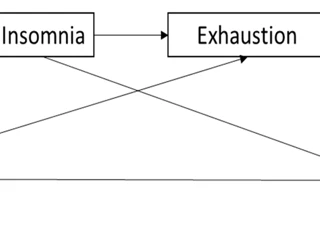
Insomnia and stress, two seemingly unrelated issues, have a deeper connection that affects countless individuals worldwide. The relentless grip of insomnia can leave one feeling exhausted, agitated, and desperate for a good night’s sleep. On the other hand, stress, the silent intruder, creeps into our lives, disrupting our peace and harmony. What many may not realize is the intricate dance between insomnia and stress—their cause and effect, their symbiotic relationship. This article aims to delve into this complex connection, exploring the ways in which stress affects sleep patterns and how insomnia, in turn, intensifies stress levels. By understanding this link, we can identify the key factors contributing to stress-induced insomnia, implement coping strategies, and seek professional help when necessary. So let’s embark on this insightful journey, peeling back the layers of this enigmatic partnership to pave the way for a restful and rejuvenating slumber.
1. Definition of Insomnia
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or experiencing non-restorative sleep. It can leave individuals feeling fatigued, irritable, and unable to function optimally during the day. Insomnia is typically classified into two categories: acute and chronic. Acute insomnia occurs for a short duration, often triggered by external factors such as stress, jet lag, or changes in environment. It commonly resolves on its own without the need for medical intervention. On the other hand, chronic insomnia is more persistent and can last for months or even years. It is often associated with underlying medical conditions, psychological disorders, or lifestyle factors. Chronic insomnia requires thorough evaluation and professional intervention for long-term management. It’s important to note that the definition of insomnia may vary among individuals, as sleep patterns and needs differ. While some individuals may function well on just a few hours of sleep, others may require a solid 8 hours to feel rested and refreshed. Understanding the definition and various forms of insomnia is essential in recognizing and addressing sleep issues effectively. Additionally, addressing underlying causes such as poor sleep hygiene, stress, or medical conditions may help in managing and improving sleep quality. For further information on managing insomnia through diet, one can refer to the diet section.
The Link Between Insomnia and Stress
The link between insomnia and stress is a complex and intertwined relationship that can significantly impact an individual’s well-being. Stress, both acute and chronic, can disrupt normal sleep patterns and make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. When we experience stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol, which is known as the “stress hormone.” Elevated levels of cortisol can interfere with the natural sleep-wake cycle, making it harder to achieve restorative sleep. The connection between insomnia and stress is bidirectional, meaning that not only does stress disrupt sleep, but a lack of quality sleep can also contribute to increased stress levels. This vicious cycle can lead to a range of negative effects on physical and mental health. Chronic insomnia, in particular, has been linked to an increased risk of developing mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. The impact of insomnia on mental health can exacerbate existing conditions, making them more difficult to manage. To learn more about the link between insomnia and depression, you can refer to the insomnia-depression link section. It is crucial to understand and address the connection between insomnia and stress in order to implement effective strategies for improving both sleep and overall well-being.
2. How Stress Affects Sleep Patterns
Stress, the silent intruder, can have a profound impact on sleep patterns, disrupting the delicate balance necessary for a restful night. When we experience stress, our bodies release a hormone called cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone.” Elevated cortisol levels can lead to a state of hyperarousal, making it difficult to relax and fall asleep. Additionally, stress can manifest as racing thoughts, worries, and anxiety, further hindering the ability to drift into slumber. Sleep quality is compromised as stress interferes with the natural sleep cycle, resulting in fragmented sleep, frequent awakenings, and difficulty staying asleep. This can lead to a decrease in the overall duration of sleep, leaving individuals feeling fatigued and less rejuvenated upon waking. The negative impact of stress on sleep patterns can create a vicious cycle, where inadequate sleep exacerbates stress levels, further fueling the cycle of sleeplessness. To learn more about the intricate relationship between insomnia and mental health, refer to the informative article on the impact of insomnia on mental health.
