The Enigmatic Sphinx: Uncovering Its Symbolism in Egyptian Mythology
In the vast landscape of ancient Egypt, a sublime and mysterious creature known as the Sphinx emerges with its enigmatic presence. This extraordinary monument, with the body of a lion and the head of a human, has intrigued scholars, archaeologists, and dreamers for centuries. Its origins shrouded in uncertainty, the Sphinx stands as a testament to the ancient Egyptian beliefs, evoking a sense of awe and wonder in those who encounter it. Join us on a journey as we delve into the history, symbolism, unsolved riddles, and enduring influence of this colossal guardian of the past. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of the Sphinx and unlock the secrets of its symbolic significance in Egyptian mythology.
History of the Sphinx
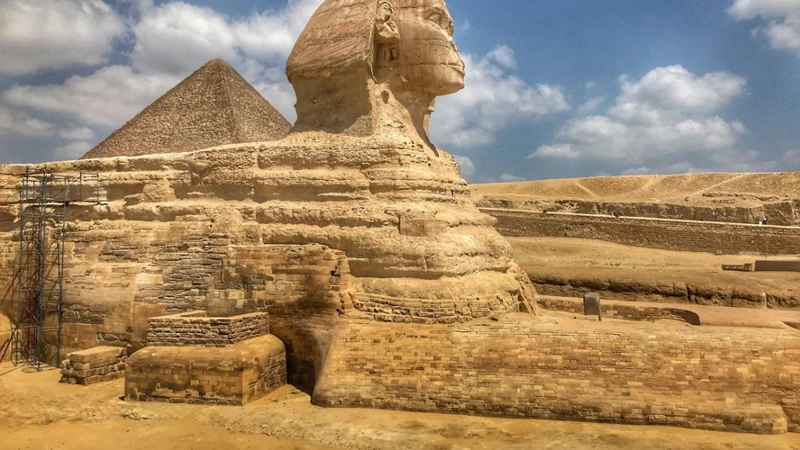

In ancient Egypt, the Sphinx held profound significance in the religious and cultural beliefs of the civilization. It is believed that the concept of the Sphinx originated during the Old Kingdom period, around 2500 BCE. The ancient Egyptians revered the Sphinx as a guardian deity, representing strength and protection. Its lion body symbolized power, while the human head was associated with wisdom and intelligence. The Sphinx was often associated with the sun god Ra, embodying a divine connection between the earthly and celestial realms. To truly understand the Sphinx, we must explore the rich mythological tapestry of ancient Egypt, where mythical creatures held immense significance in the grand narrative of creation and cosmology. (*link to /egyptian-mythical-creatures-significance/)
Over time, depictions and interpretations of the Sphinx evolved, reflecting the changing beliefs and artistic styles of various Egyptian dynasties. The earliest known Sphinx, located in Giza, is commonly referred to as the “Great Sphinx.” It was built during the reign of Pharaoh Khafre in the 26th century BCE and stands as a testament to the skill and craftsmanship of ancient Egyptian artisans. As the centuries passed, the Sphinx underwent subtle alterations, with different pharaohs leaving their mark on the monument. These modifications showcased the evolving aesthetics and cultural ideologies of different periods in Egyptian history. The depictions of the Sphinx also varied across temples, tombs, and other structures, demonstrating the multifaceted nature of this enigmatic creature. To truly comprehend the history of the Sphinx, one must explore its ever-changing representations throughout ancient Egypt.
Continue reading here to learn more about the significance of mythical creatures in ancient Egyptian culture. (*link to /egyptian-mythical-creatures-significance/)
Ancient Egyptian Beliefs
In ancient Egyptian beliefs, the Sphinx held a prominent role as a symbol of divine power and protection. The ancient Egyptians worshiped a pantheon of gods and believed in the existence of multiple realms and forces that governed their lives. The Sphinx, with its unique combination of a lion’s body and a human head, encapsulated the duality and harmony between the animal and human realms. This hybrid form represented the concept of therianthropy, blending the attributes of animals and humans, a common theme in Egyptian mythology.
