Throughout history, humanity has looked up at the night sky with a sense of wonder and awe. The celestial bodies that adorn the cosmos have captivated our collective imagination and shaped the myths and legends that have been passed down through generations. From solar eclipses that seemingly darken the sun to shooting stars that streak across the heavens, astronomical events have played a significant role in shaping mythology. These celestial phenomena have been both feared and revered, with cultures around the world attributing divine significance to these cosmic occurrences. In this article, we will explore how astronomical events have influenced and shaped mythology, delving into the cultural significance, portrayal in different cultures, and the symbolic messages they convey. Join us on a journey through the cosmos as we unravel the mysteries behind the celestial phenomena that have shaped our mythical narratives.
1. Solar Eclipses
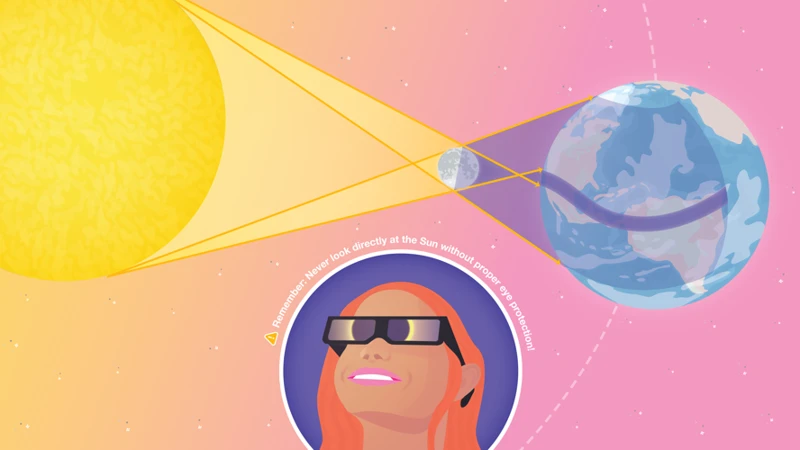

Solar eclipses have long been a source of intrigue and fascination. These rare events, where the moon passes between the Earth and the sun, casting a shadow over the land, have played a significant role in shaping mythology. In ancient times, solar eclipses were seen as celestial battles between gods and other supernatural beings. In Norse mythology, for example, it was believed that the sun was being devoured by a monstrous wolf during a solar eclipse. In ancient China, people would bang drums and pots to scare away the dragon they believed was swallowing the sun. The cultural significance of solar eclipses was profound, often seen as harbingers of doom or divine messages. These awe-inspiring celestial events influenced and guided the beliefs, rituals, and behaviors of ancient civilizations. Solar eclipses were seen as powerful omens, prophecies, and reminders of the intricate connection between the celestial realm and humanity. To learn more about the influence of astronomical events on ancient civilizations, visit ancient civilizations and starlore.
1.1 Solar Eclipses in Mythology
Solar eclipses have played a significant role in mythology, giving rise to fascinating tales and legends across different cultures. In ancient Greece, for example, the solar eclipse was often interpreted as a sign of divine displeasure or impending doom. The Greek historian Herodotus wrote about a solar eclipse that occurred in 585 BCE, which halted a battle between the Lydians and the Medes. The sudden darkness was seen as a clear indication from the gods to cease the fight. Similarly, in Aztec mythology, solar eclipses were associated with the devouring of the sun by mythical creatures. The Aztecs believed that during an eclipse, the sun was under attack, and rituals and sacrifices were performed to protect it. Native American tribes also wove solar eclipses into their folklore, viewing them as battles between celestial beings or as a time of transformation and renewal. These vivid myths surrounding solar eclipses demonstrate the profound impact these celestial events had on the human imagination, instilling a mix of fear, awe, and a search for meaning. To delve deeper into the history of astrological divination, explore the fascinating connections between the cosmos and human destiny by visiting astrological divination throughout history.