3. Effects of Insomnia on Stress Levels
The effects of insomnia on stress levels can create a vicious cycle that intensifies both conditions. When we don’t get enough restful sleep, our body’s stress response system becomes more sensitive, leading to an increase in stress hormones such as cortisol. This heightened stress response can make it harder for us to fall asleep and stay asleep, perpetuating the cycle of insomnia. Additionally, the lack of sleep can impair our cognitive function, making it difficult to cope with daily stressors effectively. We may become irritable, easily overwhelmed, and less able to manage stress. Poor sleep also affects our emotional regulation, making us more prone to negative emotions, anxiety, and depression. These negative psychological states further contribute to increased stress levels. The combination of physical and psychological effects of insomnia can severely impact our overall well-being, creating a detrimental feedback loop between insomnia and stress. Recognizing these effects and addressing them holistically is crucial in breaking the cycle and finding relief. For more information on the link between insomnia and depression, one can refer to the insomnia-depression link. Additionally, understanding the impact of insomnia on mental health is vital in comprehending the broader consequences of this sleep disorder. For further reading, refer to the article on the impact of insomnia on mental health.
Understanding the Impact

Understanding the impact of the relationship between insomnia and stress is crucial in comprehending the toll it takes on our overall well-being. The intertwined nature of these two conditions can have profound effects on our physical and mental health. Stress-induced insomnia, which is triggered by heightened anxiety and worry, can cause a multitude of issues. It disrupts the normal sleep-wake cycle, leading to difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, and early morning awakenings. The lack of quality sleep further exacerbates stress levels, creating a vicious cycle. Chronic insomnia, characterized by persistent sleep difficulties, amplifies the impact of stress on our bodies and minds. The constant fatigue and sleep deprivation can impact cognitive function, mood regulation, and immune system integrity. It hampers our ability to cope with stressful situations, leaving us more vulnerable to the harmful effects of stress. The bidirectional relationship between insomnia and stress underscores the intricate connection between our sleep patterns and mental well-being. By recognizing the impact of this relationship, we can begin to address the underlying factors contributing to stress-induced insomnia and seek solutions for better sleep and stress management strategies.
4. Stress-Induced Insomnia: Causes and Symptoms
Stress-induced insomnia, as the name suggests, is insomnia that is triggered or exacerbated by stress. When we experience stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol, which can interfere with our sleep patterns. Stress can disrupt our ability to relax, quiet our minds, and fall asleep easily. It can also lead to frequent awakenings during the night, making it difficult to maintain a deep and restful sleep. The causes of stress-induced insomnia can vary from person to person, but common triggers include work-related pressures, financial worries, relationship problems, health concerns, and major life events. Additionally, individuals with preexisting anxiety or mood disorders may be more susceptible to stress-induced insomnia. The symptoms of stress-induced insomnia include difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently during the night, early morning awakenings, non-restorative sleep, and feeling tired or unrefreshed upon waking. These symptoms can further contribute to stress levels, creating a vicious cycle of sleeplessness and anxiety. Recognizing the causes and symptoms of stress-induced insomnia is crucial in finding effective coping mechanisms and seeking appropriate treatment. By addressing and managing stress levels, individuals can not only improve their sleep quality but also enhance their overall well-being. For further understanding of the link between insomnia and depression, one can refer to the informative article on the insomnia-depression link.
5. Chronic Insomnia and Its Influence on Stress
Chronic insomnia, a persistent sleep disorder, can have a profound influence on stress levels. When individuals consistently struggle with falling asleep or staying asleep, it disrupts the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and impairs the restorative benefits of sleep. This can lead to increased feelings of stress and anxiety. Insufficient sleep affects the body’s ability to regulate emotions, resulting in heightened sensitivity and irritability. Chronic insomnia can impair cognitive function, making it difficult to concentrate and handle everyday tasks effectively. These challenges can contribute to a sense of overwhelm and further exacerbate stress levels. The impact of chronic insomnia on stress is also bi-directional, as stress itself can be a contributing factor to ongoing sleep issues. Stress triggers a cascade of physiological responses, including the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can disrupt the sleep-wake cycle and make it difficult to achieve restful sleep. This creates a vicious cycle, where stress causes insomnia, and insomnia amplifies stress, creating a cycle of sleep deprivation and heightened stress levels. Breaking this cycle is crucial in managing both chronic insomnia and the associated stress. By implementing stress management techniques and adopting healthy sleep habits, individuals can create a more conducive environment for restful sleep and stress reduction.
