The night sky has always fascinated humanity, sparking wonder and curiosity about the cosmos. One of the most captivating aspects of the night sky is the presence of constellations, patterns of stars that have been observed and interpreted for centuries. Understanding the ancient origins and symbolism of constellations takes us on a journey through time, exploring the early observations of the night sky, their cultural significance, and the myths and stories behind these celestial formations. By delving into the rich tapestry of constellations across different cultures and their modern scientific classification, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and meaning they hold in our collective human experience.
Understanding Constellations

The concept of constellations has deep roots in human history, spanning across cultures and time periods. The early observations of the night sky by ancient civilizations laid the foundation for our understanding of constellations. These early astronomers meticulously studied the stars and noticed patterns, creating stories and mythologies around them. Cultural significance was attributed to constellations, as they played a role in navigation, tracking time, and understanding the natural world. The ancient origins of constellations can be traced back to prehistoric times, where early humans recognized patterns in the stars and used them as seasonal markers, as seen in the agricultural societies. Ancient mythologies from different cultures, such as Greek and Roman, incorporated constellations into their stories, giving them symbolic meaning. The symbolism of constellations is multi-faceted, intertwining stories, legends, and spiritual interpretations. Today, we continue to explore and appreciate the beauty of constellations, with scientific classification and naming methods providing a modern perspective on these celestial formations. Stars and galaxies are like pieces of a cosmic puzzle, and constellations help us make sense of their vastness and complexity. Let us embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries and revelations of constellations across different cultures and time periods.
1. Early Observations of the Night Sky
Early observations of the night sky form the foundation of our understanding of constellations. Ancient civilizations, such as the Mesopotamians, Egyptians, and Greeks, were among the first to observe and study the stars. These early astronomers recognized patterns in the night sky and began connecting the dots to form constellations. They noticed how certain constellations would rise and set at different times of the year, providing valuable information for navigation, agriculture, and celestial events. The Mesopotamians specifically documented their observations on clay tablets, recording the movements of stars and planets. Egyptian astronomers also observed the night sky, using constellations to align their monumental architecture with celestial bodies. The Greeks, on the other hand, embraced a more mythological approach to constellations, incorporating stories and legends into their interpretations. This early exploration of the night sky laid the groundwork for future advancements in astronomy and our understanding of the universe. To this day, we continue to marvel at the stars and the insight they provide into our existence. If you want to learn more about the impact of planetary alignment on Earth’s tides, you can read our article on planetary alignment and Earth tides. Additionally, exploring the breathtaking beauty of nebulas in outer space can further enhance our appreciation for the wonders of the night sky.
2. Cultural Significance of Constellations
The cultural significance of constellations is deeply embedded in the history of human civilizations. These celestial patterns have played essential roles in various cultures, serving as navigational aids, timekeepers, and even sources of inspiration for art, literature, and religious beliefs. In ancient times, constellations were used by sailors and explorers to navigate vast oceans and unfamiliar territories. By observing the positions of specific constellations relative to the horizon, mariners could determine their latitude and navigate their way safely. Constellations also served as vital seasonal markers for agricultural societies, helping to indicate the changing seasons and guiding planting and harvesting practices.
But beyond their practical uses, constellations held a special place in the cultural and spiritual beliefs of many civilizations. They became the backdrop for myths, legends, and stories that explained natural phenomena and the origins of the universe. Ancient civilizations, such as the Greeks and Romans, developed elaborate mythologies around constellations, tying them to gods, heroes, and mystical creatures. These stories not only entertained, but also provided moral lessons and insights into the human condition.
Constellations continue to inspire and captivate artists, poets, and astronomers alike. Their celestial beauty has been immortalized in artwork across centuries, where constellations appear as prominent motifs in paintings, sculptures, and tapestries. Today, the cultural significance of constellations is not limited to a single civilization or era. People from different cultures and backgrounds still gaze at the night sky, marveling at the interconnectedness of the stars and the universe. Exploring the breathtaking beauty of the cosmos, including nebulas and other celestial wonders, continues to deepen our appreciation for the cultural significance of constellations and our place in the vastness of space.