The Sphinx was often associated with the sun god Ra, who held great importance in Egyptian cosmology. Ra was believed to be the creator of all life and the ruler of the celestial world. The Sphinx’s connection to Ra represented its role as a mediator between the physical world and the divine. As a guardian deity, the Sphinx was believed to protect sacred spaces, such as temples and tombs, from evil spirits and malicious forces. Its presence was thought to ward off chaos and ensure the harmony of the universe.
The Sphinx embodied the wisdom and intelligence of the human mind. Its human head represented the powers of higher consciousness and divine knowledge. The Egyptians believed that the Sphinx possessed deep insight and possessed the ability to see through riddles and mysteries. This association with wisdom made the Sphinx a revered figure in ancient Egyptian society, sought after for its guidance and prophetic abilities.
To gain a deeper understanding of the ancient Egyptian beliefs surrounding the Sphinx and its connection to the sun god Ra, explore the fascinating story of Ra’s creation in Egyptian mythology (*link to /creation-myth-ancient-egypt-exploring-story-ra/). Additionally, delve into the captivating world of hieroglyphic symbols, where the Sphinx was often depicted as a powerful guardian and symbol of divine protection (*link to /fascinating-hieroglyphic-symbols/).
Evolving Depictions
Throughout history, the depictions of the Sphinx in Egyptian art and architecture have evolved, reflecting the changing artistic styles and cultural beliefs of the ancient Egyptians. In its early representations, during the Old Kingdom period, the Sphinx had a simpler and more abstract form, with less defined facial features. As the centuries passed, the depictions of the Sphinx became more intricate and detailed, showcasing the artistic prowess of the Egyptian civilization.
During the Middle Kingdom period, the Sphinx started to acquire more human-like facial features, with its nose appearing more prominent. It was during this time that the Sphinx became associated with the pharaohs, symbolizing their divine power and authority. One notable example of this evolution can be seen in the Sphinx statues found at the mortuary complex of Amenemhat II in Dahshur, where the Sphinx is depicted with a serene and regal expression.
In the New Kingdom period, the Sphinx began to be depicted with the facial features of specific pharaohs, essentially merging their individual identities with the divine symbol of the Sphinx. One famous example of this is the Sphinx of Amenhotep II, which features the face of the pharaoh himself, complete with his distinctive facial characteristics.
Additionally, during the Ptolemaic period, Greek influences started to blend with Egyptian art, resulting in a hybridized Sphinx with more Hellenistic features, such as almond-shaped eyes and a leaner body structure. These depictions further showcased the cultural exchange and syncretism that occurred during this period of Egyptian history.
The evolving depictions of the Sphinx not only reflected the aesthetic preferences of different eras but also conveyed the evolving religious and cultural beliefs of the ancient Egyptians. It is through these artistic representations that we can trace the development and transformation of the Sphinx as a symbol of power, divinity, and enigmatic allure.
Symbolic Significance

The Sphinx holds profound symbolic significance in Egyptian mythology, representing various concepts and ideas that were central to the ancient Egyptian worldview.
The Guardian of the Pyramids: One of the primary roles of the Sphinx was to serve as a guardian deity, protecting the sacred necropolis and the pharaoh’s burial site. Positioned near the pyramids of Giza, the Sphinx stood as a vigilant sentinel, ensuring the eternal safety of the pharaohs and their treasures. Its imposing presence and mythical aura were believed to ward off evil spirits and prevent unauthorized access to the sacred tombs.
Divine Wisdom and Mystery: The Sphinx’s human head was seen as a symbol of wisdom and knowledge. It represented the divine intellect of the gods and their ability to comprehend the arcane mysteries of the universe. The enigmatic expression on the Sphinx’s face further emphasized its association with the unknown and the unfathomable depths of cosmic understanding. The Sphinx was also thought to possess the ability to answer riddles and unlock hidden truths, enhancing its alignment with divine wisdom.
Mythological Connections: The Sphinx featured prominently in Egyptian mythology, often associated with the sun god Ra and the god of the underworld, Osiris. In some myths, the Sphinx was believed to be a manifestation of Ra, guarding the sunrise and sunset on the horizon. Its presence bridged the realms of the living and the divine, symbolizing the cyclical nature of life, death, and rebirth. The Sphinx’s connection with Osiris was rooted in the belief that it watched over the pharaoh’s journey into the afterlife, ensuring their safe passage and resurrection.