6. The Vicious Cycle: The Bidirectional Relationship
The relationship between insomnia and stress is a vicious cycle that can exacerbate both conditions, creating a challenging loop from which it may be difficult to escape. When stress levels are high, the ability to fall asleep and stay asleep becomes compromised. Racing thoughts, anxiety, and heightened arousal keep the mind awake, preventing the onset of restful sleep. As a result, individuals may experience insomnia, leading to a lack of quality sleep. This insufficient sleep then further contributes to increased stress levels. The body and mind are unable to recover and rejuvenate during sleep, intensifying the physical and psychological strain. With heightened stress, the sleep quality continues to suffer, perpetuating the cycle of insomnia and stress. This bidirectional relationship can be overwhelming, and breaking the cycle is crucial for overall well-being. Implementing stress reduction techniques, improving sleep hygiene, and seeking professional help can help interrupt this cycle and restore balance. By addressing both insomnia and stress simultaneously, individuals can work towards lasting relief and better quality of life. To learn more about how insomnia impacts mental health, you can refer to the informative article on the impact of insomnia on mental health.
Identifying the Key Factors

Identifying the key factors that contribute to the link between insomnia and stress is crucial in understanding and managing this complex relationship. These factors can vary from person to person, but some common stressors that contribute to insomnia include:
1. Work-related stress: Excessive workload, long hours, demanding deadlines, and job dissatisfaction can significantly impact sleep quality. The pressure and anxiety associated with work-related stress can make it difficult to relax and unwind at the end of the day.
2. Financial stress: Financial instability, debt, and worries about money can create a constant state of anxiety, making it hard to fall asleep and stay asleep.
3. Relationship issues: Conflicts, arguments, or relationship difficulties can cause emotional stress, leading to sleep disturbances. Relationship issues can weigh heavily on the mind, causing racing thoughts and preventing restful sleep.
4. Traumatic events: Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as an accident, natural disaster, or personal loss, can trigger insomnia due to the emotional distress and psychological impact it has on an individual.
5. Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy habits such as excessive caffeine intake, irregular sleep schedules, lack of physical activity, and poor nutrition can contribute to both stress and insomnia. These factors disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and can worsen the symptoms of stress-induced insomnia.
Recognizing these key stressors in one’s life is the first step in managing both stress and insomnia. By identifying the sources of stress, individuals can take proactive steps to address and mitigate them. This may involve seeking support from loved ones, making positive lifestyle changes, and implementing stress-reduction techniques. Individuals may find it helpful to incorporate stress management techniques, such as relaxation exercises, mindfulness practices, or seeking professional therapy to better cope with stress and improve sleep quality.
7. Stressors That Contribute to Insomnia
Stressors play a significant role in contributing to insomnia, exacerbating sleep difficulties and hindering the ability to achieve restful sleep. These stressors can manifest in various forms and impact individuals differently. Understanding the common stressors associated with insomnia can help in identifying and addressing the underlying causes.
Here are some stressors that commonly contribute to insomnia:
1. Work-related stress: Heavy workloads, tight deadlines, and job uncertainties can create a constant state of stress that makes it difficult to unwind and fall asleep.
2. Relationship problems: Conflict with a spouse, family member, or friend can cause emotional distress, leading to heightened anxiety and difficulty in falling asleep.
3. Financial worries: Financial constraints, debt, or job insecurity can create immense stress, making it challenging to relax and drift into a restful sleep.
4. Health concerns: Chronic pain, physical ailments, or a new diagnosis can cause anxiety and disrupt sleep patterns, resulting in insomnia.
5. Life changes: Major life transitions such as moving, divorce, or the loss of a loved one can trigger significant stress, leading to sleep disturbances.
6. Traumatic events: Past traumas or ongoing post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can create a constant sense of anxiety and hyperarousal that interferes with sleep.
7. Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as excessive caffeine intake, irregular sleep schedules, or engaging in stimulating activities close to bedtime can contribute to increased stress and disrupted sleep.
It is important to identify and address these stressors to alleviate the impact on sleep. Implementing stress management techniques, seeking support from loved ones or professionals, and making lifestyle changes can all contribute to reducing the stressors that contribute to insomnia. By effectively managing stress, one can pave the way for improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
8. Sleep Hygiene and Stress Management Techniques
When it comes to combating insomnia and managing stress, implementing good sleep hygiene practices and stress management techniques is crucial. Here are some tips for improving sleep hygiene:
- Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep.
- Create a Calming Bedtime Routine: Engage in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing deep breathing exercises. Avoid stimulating activities or screens that emit blue light, as they can interfere with your sleep.
- Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use earplugs, eye shades, or white noise machines if necessary.
- Avoid Stimulants: Limit your intake of caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially close to bedtime. These substances can disrupt your sleep patterns and exacerbate stress.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity during the day can help promote better sleep. However, avoid exercising too close to bedtime, as it may energize you and make it harder to fall asleep.