The Ancient Origins of Constellations
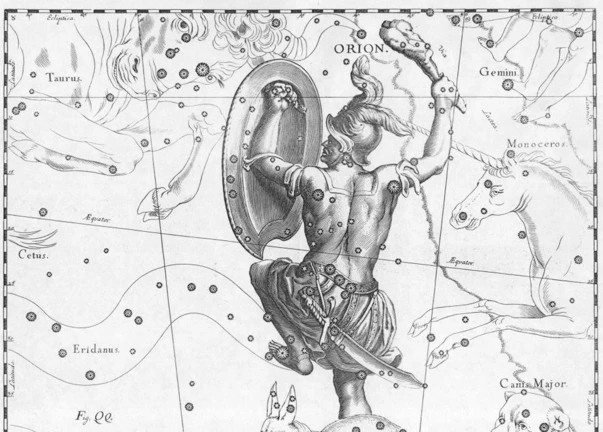
The ancient origins of constellations date back to prehistoric times, when early civilizations began to identify and recognize patterns in the night sky. These prehistoric constellation patterns were likely used as a way to navigate and understand the changing seasons. As agricultural societies emerged, constellations became important markers for planting and harvesting crops. The significance of constellations extended beyond practical applications and entered the realm of mythology and storytelling. Ancient cultures incorporated constellations into their mythologies, attributing them to the deeds of gods, heroes, and mythical creatures. From the Greek interpretation of Orion the Hunter to the Chinese legend of the Dragon, constellations held symbolic meaning and cultural significance. These ancient origins set the stage for the continuing fascination and study of constellations throughout history and into the present day.
1. Prehistoric Constellation Patterns
In exploring the origins of constellations, it is fascinating to delve into prehistoric constellation patterns. Before the advent of modern technology, ancient civilizations relied on the night sky to navigate, tell time, and understand their environment. Prehistoric humans, with their keen observation skills, noticed recurring patterns in the stars and began associating them with various elements of their existence. These early astronomers identified clusters of stars that resembled animals, objects, or significant cultural symbols. For example, the Pleiades star cluster, also known as the Seven Sisters, was believed to represent a group of important female figures in many ancient civilizations. The hunter-gatherer societies of the Paleolithic era paid particular attention to the movement of stars and used them to track seasonal changes, essential for their survival and the timing of hunt and harvest. This knowledge was often passed down through oral traditions and encoded in ancient artifacts. These prehistoric constellation patterns form the foundation of our understanding of constellations and provide insight into the deep connection our ancestors had with the celestial world.
| Ancient Constellation | Symbolism |
|---|---|
| Ursa Major (Great Bear) | The constellation was associated with the bear, a symbol of power, strength, and the cycle of hibernation. |
| Orion (The Hunter) | Orion was often associated with gods or mythological figures known for their bravery and hunting skills. |
| Taurus (The Bull) | In ancient mythology, Taurus represented strength, fertility, and the embodiment of powerful deities. |
The understanding of prehistoric constellation patterns gives us a glimpse into the deep-rooted belief systems and cultural significance assigned to the stars by our ancestors. These early observations and interpretations laid the groundwork for the development of more complex celestial maps and the mythologies that evolved around them.
2. Early Agricultural Societies and Seasonal Markers
Early agricultural societies were deeply connected to the natural world, relying on the changing seasons for their survival and livelihood. The observation of celestial phenomena, including constellations, played a crucial role in these societies as seasonal markers. By closely monitoring the movement and positions of stars and constellations, these societies were able to accurately predict and plan their agricultural activities.
One example of this is the ancient Egyptian civilization, which developed an intricate calendar system based on the rising and setting of specific constellations. The Nile River played a vital role in the agricultural practices of the Egyptians, and they relied on the annual flooding of the river to nourish their crops. The rising of the star Sirius, known as the “Dog Star,” was a significant event for them as it marked the impending floodwaters and the beginning of the planting season. By aligning their agricultural practices with the movements of the stars, they were able to optimize their harvests and ensure their survival.