The symbolic significance of the Sphinx in Egyptian mythology reflects the multifaceted nature of ancient Egyptian beliefs, where deities and mythical creatures held immense power and invoked a sense of wonder and reverence for the mysteries of the universe.
The Guardian of the Pyramids
The Sphinx holds a prominent role as the guardian of the pyramids in ancient Egyptian mythology and culture. Positioned near the great pyramids of Giza, the Sphinx served as a protective deity, watching over these monumental structures and the pharaohs who rested within them. Its symbol of strength and power embodied the role it played in safeguarding the sacred necropolis. The Sphinx was believed to possess the ability to ward off evil spirits and protect the tombs from desecration. Its imposing presence and enigmatic gaze were intended to deter any potential intruders. The connection between the Sphinx and the pyramids goes beyond its protective role, as it symbolizes the harmonious relationship between human and divine, mortality and eternity. This guardian of the pyramids stands as a testament to the grandeur and spiritual beliefs of the ancient Egyptian civilization.
Divine Wisdom and Mystery
Within the symbolism of the Sphinx in ancient Egyptian mythology, there is a strong association with divine wisdom and profound mystery. The amalgamation of a human head atop a lion’s body underscores the duality of characteristics inherent in the Sphinx. The human aspect represents intellectual prowess and higher consciousness, while the lion represents courage, strength, and the primal forces of nature. This combination creates a powerful metaphor for the balance between primal instincts and the pursuit of knowledge.
The Sphinx’s presence evokes a sense of awe and wonder, standing as a testament to the incomprehensible mysteries of the universe. Its enigmatic visage portrays the profound depths of ancient wisdom that elude our understanding. Many believe that the Sphinx intentionally conceals knowledge and secrets within its stoic expression, challenging humanity to search for higher truths and unravel the greater mysteries of existence. Egyptian mythology often intertwines the Sphinx with riddles and puzzles, suggesting that the pursuit of knowledge requires not only intelligence but also the ability to decipher the hidden truths within the enigmatic questions.
The Sphinx’s divine wisdom stems from its association with various deities, particularly the sun god Ra. As the Sphinx watches over the pyramids, it possesses the knowledge of the heavens and the connection between the earthly and celestial realms. It serves as a guardian, protecting the sacred burial sites of the pharaohs and guiding souls to the afterlife. The Sphinx’s unwavering gaze signifies its omniscient nature, forever observing and possessing profound insight into the mysteries of life and death.
The Sphinx in Egyptian mythology represents both the pursuit of divine wisdom and the awe-inspiring mystery that lies beyond mortal comprehension. Its unique amalgamation of human and animal characteristics embodies the complexities of human existence and the inscrutable mysteries of the universe. The Sphinx challenges us to explore the depths of knowledge, to seek and comprehend the unknown, and to unravel the profound truths that lie shrouded in its enigmatic presence.
Mythological Connections
The mythological connections of the Sphinx in Egyptian culture are deeply intertwined with the pantheon of gods and the cosmological beliefs of the ancient civilization. In Egyptian mythology, the Sphinx is believed to embody the essence of the sun god Ra and the solar aspect of divinity. Ra, as the creator and supreme god, represented the life-giving force of the sun. The Sphinx, with its majestic and regal presence, is often seen as an earthly representation of Ra’s power and wisdom.
Additionally, the Sphinx is closely associated with the goddess Sekhmet, who was the lioness-headed goddess of war and healing. Sekhmet possessed great strength and ferocity, much like the Sphinx, and was venerated for her protective and nurturing qualities.
In the mythological realm, the Sphinx is also connected with the story of the pharaohs and their divine heritage. The Sphinx is believed to guard the entrance to the underworld, where the pharaohs would journey upon their death. It served as a protector of the sacred tombs and ensured the safe passage of the pharaohs into the afterlife.