1.2 Cultural Significance of Solar Eclipses
Solar eclipses held immense cultural significance in various ancient civilizations. These celestial events were seen as powerful omens and often invoked a sense of fear, uncertainty, and awe. Ancient Egyptians believed that the sun was temporarily swallowed by a cosmic serpent during an eclipse, prompting them to perform rituals and recite spells to ward off the darkness. In ancient Mesopotamia, solar eclipses were important for royal authority, as they were seen as a reflection of the ruler’s relationship with the gods. Persian cultures believed that solar eclipses were battles between the forces of light and darkness, while the Aztecs associated eclipses with impending destruction and saw them as a sign of cosmic disorder. The cultural significance of solar eclipses extended to other civilizations as well. In ancient Greece, for example, it was believed that solar eclipses were a time when the gods intervened in human affairs, often interpreted as a sign of divine displeasure. The rich tapestry of cultural beliefs and interpretations surrounding solar eclipses speaks to the deep connection between celestial events and the human experience. To learn more about the role of astrology and celestial phenomena in ancient cultures, visit ancient astrology and cultures.
2. Comets and Shooting Stars

Comets and shooting stars have always captured the human imagination, leaving observers in awe of their fiery trails across the night sky. In mythology, these celestial phenomena often carried significant symbolic meaning. Comets, with their long, streaming tails, were associated with messages from the gods or impending doom. They were seen as celestial messengers, carrying divine omens and prophecies. In ancient cultures, comets were believed to herald the birth or death of important figures, or the onset of significant events. Shooting stars, on the other hand, were considered to be the sparks of the gods, glimpses of their divine presence in the mortal world. They were associated with luck, wishes, and even the souls of departed loved ones. The impact of comets and shooting stars on mythology is evident across different cultures, each with their unique interpretations and stories. To explore further the history of astrological divination and the role of shooting stars and comets in ancient cultures, visit astrological divination.
2.1 The Impact of Comets and Shooting Stars on Mythology
Comets and shooting stars have left an indelible mark on mythology, captivating the curiosity and imagination of ancient civilizations. The sudden appearance of a blazing comet streaking across the night sky or a shooting star blazing through the atmosphere was seen as a celestial spectacle, often interpreted as divine messages or omens of great significance. In many cultures, comets and shooting stars were associated with the arrival or departure of important figures or the occurrence of momentous events. For example, in Greek mythology, comets were believed to be the transportation of gods or the souls of heroes. Similarly, in Chinese folklore, shooting stars were thought to be the manifestation of divine beings descending to Earth. The impact of these celestial phenomena was not limited to mythological tales alone; they also influenced cultural practices and rituals. For instance, ancient Romans would make wishes upon shooting stars, hoping their desires would be granted. The mysterious and awe-inspiring nature of comets and shooting stars continues to permeate our collective consciousness, reminding us of the mystical connections between the heavens and Earth. Explore the fascinating history of astrological divination and the impact of celestial events on human civilization by visiting astrological divination throughout history.
2.2 Portrayal of Comets and Shooting Stars in Different Cultures
Comets and shooting stars have captivated the imaginations of people across different cultures throughout history. These celestial phenomena have been portrayed in a variety of ways, each reflecting the unique beliefs and mythologies of different societies. In ancient Greece, comets were often seen as harbingers of significant events, such as the impending death of a king or a sign of war. They were believed to be messages from the gods, carrying important information or prophecies. In Chinese culture, comets were viewed as both lucky and unlucky omens, depending on their appearance and trajectory. Shooting stars, on the other hand, were often seen as fleeting celestial messengers, carrying messages from the heavens. In Native American cultures, shooting stars were believed to be the souls of ancestors, passing by to offer guidance or protection. In Norse mythology, shooting stars were seen as arrows shot by the gods in the midst of a great cosmic battle. The portrayal of comets and shooting stars in different cultures showcases the rich diversity of human interpretation and the profound impact of these astronomical events on our collective imagination. To delve deeper into the history of astrological divination and its influence on ancient cultures, visit astrological divination history.
