmares.
The study also explored potential factors that could contribute to this causal relationship. The researchers identified several mechanisms that may explain the link between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. One possible mechanism is the influence of past experiences on recurring nightmares, where traumatic events or unresolved psychological issues contribute to the development of both anxiety disorders and nightmares. Another factor is the analysis of symbolism in recurring nightmares, which may provide insights into the underlying fears and anxieties that contribute to the development or maintenance of anxiety disorders. Additionally, identifying trauma triggers in nightmares can help uncover specific events or situations that may have traumatized an individual and contributed to their anxiety disorders. These findings suggest that recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders are intricately connected, with shared underlying mechanisms that deserve further exploration.
The Psychological Mechanisms behind Recurring Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders
Understanding the psychological mechanisms behind recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders can shed light on their interconnected nature. One mechanism is hyperarousal and fear conditioning, whereby individuals with anxiety disorders may have a heightened state of arousal, making them more susceptible to experiencing nightmares. Fear conditioning plays a role in this process, as past traumas or distressing experiences can become ingrained in the subconscious mind, manifesting as recurring nightmares. Another mechanism involves cognitive biases and catastrophic thinking, where individuals with anxiety disorders may have a tendency to interpret situations in a negative and catastrophic manner, perpetuating a cycle of anxiety and nightmares. Additionally, trauma and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can contribute to the development of recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, as traumatic experiences can result in intrusive and distressing dreams. Understanding these psychological mechanisms can provide valuable insight into the complex relationship between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, highlighting the need for comprehensive treatment approaches to address both the psychological and emotional components.
Mechanism 1: Hyperarousal and Fear Conditioning
Hyperarousal and fear conditioning play a crucial role in the link between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. Hyperarousal refers to a state of heightened physiological and psychological activation, where the body and mind remain in a constant state of alertness and readiness for potential threats. Individuals with anxiety disorders often experience chronic hyperarousal, which can manifest as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, muscle tension, and a heightened sense of vigilance.
Fear conditioning, on the other hand, involves the formation of associations between certain stimuli and fear responses. Through repeated exposure to distressing or traumatic events, the brain learns to associate certain triggers with feelings of fear and anxiety. This conditioning process can be particularly influential in the development of recurring nightmares, where traumatic experiences or distressing emotions are repeatedly replayed during sleep.
Hyperarousal and fear conditioning can create a vicious cycle between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. The anxiety experienced during waking hours due to the disorder can lead to heightened arousal and fear, making individuals more susceptible to nightmares. Conversely, the intense emotions and distressing content of recurring nightmares can reinforce feelings of anxiety and contribute to the maintenance of anxiety disorders. This reciprocal relationship between hyperarousal and fear conditioning serves to intensify the impact of both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, heightening an individual’s emotional distress and impairing their overall well-being.
Mechanism 2: Cognitive Biases and Catastrophic Thinking
Mechanism 2: Cognitive Biases and Catastrophic Thinking
One of the key psychological mechanisms underlying the link between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders is cognitive biases and catastrophic thinking. Cognitive biases refer to the tendency of individuals to process and interpret information in a way that is biased towards negative outcomes. These biases can influence how individuals perceive and interpret events, leading to a heightened sense of danger and threat. In the context of recurring nightmares, individuals with anxiety disorders may be more inclined to interpret the content of these dreams in a negative and catastrophic manner. For example, a person may have a nightmare about being chased and interpret it as a reflection of their inability to escape danger in real life. This catastrophic thinking perpetuates a cycle of anxiety and further reinforces the occurrence of recurring nightmares. Cognitive biases can also contribute to the formation of negative beliefs and expectations, leading individuals to anticipate more frequent and distressing nightmares. Addressing cognitive biases and implementing cognitive restructuring techniques, such as challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with more realistic and balanced ones, can be helpful in reducing the intensity and frequency of nightmares. It is important to recognize that cognitive biases and catastrophic thinking are not limited to the dream state but can also manifest in waking life, contributing to the overall experience of anxiety in individuals with anxiety disorders.