In addition to these sleep hygiene practices, incorporating stress management techniques is essential for breaking the cycle of insomnia and stress. Here are some effective techniques to manage stress:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing has a calming effect on the body, promoting relaxation and reducing stress. Practice deep breathing techniques before bed to prepare your body for sleep.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): PMR involves tensing and then relaxing individual muscle groups, helping release tension from the body and promote a more relaxed state.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness and meditation practices can help shift your focus away from stress and promote a sense of calmness. Consider incorporating guided meditation or mindfulness apps into your daily routine.
- Journaling: Writing down your thoughts and feelings in a journal can be a therapeutic way to process stress, declutter your mind, and promote relaxation before bed.
- Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Engage in activities that you find enjoyable and help you unwind, such as listening to music, practicing yoga, or spending time in nature.
By adopting these sleep hygiene practices and stress management techniques, you can create a more conducive environment for restful sleep and effectively manage stress, ultimately breaking the cycle of insomnia and stress.
Breaking the Cycle: Coping Strategies
Breaking the cycle of insomnia and stress requires implementing effective coping strategies. These strategies aim to address both the underlying causes of stress and the sleep disruptions caused by insomnia. Here are some key coping strategies to consider:
1. Stress Reduction Techniques: Managing stress is crucial for improving sleep quality. Engaging in activities such as yoga, deep breathing exercises, or meditation can help calm the mind and alleviate stress. Additionally, regular physical exercise can release endorphins, reduce anxiety, and promote better sleep.
2. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for Insomnia: CBT is a widely recognized therapy that helps individuals identify negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with insomnia. Through various techniques, such as sleep restriction, stimulus control, and cognitive restructuring, CBT aims to improve sleep habits and regulate sleep-wake patterns.
3. Meditative Practices and Mindfulness: Practices such as mindfulness meditation, guided imagery, and progressive muscle relaxation can promote a state of relaxation and calmness, helping individuals unwind before bedtime. These practices can also enhance self-awareness and help individuals cope with stress more effectively.
4. Sleep Hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep routine and creating a sleep-friendly environment is crucial for better sleep. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, limiting exposure to electronics before bed, and creating a calm and dark sleep environment.
5. Relaxation Techniques: Utilizing relaxation techniques such as taking a warm bath, listening to soothing music, or using aromatherapy can promote relaxation and prepare the mind and body for sleep. These techniques can help alleviate stress and encourage a restful sleep environment.
It’s important to remember that coping strategies may vary for each individual. What works for one person may not work for another. It may take some trial and error to find the most effective coping strategies for managing stress and breaking the cycle of insomnia. Taking a holistic approach that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of sleep can contribute to long-term improvement in sleep quality and overall well-being.
9. Stress Reduction Techniques for Better Sleep
Stress reduction techniques can play a significant role in improving sleep quality and combating insomnia. By implementing these techniques, individuals can create a peaceful and conducive environment for a restful night’s sleep. One effective approach is practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, or guided imagery. These techniques promote a state of calm and help reduce stress and anxiety before bedtime. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as yoga or moderate aerobic exercise, can also have a positive impact on sleep by reducing tension and promoting relaxation. Additionally, establishing a relaxing bedtime routine can signal to the body and mind that it is time to unwind and prepare for sleep. This can include activities like reading, taking a warm bath, or listening to soothing music. Creating a sleep-friendly environment is crucial for reducing stress and promoting better sleep. This involves keeping the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet, and using comfortable bedding and pillows. It may also be helpful to limit exposure to electronic devices before bed, as the blue light emitted by screens can interfere with sleep patterns. Lastly, practicing stress management techniques throughout the day, such as mindfulness meditation or journaling, can help individuals cope with stress and prevent it from escalating at night. By incorporating these stress reduction techniques into daily life, individuals can cultivate a sense of relaxation and calm, leading to improved sleep quality and overall well-being.
10. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a highly effective and evidence-based treatment approach that helps individuals overcome the challenges of insomnia and restore healthy sleep patterns. Unlike traditional therapies that primarily focus on medication, CBT-I targets the underlying causes and factors contributing to insomnia, aiming to modify negative thoughts, behaviors, and beliefs associated with sleep. The therapy involves several key components, including sleep restriction, stimulus control, relaxation techniques, and cognitive restructuring. Sleep restriction involves creating a strict schedule that limits the time spent in bed to the actual sleep time, reducing the time spent tossing and turning. This process helps strengthen the association between the bed and sleep, promoting a faster and more restful sleep onset. Stimulus control techniques focus on creating a conducive sleep environment and establishing a consistent bedtime routine. This may include avoiding stimulating activities in bed, using the bedroom only for sleep and intimacy, and implementing relaxation techniques before bed. Cognitive restructuring aims to identify and challenge negative and distorted thoughts and beliefs about sleep, replacing them with more realistic and positive ones. The therapist works closely with the individual to identify and address any underlying anxieties or stressors that may disrupt sleep. CBT-I is typically delivered in a structured format over several weeks, with regular sessions and homework to reinforce the learned techniques. It empowers individuals to take control of their sleep patterns, providing long-lasting benefits and reducing the reliance on medications. Numerous research studies have highlighted the effectiveness of CBT-I in improving sleep quality, reducing the time it takes to fall asleep, and enhancing overall daytime functioning. If you’d like to explore more about the impact of insomnia on mental health, you can refer to the relevant section on our site: The Impact of Insomnia on Mental Health.
11. Meditative Practices and Mindfulness
Meditative practices and mindfulness techniques have gained significant recognition as effective tools in managing stress and promoting better sleep. Incorporating these practices into your daily routine can help calm the mind, relax the body, and enhance overall well-being. Meditation involves focusing your attention and eliminating the stream of thoughts that often clutter the mind, providing a sense of calm and clarity. Mindfulness, on the other hand, involves being fully present in the moment, non-judgmentally observing your thoughts, emotions, and sensations. By practicing these techniques regularly, you can cultivate a sense of inner peace and reduce the negative impact of stress on your sleep. One popular form of meditation is mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), which combines mindfulness meditation with gentle yoga exercises and body awareness. Another technique is focused breathing, where you concentrate on your breath to anchor your attention and calm the mind. Progressive muscle relaxation is another effective practice where you systematically tense and release different muscle groups, promoting physical and mental relaxation. Guided imagery, where you visualize calming and peaceful scenes, can also induce a state of relaxation. Experiment with different techniques to find what works best for you, and consider incorporating meditation and mindfulness into your daily routine. Not only can these practices improve your sleep quality, but they can also enhance overall mental and emotional well-being.
Seeking Professional Help
When struggling with the complex relationship between insomnia and stress, seeking professional help can be a crucial step towards finding effective solutions. Consulting a healthcare provider, such as a primary care physician or a sleep specialist, can provide valuable insights and guidance tailored to individual needs. These professionals have the expertise to identify potential underlying causes of insomnia and develop a comprehensive treatment plan. Additionally, sleep specialists can conduct diagnostic tests, such as polysomnography or sleep studies, to obtain a detailed assessment of sleep patterns and any potential sleep disorders. These assessments can help uncover any hidden factors contributing to insomnia and may lead to targeted treatments. In some cases, therapy may be recommended to address the psychological aspects related to sleep disturbances. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a commonly recommended therapeutic approach. It focuses on addressing negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to sleep difficulties, promoting healthy sleep habits, and enhancing relaxation techniques. Seeking the help of therapists who specialize in sleep disorders and stress management can also provide valuable support. These therapists can offer guidance, coping strategies, and techniques to effectively manage stress and improve sleep quality. Together, these healthcare providers and specialists offer a comprehensive approach to tackling insomnia and stress, ensuring that appropriate treatment plans are devised to meet individual needs and enhance overall well-being. So, don’t hesitate to reach out to professionals when necessary to break free from insomnia’s grip and restore peaceful slumber.
12. Consulting a Healthcare Provider
When struggling with insomnia and its connection to stress, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for comprehensive evaluation and guidance. A healthcare provider, such as a primary care physician or a sleep specialist, can play a vital role in assessing the underlying causes of insomnia and developing an appropriate treatment plan. They will conduct a thorough medical history assessment, including asking about sleep patterns, stress levels, and any potential contributory factors. Additionally, healthcare providers may utilize various diagnostic tools, such as sleep studies, to better understand the individual’s sleep architecture and identify any potential sleep disorders. Based on the evaluation, they may propose lifestyle modifications, stress management techniques, or recommend specific therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I). In some cases, medication may be prescribed for short-term relief or to address underlying medical conditions contributing to insomnia. Seeking professional help can greatly assist in breaking the cycle of insomnia and stress, providing valuable insights and personalized treatment options to promote better sleep and overall well-being. It is important to remember that each individual’s situation is unique, and consulting a healthcare provider is integral to receiving the most appropriate and effective interventions tailored to one’s specific needs and circumstances.