3. Planets and Divine Beings
Planets have always held a special place in the realm of mythology, as they were often associated with divine beings and celestial powers. The movements and alignments of planets were observed and revered by ancient civilizations, who believed that they held great influence over human affairs. In ancient Greece, each planet was linked to a god or goddess, and their characteristics were believed to be reflected in the behavior of these divine beings. For example, Jupiter, the largest planet, was associated with Zeus, the king of the gods, symbolizing power and authority. Venus, the planet of love and beauty, was linked to the goddess Aphrodite. These planetary associations not only shaped the mythology surrounding these gods and goddesses but also influenced the interpretation of celestial events. Astrological divination, the practice of predicting the future and understanding human personalities based on planetary alignments, was developed by ancient cultures and is still studied and followed in modern times. To delve deeper into the history and practice of astrological divination, visit astrological divination in history.
3.1 Planetary Alignments in Mythology
Planetary alignments have held great significance in mythology across various cultures. Ancient civilizations, such as the Mayans and Egyptians, carefully observed the movements of the planets and attributed divine meaning to their alignments. The alignment of planets was often associated with the presence and influence of gods and goddesses in human affairs. The Romans and Greeks believed that planetary alignments symbolized the interaction and communication between gods and mortals. For instance, the alignment of Venus, Jupiter, and Mars was considered a sign of great fortune and blessings from the gods. In Hindu mythology, the alignment of specific planets during important celestial events like eclipses or equinoxes was believed to have a profound impact on human destiny and cosmic energy. These planetary configurations were seen as powerful omens, indicating shifts in power, impending wars, or the birth of great leaders. The intricacies of planetary alignments and their interpretations varied across cultures, but the underlying belief in their significance in shaping human lives and the world at large remains a common thread. To further explore the history and practices of astrological divination in ancient cultures, visit astrological divination in history.
3.2 The Influence of Planets on Gods and Goddesses
The planets, with their prominent presence in the night sky, have long been associated with gods and goddesses in various mythological traditions. The influence of planets on deities is a recurring theme in mythology, often representing different attributes, powers, or domains of the divine beings. In ancient Mesopotamia, for example, the seven celestial bodies known as the “planets” were believed to be physical manifestations of gods themselves. Each planet was associated with a specific god or goddess, and their movements and positions were thought to have a direct impact on the affairs of humanity. The planet Venus, for instance, was associated with Inanna, the goddess of love and beauty, while Jupiter was connected to Marduk, the chief god of Babylon. The influence of these planetary deities was believed to shape human emotions, actions, and even the outcomes of battles and events. The association between planets and gods and goddesses was not limited to Mesopotamia but was prevalent in various other cultures as well. In ancient Greece, the planet Mars corresponded to the god of war, Ares, whereas the planet Mercury was linked to the messenger of the gods, Hermes. This connection between planets and divine beings served as a way to explain and understand the cosmos, as well as to establish a symbolic link between the celestial and earthly realms. The influence of planets on gods and goddesses thus played a significant role in shaping the characteristics and roles attributed to these divine entities in mythology.
4. Constellations and Heroes
Constellations have long been intertwined with the heroic tales of ancient civilizations. These groupings of stars in the night sky inspired myths and legends, depicting powerful heroes and epic adventures. In ancient Greece, the constellation of Orion was associated with the legendary hunter of the same name, known for his immense strength and prowess. According to mythology, Orion’s exploits included battles against formidable creatures such as the Scorpion. In Norse mythology, the constellation Ursa Major represented the great warrior known as Thor, whose thunderous hammer could shake the heavens. These celestial arrangements served as guides and symbols for ancient cultures, providing a sense of wonder and inspiration. They offered a connection between the mortal realm and the divine, immortalizing the heroic feats of legendary figures and ensuring their stories would endure.
4.1 Constellations in Ancient Tales
Constellations have been a source of inspiration for storytelling since ancient times. In many ancient tales and myths, constellations served as a way to navigate the night sky and tell stories about gods, heroes, and legendary creatures. One well-known example is the constellation Orion, which is associated with a mighty hunter in Greek mythology. According to the myth, Orion was a hunter of great strength who was eventually killed by a scorpion and placed among the stars as a constellation. Similarly, the constellation Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, played a prominent role in various mythologies around the world. In Greek mythology, Ursa Major represented Callisto, a nymph who was transformed into a bear by the goddess Hera out of jealousy. These tales often incorporated the movements and positions of the constellations as a way to explain natural phenomena, human experiences, and the relationships between gods and mortals. The rich tapestry of ancient tales involving constellations continues to captivate our imaginations and connect us to the wonders of the cosmos.