The Sphinx’s enigmatic nature and riddles have drawn parallels to the ancient Egyptian concept of Ma’at, which represents truth, order, and balance in the universe. Just as the Sphinx poses a riddle that must be solved, the Egyptians believed that the world was governed by hidden truths and cosmic laws that needed to be deciphered.
The mythological connections of the Sphinx in Egyptian culture encompass its association with the gods Ra and Sekhmet, its role as a guardian of the underworld, and its embodiment of the enigmatic wisdom and cosmic order. The Sphinx stands as a symbol of the intricate web of myths and beliefs that defined ancient Egyptian civilization.
Unsolved Riddles and Secrets

The enigmatic Sphinx holds within itself a multitude of unsolved riddles and secrets that continue to captivate the imagination of scholars and archaeologists. One of the most well-known mysteries surrounding the Sphinx is the absence of its nose. The exact circumstances surrounding the missing nose of the Sphinx remain unclear, with various theories proposed over the years. Some argue that it was destroyed by Napoleon’s troops during their occupation of Egypt, while others believe that it fell victim to erosion or deliberate defacement. Regardless of the true cause, the absence of the nose adds an air of intrigue and mystique to this ancient monument.
In addition to the missing nose, the Sphinx is believed to house hidden chambers and passages yet to be discovered. Rumors have circulated for centuries about the possibility of secret chambers lying beneath the statue, containing treasured artifacts or even the answers to age-old mysteries. Despite numerous attempts to explore the depths of the Sphinx, its secrets remain elusive. It is a testament to the enduring allure and enigma of this iconic structure.
The origins of the Sphinx itself also contribute to the overall enigma surrounding this ancient monument. While the most widely accepted theory attributes its construction to Pharaoh Khafre during the Old Kingdom, some researchers propose alternative origins. These theories range from the Sphinx being much older, possibly predating the ancient Egyptians, to it being constructed by an entirely different civilization altogether. The true origins of the Sphinx remain a subject of debate and speculation, adding to its allure and enigmatic nature.
The Sphinx continues to be a captivating symbol of mystery, intriguing us with its unanswered questions and concealed secrets. As we unravel the enigmas surrounding the Sphinx, we are drawn deeper into the history and symbolism of this awe-inspiring creature. The enigmatic Sphinx stands as a reminder of our ceaseless pursuit of knowledge and the boundless mysteries that still await us in the ancient world.
The Missing Nose
The tale of the missing nose of the Sphinx has intrigued and perplexed scholars and visitors alike. Many wonder what happened to the nose of this majestic monument. The truth is, the exact circumstances surrounding the missing nose remain a mystery. There are several theories and legends that attempt to explain its absence. One popular story suggests that the nose was deliberately damaged during the French invasion of Egypt in the late 18th century. According to this account, soldiers used the Sphinx for target practice, resulting in the destruction of the nose. Another theory proposes that the nose was chiseled off by a Sufi Muslim named Muhammad Sa’im al-Dahr, who believed that the Sphinx represented paganism. However, these explanations are speculative at best, and the true origin of the missing nose remains uncertain. Interestingly, the nose is not the only part of the Sphinx that has been damaged over time. The Sphinx has also suffered erosion and weathering, which further adds to its enigmatic allure. Despite its damaged state, the Sphinx continues to captivate the imagination of all who behold it.
The Hidden Chambers
The Sphinx has long been associated with hidden chambers and mysterious passages that lie beneath its colossal form. This notion of concealed chambers fuels the imagination and curiosity of archaeologists and treasure hunters alike. While explorations have been conducted, no undisputed evidence of hidden chambers directly linked to the Sphinx has been found. However, there have been intriguing discoveries and theories that add a layer of intrigue to this ancient enigma. One such theory proposes that a concealed cavity exists beneath the Sphinx’s paws, potentially holding ancient artifacts or even the long-lost records of the Egyptian civilization. Egyptian authorities have conducted limited excavation and ground-penetrating radar surveys in an attempt to unravel the secrets of the Sphinx’s hidden chambers. These investigations, while inconclusive, continue to captivate the interest of scholars and enthusiasts who yearn to unlock the mysteries concealed within the depths of this age-old monument.