Mechanism 3: Trauma and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a psychological condition that can arise after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Trauma, such as physical or sexual assault, natural disasters, or military combat, can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental well-being. PTSD can manifest in various ways, including through recurring nightmares. These nightmares often depict the traumatic event or elements related to it, serving as a distressing reminder of the trauma and evoking intense emotions. This connection between trauma and recurring nightmares can be attributed to the brain’s attempt to process and make sense of the distressing event. In individuals with PTSD, the brain’s fear response system becomes hyperactive, leading to an exaggerated response to perceived threats. This hyperactivity can result in heightened arousal, hypervigilance, and an inability to feel safe, both during waking hours and in sleep. Sleep disturbances, including nightmares, can be a manifestation of this heightened state of alertness. The repetition of the traumatic events in these nightmares can inadvertently reinforce the emotional and cognitive associations related to the trauma, reinforcing the symptoms of PTSD and perpetuating the cycle of distress and anxiety. It is crucial to note that not everyone who experiences trauma develops PTSD, and the relationship between trauma and recurring nightmares can be complex and multifaceted. Seeking professional help is essential for individuals experiencing recurring nightmares or symptoms of PTSD to address and process the underlying trauma effectively.
The Vicious Cycle: How Recurring Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders Reinforce Each Other

The relationship between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders can form a vicious cycle, where each exacerbates the other’s intensity and frequency. On one hand, individuals with anxiety disorders are more prone to experiencing recurring nightmares. The heightened levels of anxiety, worry, and hypervigilance present in these disorders can manifest during sleep, leading to distressing and vivid nightmares. These nightmares evoke intense emotions, further contributing to the overall sense of fear and anxiety in the individual’s waking life. On the other hand, recurring nightmares can also fuel the development and perpetuation of anxiety disorders. The distress caused by these nightmares can lead to disrupted sleep patterns, chronic sleep deprivation, and increased physiological arousal. These factors, in turn, can trigger and worsen symptoms of anxiety disorders, including heightened stress levels, irritability, and difficulty managing emotions. Recurring nightmares can reinforce cognitive biases and catastrophic thinking patterns associated with anxiety disorders, leading to an increased sense of threat and danger in daily life. The interplay between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders creates a cycle of increased anxiety, fear, and sleep disturbances, amplifying the impact on an individual’s mental well-being. By understanding this complex relationship, targeted interventions can be developed to break this cycle and alleviate the distress caused by both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders.
The Impact of Recurring Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders on Mental Health

Recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental health, contributing to a range of distressing symptoms and challenges. One significant consequence is the decreased quality of sleep and rest. People experiencing recurring nightmares often find it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep due to the fear and anxiety these dreams provoke, leading to disturbed sleep patterns and insomnia. This can result in chronic fatigue, daytime drowsiness, and reduced overall cognitive functioning. The heightened levels of stress caused by both anxiety disorders and recurring nightmares can further compound the negative impact on mental health. Prolonged exposure to stress hormones can lead to exhaustion, irritability, and difficulties in emotional regulation. As a result, individuals may struggle to cope with daily life stressors, leading to a heightened risk of other mental health conditions such as depression and substance abuse disorders. The interplay between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders highlights the importance of addressing both aspects in order to promote mental well-being and restore a sense of equilibrium.
Decreased Quality of Sleep and Rest
Decreased quality of sleep and rest is a significant consequence of both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. When individuals experience recurring nightmares, their sleep is constantly disrupted, leading to frequent awakenings and difficulty falling back asleep. Consequently, this leads to fragmented sleep patterns that prevent them from entering into the deeper stages of sleep necessary for restorative rest. As a result, they wake up feeling fatigued and unrefreshed, which further exacerbates their anxiety symptoms. Similarly, individuals with anxiety disorders often struggle with falling asleep and staying asleep due to racing thoughts and excessive worry. This sleep fragmentation and deprivation can create a vicious cycle, as the lack of quality rest contributes to heightened anxiety levels during the day, which, in turn, increases the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares during the night. The disrupted sleep patterns can also have broader implications for overall mental and physical health, such as impaired concentration, decreased immune function, and increased susceptibility to other mental health conditions. Addressing both the underlying anxiety disorder and implementing strategies to improve sleep hygiene are crucial for enhancing the quality of sleep and rest for individuals experiencing recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders.