Similarly, in ancient Mesopotamia, the Babylonians observed and studied the night sky to determine the changing seasons. They identified specific constellations, such as Taurus the Bull, which signaled the onset of spring and the time for planting crops. These constellations served as a celestial calendar, guiding them in their agricultural activities and allowing them to thrive in an otherwise harsh environment.
Other agricultural societies, such as the Mayans and the ancient Chinese, also recognized the importance of constellations as seasonal markers. They developed their own systems to track the positions of stars and constellations, helping them determine the optimal timing for planting, harvesting, and other agricultural practices.
The close connection between early agricultural societies and the observation of constellations highlights the practicality and significance of these celestial formations in the daily lives of ancient people. The knowledge of seasonal markers provided by constellations not only ensured the success of their agricultural endeavors but also shaped their cultural practices and beliefs, reinforcing the intimate relationship between humans and the cosmos.
3. Constellations in Ancient Mythology
In ancient mythology, constellations held a prominent place, with each culture weaving unique stories and legends around these celestial formations. Let’s explore some fascinating examples of constellations in ancient mythology:
1. Greek Mythology: Greek mythology is rich with tales of gods, heroes, and mythical creatures, many of whom are immortalized in the night sky. Among the famous Greek constellations is Orion, a hunter who was known for his exceptional skill. According to the myth, Orion was placed among the stars after his death, forming the constellation that bears his name. Another well-known constellation is Ursa Major, the Great Bear, associated with the myth of Callisto. Zeus transformed Callisto into a bear, and she was eventually placed in the sky, forming the bear constellation.
2. Egyptian Mythology: In Egyptian mythology, the constellation of Orion held great significance. The Egyptians believed that Orion was representative of Osiris, the god of the afterlife and rebirth. They associated Orion’s presence in the night sky with Osiris guiding the souls of the deceased to the afterlife. Another important constellation in Egyptian mythology is Draco, the serpent creature that was part of the creation myth.
3. Norse Mythology: Norse mythology has its own constellation tales, with one of the most notable being the constellation of the Big Dipper or Ursa Major. In Norse mythology, this constellation represents Thor’s chariot, with the stars forming the wheels. It was believed that Thor used this chariot to ride across the sky, creating the rumble of thunder with his mighty hammer, Mjolnir.
4. Chinese Mythology: Chinese mythology also has a rich tapestry of constellation stories. One of the most well-known constellations is the Azure Dragon, representing the guardian of the East and symbolizing spring and wood. Another important constellation is the Vermilion Bird, symbolizing fire and summer, often associated with the mythological figure of the Empress or the concept of love and relationships.
These are just a few examples of the many constellation stories found in ancient mythology across different cultures. The tales behind these constellations not only offered explanations for the natural world but also served as a way for ancient civilizations to connect with the sky above and seek guidance from the celestial realm.
The Symbolism of Constellations
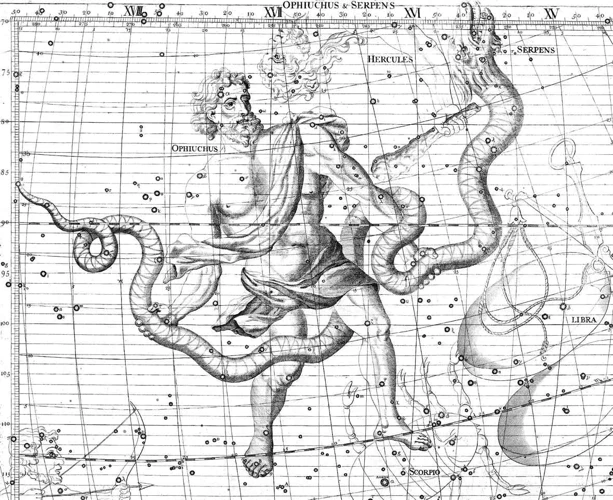
Constellations hold a profound symbolism that transcends time and culture. Each constellation carries its own unique stories and legends, offering a glimpse into the shared human experience and our ancient understanding of the cosmos. From ancient Greek and Roman mythology to indigenous cultures across the globe, the stories and legends behind the stars offer insights into the beliefs, values, and aspirations of civilizations past. These celestial tales often revolve around heroes, gods, and mythical creatures, portraying love, tragedy, and triumph. Constellations have long been associated with spiritual and astrological interpretations. They are believed to hold cosmic energy and influence on our lives, guiding us through the journey of existence and providing insights into our personalities and destinies. Whether viewed as celestial storytellers or cosmic guides, the symbolism of constellations continues to awe and inspire us, connecting us to the wonders of the universe.