Theorized Origins
The origins of the Sphinx have remained a subject of debate and speculation among historians and archaeologists. Several theories have emerged in an attempt to unravel the mystery behind this majestic creature. One prominent theory suggests that the Sphinx was built during the reign of Pharaoh Khafre, around 2500 BCE, as a tribute to the king. This theory is supported by the close proximity of the Great Sphinx to the Pyramid of Khafre. It is believed that the Sphinx was intended to serve as a symbol of the pharaoh’s divine power and authority. Another theory proposes that the Sphinx predates the reign of Khafre and was originally built by an earlier civilization, such as the mysterious Atlanteans or an advanced pre-dynastic civilization of ancient Egypt. The proponents of this theory argue that the erosion patterns on the Sphinx’s body indicate a much older age, possibly dating back thousands of years before the reign of Khafre. This hypothesis raises intriguing questions about the possibility of lost civilizations and ancient wisdom that predates recorded history. While the exact origins of the Sphinx remain elusive, each theory adds another layer of fascination and intrigue to this timeless enigma.
Influence on Art and Culture
The Sphinx’s influence extends far beyond its ancient origins, permeating the realms of art and culture throughout history. Egyptian art prominently features the Sphinx as a symbol of power, eternity, and the divine. Representations of the Sphinx adorned temple walls, sarcophagi, and tombs, depicting its majestic form in intricate detail. The image of the Sphinx became synonymous with Egypt itself, attracting countless artists, writers, and travelers who sought to capture its allure. In literature, the Sphinx often appeared as a metaphorical representation of mystery and enigma. The mesmerizing presence of the Sphinx inspired timeless works such as Edgar Allan Poe’s “The Sphinx” and Gustave Flaubert’s “The Temptation of Saint Anthony.” Even in modern times, the Sphinx continues to captivate the imagination. Its image can be found in advertising, film, and popular culture, further solidifying its place as an enduring symbol of ancient Egypt and its mythical past.
Experience the fascinating hieroglyphic symbols frequently associated with Egyptian art. (*link to /fascinating-hieroglyphic-symbols/) These intricate characters played a vital role in conveying stories, myths, and religious beliefs in ancient Egypt. By delving into the world of hieroglyphs, one can grasp the depth and intricacy of the artistic language that surrounded the enigmatic Sphinx.
Seeking deeper insights into the Sphinx’s influence, psychological interpretations come into play. Carl Jung, a renowned Swiss psychologist, considered the Sphinx as an archetypal symbol of the human psyche’s mysterious depths. According to Jung’s theories, the Sphinx represents the union of opposites – the animalistic instincts and the intelligence of the human mind. Its presence evokes the need for introspection and self-discovery, urging individuals to confront their own inner mysteries. This psychological interpretation adds another layer of complexity to the Sphinx’s influence on art and culture, transcending its physical form and delving into the realms of the human psyche.
The Sphinx’s impact on art and culture is undeniable. Its representation in Egyptian art, its role in literature, its appearance in popular culture, and its association with the human psyche all contribute to its enduring influence. The Sphinx continues to inspire and challenge our imaginations, leaving an indelible mark on the artistic and cultural landscape of the world.
The Sphinx in Egyptian Art
The Sphinx’s presence in Egyptian art spans thousands of years, illustrating its enduring significance and captivating allure. This majestic creature was a popular subject for ancient Egyptian artists and can be found depicted in various forms across a range of mediums. Sculptures, reliefs, paintings, and even small amulets showcase the Sphinx’s prominence in Egyptian art. One notable representation is the colossal Sphinx of Giza, which stands as a masterful example of ancient Egyptian sculpture. Carved from a single limestone outcrop, the Great Sphinx epitomizes the harmony between nature and artistry. Its meticulous craftsmanship and attention to detail reveal the skill and precision of the sculptors who dedicated themselves to immortalizing this mythical creature. The Sphinx also appears in intricate relief carvings on temple walls, depicting scenes of royal rituals and religious ceremonies. The Egyptians cherished this creature as a symbol of protection and power, and its inclusion in artistic compositions emphasized its divine significance. From the grandeur of temple complexes to the smallest amulets found in tombs, the Sphinx’s presence in Egyptian art immortalizes its mythical status and evokes a sense of awe that continues to captivate art enthusiasts and historians alike.