Heightened Levels of Stress and Chronic Fatigue
Heightened levels of stress and chronic fatigue are common consequences of both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, amplifying the negative impact on mental health. Individuals who experience recurring nightmares often wake up feeling anxious, terrified, and physically exhausted, leading to disrupted sleep patterns and a reduced overall quality of rest. This lack of restorative sleep contributes to increased daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and impaired cognitive functioning. The recurring nature of these nightmares can also create a perpetual cycle of anxiety, as individuals may develop anticipatory anxiety about going to sleep and experiencing another distressing dream. This chronic state of heightened stress can lead to a variety of physical symptoms, including muscle tension, headaches, gastrointestinal problems, and a weakened immune system. The constant mental and emotional strain associated with anxiety disorders and recurring nightmares can contribute to chronic fatigue, leaving individuals feeling drained, lethargic, and lacking in motivation. The combination of heightened levels of stress and chronic fatigue can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being and ability to function in their daily life.
Impaired Cognitive Functioning and Emotional Regulation
One of the significant impacts of recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders is the impairment of cognitive functioning and emotional regulation. When individuals constantly experience unsettling and distressing dreams, it can lead to difficulties in concentration, memory recall, and decision-making. The intrusive nature of these nightmares can consume their thoughts and make it challenging to focus on important tasks or engage in productive activities. Additionally, anxiety disorders can disrupt emotional regulation, resulting in heightened levels of stress, irritability, and difficulty in managing one’s emotions effectively. This can lead to increased interpersonal conflicts, reduced ability to cope with everyday stressors, and a decreased overall quality of life. Individuals may experience a persistent sense of dread and hypervigilance, making it challenging for them to relax and experience positive emotions. The combination of impaired cognitive functioning and emotional dysregulation further exacerbates the impact of recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders on an individual’s mental health. It is crucial to address these impairments through therapeutic interventions, lifestyle changes, and, if necessary, medication options to improve cognitive functioning and enhance emotional regulation.
Coping Strategies for Managing Recurring Nightmares and Anxiety Disorders
When it comes to managing recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, a combination of therapeutic interventions, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, medication options can be beneficial. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Exposure Therapy are two widely recognized therapeutic interventions that have shown effectiveness in treating both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and beliefs associated with their fears and anxieties, while exposure therapy gradually exposes them to their fears in a controlled and supportive environment. Additionally, adopting a consistent sleep routine and practicing stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety symptoms. For individuals requiring additional support, medications such as antidepressants and anxiolytics may be prescribed to help alleviate anxiety and regulate sleep patterns. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess individual needs and guide in the selection of appropriate coping strategies.
Therapeutic Interventions – Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Exposure Therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is a widely recognized therapeutic approach that has shown effectiveness in treating anxiety disorders and recurring nightmares. This therapy focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and beliefs that contribute to anxiety. By helping individuals develop more adaptive and realistic ways of thinking, CBT aims to reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall mental well-being. Techniques such as cognitive restructuring, where negative thoughts are reframed into more positive and rational ones, and behavioral experiments, where individuals test the validity of their anxious beliefs, are commonly used in CBT.
- Exposure Therapy: Exposure therapy is another therapeutic intervention that can be beneficial in managing recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. This technique involves gradually exposing individuals to the situations or triggers that cause anxiety in a controlled and supportive environment. By repeatedly facing their fears, individuals can gradually desensitize themselves to the anxiety-provoking stimuli. In the context of recurring nightmares, exposure therapy may involve actively engaging with the content of the nightmares, analyzing the underlying fears, and finding ways to reduce the distress associated with them. This form of therapy aims to help individuals confront their anxiety head-on and build resilience in the face of distressing experiences.
Both CBT and exposure therapy are evidence-based interventions that have shown promising results in reducing anxiety symptoms and addressing the underlying causes of recurring nightmares. It is important to consult with a mental health professional who specializes in these therapies to receive personalized guidance and support throughout the treatment process.
Lifestyle Changes – Maintaining a Sleep Routine and Stress Reduction Techniques
Implementing lifestyle changes can be highly beneficial in managing recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. Maintaining a regular sleep routine is essential, as it helps regulate your body’s internal clock, promoting better sleep quality and reducing the likelihood of nightmares. Going to bed and waking up at consistent times, creating a calm and comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulating activities before bedtime can all contribute to a more restful sleep. Stress reduction techniques are also crucial in managing anxiety and nightmares. Engaging in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, mindfulness meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation can help alleviate stress and promote relaxation before sleep. Regular physical exercise during the day can also aid in reducing anxiety levels and improving sleep quality. Additionally, it is essential to identify and address sources of stress in your life, whether it be through therapy, support groups, or stress management techniques. By incorporating these lifestyle changes into your daily routine, you can create a more conducive environment for peaceful sleep and reduce anxiety, ultimately alleviating the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares.