4.2 Myths and Legends Associated with Specific Constellations
Myths and legends associated with specific constellations have been a rich source of storytelling and cultural significance throughout history. Different cultures have interpreted and assigned unique narratives to the patterns of stars in the night sky. One example is the constellation Orion, often depicted as a mighty hunter. In Greek mythology, Orion was said to be a great hunter who boasted that he could slay any creature on Earth. In response, Gaia, the Earth goddess, sent a scorpion to kill him. Zeus, admiring Orion’s skills, placed him in the heavens as a constellation, forever locked in a celestial battle with the scorpion, represented by the constellation Scorpio.
Another constellation with a captivating story is Ursa Major, commonly known as the Big Dipper or the Plough. In Greek mythology, this constellation was associated with the story of Callisto, a beautiful nymph who caught the eye of Zeus. When Hera, Zeus’s jealous wife, discovered their affair, she transformed Callisto into a bear. Zeus, in an effort to protect her, lifted Callisto into the sky, creating the Ursa Major constellation.
In ancient Chinese mythology, the constellation Draco, the Dragon, was believed to be a divine creature that ruled the cosmos. It was said to be the guardian of heavenly palaces and the embodiment of strength and power.
These are just a few examples of the myriad of myths and legends associated with specific constellations. These tales served as a way to understand the cosmos, impart moral lessons, and create a sense of wonder and connection between the celestial realm and human existence. Constellations continue to capture our imagination, reminding us of our place in the vastness of the universe.
5. Meteor Showers and Divine Messages
Meteor showers have long been considered celestial spectacles, captivating the imaginations of people throughout history. These magnificent displays of shooting stars streaking across the night sky have been associated with divine messages in mythology. In many cultures, meteor showers were interpreted as signs from the gods, carrying symbolic significance and hidden meanings. The ancient Greeks believed that meteor showers were the sparks created when the gods ignited the heavens with their mighty power. In Chinese mythology, meteor showers were seen as a celestial visitation, with each shooting star representing the descent of a divine being to Earth. These celestial events were often interpreted as messages of fortune, change, or even warnings of impending calamity. The interpretation of celestial signs and omens, including meteor showers, played a prominent role in ancient divination practices. To discover more about the history of astrological divination, visit astrological divination in history.
5.1 The Symbolic Significance of Meteor Showers in Mythology
Meteor showers, with their breathtaking display of shooting stars streaking across the night sky, have held a deep symbolic significance in mythology. These celestial events, which occur when Earth passes through the debris left by a comet, have been associated with various myths and legends throughout history. In many cultures, meteor showers were believed to be divine messages or signs from the gods. They were seen as powerful omens, foretelling significant events such as the birth or death of a ruler, the onset of war or famine, or the coming of a major celestial event. The ancient Greeks, for instance, believed that meteor showers were a manifestation of the gods communicating with mortals. They saw shooting stars as the souls of heroes or deceased loved ones ascending to the heavens. In Norse mythology, meteor showers were associated with the fiery trail left behind by the gods as they traveled across the sky. These celestial events were seen as a symbol of the gods’ power and influence over human affairs. Meteor showers also held significance in ancient Mayan and Native American cultures, where they were seen as messages from the spirit world or ancestors. The symbolic importance of meteor showers in mythology demonstrates the deep connection between the celestial realm and human existence, as well as the belief in a greater cosmic order that influences our lives.