Symbolic Representations in Literature
Symbolic Representations in Literature
Throughout history, the Sphinx has captivated the imaginations of countless writers and poets, leading to its inclusion in various literary works. In literature, the Sphinx often embodies the duality of human nature, with its lion body representing the primal instincts, while the human head symbolizes intellect and reason. Writers have utilized the Sphinx as a metaphor for the complexities of life, posing existential questions and challenging characters to solve riddles that hold the key to their destinies. One notable example is the Greek tragedy “Oedipus Rex” by Sophocles, where the Sphinx plays a crucial role in the tragic tale. In the story, the Sphinx guards the city of Thebes and poses a riddle to anyone who wishes to enter. It is only through Oedipus’ cunning mind and ability to solve the riddle that the city’s plague is lifted, but at a great personal cost. This literary representation of the Sphinx exemplifies its symbolic significance as a guardian of knowledge and the profound consequences that arise from seeking the truth.
In contemporary literature, the Sphinx continues to hold a place of allure and mystery. Authors draw inspiration from its enigmatic nature to explore themes of identity, self-discovery, and the eternal quest for meaning. The Sphinx often serves as a symbol of wisdom or as a harbinger of both danger and enlightenment. Its presence in literature instills a sense of intrigue and introspection, prompting readers to ponder the deeper mysteries of existence. Whether in ancient Greek tragedies or modern novels, the Sphinx’s symbolic representations in literature make it a timeless and thought-provoking figure that continues to inspire authors and readers alike.
Modern Interpretations
Modern interpretations of the Sphinx have permeated various aspects of art and culture, capturing the fascination and imagination of people worldwide. In popular culture, the Sphinx is often depicted as a symbol of mystery and hidden knowledge. It has made appearances in numerous books, movies, and video games, becoming an iconic figure associated with ancient civilizations and secret societies. Notable examples include the works of Dan Brown, where the Sphinx and its enigmatic riddles play a central role in unraveling conspiracies. Psychological interpretations of the Sphinx have emerged, connecting its symbolism with the human psyche. Some interpret the Sphinx as a representation of the subconscious mind, guarding inner wisdom and the depths of one’s identity. This interpretation suggests that just as the Sphinx poses riddles to those who approach it, our subconscious mind presents us with challenges and questions to uncover our true selves. The enigmatic nature of the Sphinx continues to inspire contemporary artists, writers, and thinkers who seek to unravel its mysteries and explore its profound symbolism.
In Popular Culture
The influence of the Sphinx extends far beyond the boundaries of ancient Egyptian mythology and has found a prominent place in popular culture. This enigmatic creature has fascinated and inspired countless artists, writers, filmmakers, and creators around the world. In literature, the Sphinx has appeared in various forms, often embodying mystique, wisdom, and riddles. For example, in the famous play “Oedipus Rex” by Sophocles, the Sphinx poses a riddle to those who seek passage, challenging them to solve it or face dire consequences. The riddle of the Sphinx has become a metaphor for complex puzzles or difficult problems faced by individuals. In art, the Sphinx has been depicted in paintings, sculptures, and even tattoo designs, capturing its allure and mysterious nature. The Sphinx has also made its way into popular films, such as “The Mummy” series, where it serves as a guardian and protector of ancient treasures. Its presence in video games, such as the “Assassin’s Creed Origins,” showcases the enduring fascination with this iconic creature. From literature to art, films to video games, the Sphinx continues to captivate the imaginations of people around the world, perpetuating its legacy as a symbol of ancient Egyptian mythology and mysticism.
Psychological Interpretations
Psychological Interpretations
The Sphinx has not only captivated the ancient Egyptians but also continues to intrigue modern minds, resulting in various psychological interpretations. One such interpretation comes from famed psychologist Sigmund Freud, who saw the Sphinx as a representation of the Oedipus complex. According to Freud, the enigmatic creature symbolizes the repressed desires and conflicts between a son and his father, reflecting the inner psychological struggles that individuals face.