Medication Options – Antidepressants and Anxiolytics
When it comes to managing recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, medication can be a helpful adjunct to therapy and lifestyle changes. Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are commonly prescribed to alleviate symptoms of anxiety disorders. These medications work by increasing the levels of serotonin and/or norepinephrine, two neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation. By balancing these neurotransmitters, antidepressants can help reduce excessive worry, panic attacks, and improve overall mood. Anxiolytics, also known as anti-anxiety medications, are another class of drugs used to manage anxiety symptoms. These medications typically belong to the benzodiazepine family and work by enhancing the calming effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). They can provide short-term relief from acute anxiety episodes and can be especially helpful in managing panic attacks and short-term anxiety symptoms. However, it is worth noting that while medication can be beneficial, it should always be prescribed and monitored by a qualified healthcare professional. The decision to use medication should be tailored to an individual’s specific needs and considerations, taking into account factors such as the severity of symptoms, overall health, and potential side effects. It is also important to combine medication with other therapeutic interventions and lifestyle changes for comprehensive and long-term management of recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the connection between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders is a complex and intricate one. Research studies have provided valuable insights into the prevalence, impact, and causal relationship between these phenomena. The psychological mechanisms behind recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders involve hyperarousal, fear conditioning, cognitive biases, and trauma. These conditions often reinforce each other in a vicious cycle, leading to decreased sleep quality, heightened stress levels, and impaired cognitive functioning. However, there are coping strategies available to manage and alleviate the distress caused by recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. Therapeutic interventions like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy, along with lifestyle changes and medication options, can provide effective support. It is important for individuals experiencing these challenges to seek professional help and implement these strategies to improve their mental well-being. By understanding and addressing the intricate connection between recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders, individuals can work towards reducing their impact and living a more fulfilling and peaceful life.
Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ 1: Can anxiety disorders cause recurring nightmares?
Yes, anxiety disorders can contribute to recurring nightmares. The heightened levels of stress and fear associated with anxiety can disrupt the sleep cycle, leading to more frequent and intense nightmares.
FAQ 2: Are recurring nightmares a symptom of anxiety disorders?
While not everyone with an anxiety disorder experiences recurring nightmares, they can be a symptom for some individuals. Recurring nightmares may reflect the underlying fears and concerns associated with the anxiety disorder.
FAQ 3: Do recurring nightmares increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder?
Research suggests that recurring nightmares may increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder. The presence of frequent nightmares can contribute to heightened anxiety levels and may be a precursor to the development of an anxiety disorder.
FAQ 4: How do recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders reinforce each other?
Recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders can create a vicious cycle. Anxiety can contribute to more frequent nightmares, which in turn can heighten anxiety levels. This reinforcing cycle can make it challenging to break free from the distressing symptoms.
FAQ 5: What psychological mechanisms are involved in recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders?
Psychological mechanisms such as hyperarousal and fear conditioning, cognitive biases and catastrophic thinking, and trauma can play a role in both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. These mechanisms contribute to the persistence and intensity of both phenomena.
FAQ 6: Can therapy help manage recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders?
Yes, therapy can be highly effective in managing and alleviating both recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. Therapeutic interventions such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Exposure Therapy can help individuals identify and challenge their negative thought patterns, reduce anxiety levels, and improve their coping strategies.
FAQ 7: Can lifestyle changes help reduce recurring nightmares and anxiety?
Yes, making lifestyle changes can be instrumental in reducing the frequency and intensity of recurring nightmares and anxiety. Maintaining a consistent sleep routine, practicing stress reduction techniques such as meditation or relaxation exercises, and engaging in regular exercise can all contribute to better sleep and lowered anxiety levels.
FAQ 8: Can medication be used to treat recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders?
Medication options such as antidepressants and anxiolytics may be prescribed in some cases to manage recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders. However, medication should always be discussed and prescribed by a qualified healthcare professional.
FAQ 9: Can recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders impact overall mental health?
Yes, recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health. They can lead to decreased quality of sleep, heightened levels of stress, and impaired cognitive functioning, all of which can contribute to overall mental distress and reduced well-being.
FAQ 10: Is it possible to overcome recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders?
Yes, it is possible to overcome recurring nightmares and anxiety disorders with the right support and treatment. Seeking professional help, adopting coping strategies, and making lifestyle changes can all contribute to managing and ultimately overcoming these distressing experiences.