13. Sleep Specialists and Therapists for Comprehensive Treatment
When it comes to addressing the complex interplay between insomnia and stress, seeking professional help is crucial for comprehensive treatment. Sleep specialists and therapists are experts trained in diagnosing and treating sleep disorders, including insomnia. They have a deep understanding of the intricate relationship between sleep and mental well-being, allowing them to provide specialized care tailored to an individual’s specific needs. Sleep specialists can conduct thorough evaluations, which may involve sleep studies or other diagnostic tests, to identify the underlying causes of insomnia. They can then develop personalized treatment plans that may include a combination of medication, behavioral therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is often recommended, as it focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors associated with sleep. This therapy helps individuals develop healthier sleep habits and manage stress more effectively. Additionally, therapists experienced in sleep disorders can provide valuable support in addressing the emotional and psychological impact of insomnia and stress. Through counseling and various therapeutic techniques, they can help individuals develop coping strategies, explore underlying emotional triggers, and work towards improving overall sleep quality and mental well-being. Collaborating with sleep specialists and therapists offers a comprehensive approach to tackling the challenges of insomnia and stress, enabling individuals to break free from the vicious cycle and achieve restful, rejuvenating sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between insomnia and stress is a complex and intricate one that cannot be overlooked. Stress can disrupt our sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and further exacerbating stress levels. This bidirectional relationship creates a vicious cycle that can have a significant impact on our overall well-being. Understanding the key factors that contribute to stress-induced insomnia, such as external stressors and lifestyle habits, is critical in breaking this cycle. Implementing proper sleep hygiene and stress management techniques can also play a vital role in improving sleep quality and reducing stress levels. Coping strategies like stress reduction techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia, and mindfulness practices can provide valuable tools for better sleep and stress management. However, it is important to recognize that for some individuals, professional help may be necessary. Consulting a healthcare provider, sleep specialist, or therapist can provide comprehensive treatment options tailored to individual needs and circumstances. By addressing the underlying causes of insomnia and stress, we can work towards achieving restful sleep and a healthier, more balanced life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the common causes of insomnia?
Insomnia can be caused by various factors such as stress, anxiety, depression, certain medications, caffeine intake, irregular sleep schedule, chronic pain, and underlying medical conditions.
2. How can stress affect sleep patterns?
Stress can disrupt sleep patterns by making it difficult to quiet the mind, leading to racing thoughts and increased arousal. It can also cause physiological changes in the body, such as an increase in cortisol levels, which can interfere with the natural sleep-wake cycle.
3. Does insomnia increase the risk of developing mental health conditions?
Yes, chronic insomnia has been found to be associated with an increased risk of developing mental health conditions such as anxiety disorders and depression. Sleep disturbances can exacerbate existing mental health issues and hinder the recovery process.
4. Can changing sleep hygiene habits improve insomnia?
Yes, practicing good sleep hygiene habits can positively impact insomnia. This includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, optimizing the sleep environment, avoiding stimulating activities before bed, and limiting caffeine and alcohol intake.
5. Can chronic insomnia be treated without medication?
Yes, there are non-medication-based treatments available for chronic insomnia, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I). CBT-I focuses on identifying and modifying negative thoughts and behaviors associated with sleep and promoting healthy sleep habits.
6. How does meditation help in improving sleep?
Meditation can help improve sleep by reducing stress and promoting relaxation. It calms the mind, reduces anxiety, and enhances overall mindfulness, making it easier to unwind and fall asleep.
7. Is it necessary to consult a healthcare provider for insomnia?
If insomnia persists for more than a few weeks and significantly impacts daily life, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider. They can assess underlying causes, provide appropriate guidance, and recommend further treatment options.
8. How can managing stress levels reduce insomnia?
By employing stress management techniques such as exercise, relaxation exercises, and engaging in enjoyable activities, individuals can reduce the intensity of stress and, in turn, alleviate insomnia symptoms. Managing stress can lead to a calmer mind and better sleep quality.
9. What role does sleep medication play in treating insomnia?
Sleep medications may be prescribed for short-term use in severe cases of insomnia. They can help break the cycle of sleeplessness and provide temporary relief. However, long-term reliance on sleep medication is generally not recommended due to the potential for dependency and side effects.
10. Can addressing sleep disorders improve overall quality of life?
Absolutely. Treating sleep disorders like insomnia can have a significant positive impact on overall quality of life. Improved sleep can lead to better physical and mental health, increased productivity, sharper focus, enhanced mood, and a greater sense of well-being.