Another psychological interpretation suggests that the Sphinx embodies the realm of the unconscious mind. Just as the Sphinx guards the pyramids, it is believed to guard the secrets and mysteries of the human psyche. The Sphinx becomes a symbol of the unconscious, urging individuals to delve deeper into self-exploration and unravel the hidden aspects of their own minds.
Some interpret the Sphinx as a representation of the human ego, the part of the mind that mediates between the instincts and societal demands. Like the Sphinx, the ego seeks to maintain a balance between opposing forces and make sense of the world around us.
Psychological interpretations of the Sphinx provide a fascinating perspective, linking this ancient symbol to the complex workings of the human mind. It invites us to introspect and explore the depths of our own psyche, perhaps uncovering new insights and understanding along the way.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sphinx remains an enduring enigma, captivating the imagination of those who encounter it. Throughout history, this majestic creature has symbolized strength, wisdom, and divine connection in the ancient Egyptian culture. From its origins in the Old Kingdom to its evolving depictions in different periods, the Sphinx has held a significant place in Egyptian mythology and art. The unsolved riddles and secrets surrounding the Sphinx, such as the missing nose and hidden chambers, only add to its mystique. Over time, the Sphinx’s influence has extended beyond ancient Egypt, leaving an indelible mark on art, literature, and popular culture. Today, the Sphinx continues to intrigue and inspire, inviting us to unravel its secrets and explore the depths of its symbolic significance. Whether as a guardian of the pyramids, a symbol of divine wisdom, or a mystery waiting to be unraveled, the Sphinx remains a testament to the richness and complexity of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the purpose of the Sphinx in Egyptian mythology?
The Sphinx served as a guardian deity, symbolizing strength and protection in ancient Egyptian beliefs. It was believed to ward off evil spirits and safeguard the sacred structures, particularly the pyramids.
2. Why does the Sphinx have the head of a human and the body of a lion?
Ancient Egyptians combined the regal attributes of a lion, representing power, with the intellect and wisdom associated with humans. The combination of these elements represented a deity with both physical and intellectual strength.
3. How old is the Sphinx?
The Great Sphinx, located in Giza, is believed to have been built during the reign of Pharaoh Khafre in the 26th century BCE, making it over 4,500 years old.
4. What is the significance of the missing nose on the Sphinx?
The true cause of the Sphinx’s missing nose remains a mystery. Some theories suggest erosion, while others propose intentional damage by iconoclasts. Regardless, the missing nose adds an air of intrigue to the Sphinx’s enigmatic presence.
5. Are there any hidden chambers beneath the Sphinx?
While no definitive evidence of hidden chambers has been discovered beneath the Sphinx, there have been various theories suggesting the presence of undiscovered tunnels and chambers. Excavations and research continue to explore these possibilities.
6. Is the Sphinx connected to Egyptian creation myths?
While the Sphinx itself is not directly connected to Egyptian creation myths, it is associated with the sun god Ra. In Egyptian mythology, the sun god played a pivotal role in the creation of the world.
7. How has the Sphinx influenced Egyptian art?
The Sphinx has been a prominent subject in Egyptian art throughout history. It has appeared in relief carvings, statues, and paintings, showcasing its symbolic importance and capturing the imagination of artists who sought to depict its grandeur.
8. Are there any references to the Sphinx in literature?
Absolutely! The Sphinx has been referenced in various works of literature, both ancient and modern. Famous examples include Gustave Flaubert’s “The Temptation of Saint Antony” and Oedipus Rex, a tragedy by Sophocles.
9. How has the Sphinx been depicted in popular culture?
The Sphinx has made appearances in numerous forms of popular culture, including movies, video games, and books. Its enigmatic nature and association with mystery and riddles have made it a captivating character in storytelling.
10. Are there any psychological interpretations of the Sphinx?
Psychologists have analyzed the Sphinx as a symbol of the subconscious mind and the search for self-discovery. It represents the enigmatic and profound aspects of the human psyche, inviting individuals to explore their inner depths.