5.2 Interpretation of Celestial Signs and Omens
Interpretation of celestial signs and omens has been a prevalent practice throughout history. Ancient cultures looked to the skies for guidance and messages from the gods. Various astronomical events, such as meteor showers, comets, and planetary alignments, were seen as significant omens that held symbolic meaning. For instance, the appearance of a comet was often interpreted as a forewarning of impending disasters or the arrival of a great leader. In ancient Mesopotamia, celestial observations were meticulously recorded, and patterns in the movements of celestial bodies were believed to unlock insights into the future. These celestial signs were consulted by priests and astrologers to guide decision-making and predict the outcomes of wars, marriages, and other significant events. In ancient Egypt, the position of the stars and planets at the time of a person’s birth was believed to determine their fate and character, giving rise to the practice of astrology. The interpretation of celestial signs and omens was not limited to a single culture but spanned across diverse civilizations, including the Chinese, Greeks, Indians, and Mayans, each developing their own systems of divination and astrological practices. Whether viewed as messages from the gods or tools for predicting the future, the celestial signs and omens served as a powerful connection between the heavens and the earthly realm, influencing and shaping the beliefs and actions of ancient cultures.
6. Conclusion
The intertwining of astronomical events and mythology is a testament to the profound impact the cosmos has had on human imagination and belief systems. Solar eclipses, comets, shooting stars, planetary alignments, constellations, and meteor showers have all played significant roles in shaping the myths and legends of various cultures throughout history. These celestial phenomena were not only observed and marvelled at but were attributed with divine significance, serving as symbols, omens, and messages from the gods. They influenced the creation of gods and goddesses, the portrayal of heroes, and the interpretation of celestial signs. The cultural significance of astronomical events in mythology cannot be overstated. They served as a bridge between the earthly and the celestial, a reminder of humanity’s place in the vast cosmos. The exploration of these connections deepens our understanding of the ways in which ancient cultures viewed and interacted with the world around them. The stories and beliefs born from these celestial events continue to captivate us, offering a glimpse into the rich tapestry of human history and imagination. As we continue to gaze up at the night sky, we are reminded of the awe-inspiring wonders that have shaped the myths that have endured through the ages.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do solar eclipses occur?
Solar eclipses occur when the moon moves between the Earth and the sun, blocking the sun’s light. This alignment happens because the moon’s orbit around the Earth is at a slight angle relative to the Earth’s orbit around the sun.
2. How often do solar eclipses happen?
Solar eclipses are relatively rare events that occur a few times a year. However, the chances of witnessing a total solar eclipse in a specific location are much rarer, happening once every few hundred years.
3. Are solar eclipses dangerous to watch?
Looking directly at the sun during a solar eclipse can cause severe eye damage. It is crucial to use proper eye protection, such as eclipse glasses or specially designed solar filters, to view a solar eclipse safely.
4. How did ancient cultures interpret solar eclipses?
Ancient cultures interpreted solar eclipses as significant celestial events with supernatural implications. They often associated solar eclipses with powerful deities, cosmic battles, or predictions of future events.
5. Were solar eclipses considered omens of bad fortune?
Yes, solar eclipses were often considered omens of bad fortune in many ancient cultures. They were seen as warnings or reminders from the gods, often associated with impending disasters, political events, or changes in rulership.
6. Can solar eclipses be predicted?
Yes, solar eclipses can be predicted with great accuracy using sophisticated astronomical calculations. Scientists and astronomers use these predictions to inform the public about upcoming eclipses and their locations.
7. How do solar eclipses impact wildlife?
During a solar eclipse, animals may exhibit behavioral changes such as confusion or restlessness. Birds may return to their nests, and certain nocturnal animals may become active. However, the overall impact on wildlife is minimal and temporary.
8. Are there any cultural rituals associated with solar eclipses?
Yes, many cultures have rituals and practices associated with solar eclipses. These can include offerings to appease deities, chanting or prayers, and gathering in specific locations to witness the event as a community.
9. Is there any scientific value in studying solar eclipses?
Studying solar eclipses provides valuable scientific data for researchers. It allows scientists to study the sun’s Corona, the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere, which is otherwise too bright to observe directly.
10. Is it possible to photograph a solar eclipse?
Yes, it is possible to photograph a solar eclipse with the right equipment and proper techniques. However, it is crucial to use suitable solar filters to protect the camera and lens from the intense sunlight.