1. Stories and Legends Behind the Stars
The stories and legends behind the stars are as diverse and rich as the cultures that created them. These ancient tales often sought to explain the origins of constellations as well as the natural phenomena associated with them. In Greek mythology, for example, the constellation Orion is believed to represent a hunter of great skill and strength. According to the myth, Orion was the son of Poseidon, the god of the sea. His exceptional hunting abilities caught the attention of the goddess Artemis, who fell in love with him. However, Orion’s life was tragically cut short when he was stung by a scorpion, represented by the constellation Scorpius. This myth explains the placement of these two constellations in the night sky, forever locked in an eternal chase.
Another intriguing legend is found in Chinese mythology, involving the constellations of the Ox and the Weaver Girl. The story tells of a celestial love affair between Zhinü, the Weaver Girl, and Niulang, a mortal cowherd. Forbidden by the gods to be together, the couple can only reunite once a year on the 7th day of the 7th lunar month, when a bridge, formed by a flock of magpies, allows them to meet. This myth is associated with the constellation Aquila, representing the magpies, as well as the two separate constellations of the Ox and the Weaver Girl.
In Norse mythology, the mighty warrior known as the Valkyrie is said to guide fallen heroes to the afterlife. The constellation Cassiopeia is linked to the story of the Valkyrie Sigrun, who was transformed into a swan and placed among the stars. Cassiopeia, depicted as a Queen sitting on a throne, represents Sigrun’s regal and imposing presence in the night sky.
These stories and legends serve as a testament to the human fascination with the stars and our relentless desire to weave narratives around them. They allow us to connect with the celestial realm on a deeper level, infusing constellations with mystery, wonder, and profound meaning.
2. Spiritual and Astrological Interpretations
Spiritual and astrological interpretations of constellations have played a significant role in various cultures throughout history. These interpretations are based on the belief that the position of the stars and planets at the time of a person’s birth can have an impact on their personality, traits, and destiny. Astrology, often considered a pseudoscience, examines the alignment of celestial bodies to make predictions and provide insight into individuals’ lives.
In spiritual interpretations, constellations are seen as divine symbols and representations of cosmic forces. Each constellation is associated with specific qualities, energies, or archetypal figures within spiritual traditions. For example, the constellation Orion is often seen as a symbol of strength and courage, while the constellation Pisces is associated with intuition and empathy.
Astrological interpretations work within the context of zodiac signs, which are divided into twelve equal parts, each representing different periods within the year. These divisions align with specific constellations, such as Aries, Taurus, or Gemini. Individuals born under these signs are believed to possess particular characteristics associated with the corresponding constellation.
Astrologers create birth charts, or horoscopes, based on an individual’s date, time, and location of birth. These charts analyze the positions and aspects of celestial bodies at the time of birth to generate insights into the individual’s personality, relationships, and future events. Astrological interpretations of constellations have been influential in many cultures, including ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Egyptians, as well as in modern times where horoscopes are commonly found in newspapers and magazines.
While the scientific validity of astrology is a subject of debate, its cultural and spiritual significance cannot be overlooked. Many individuals find comfort, guidance, and a sense of connection to the cosmos through astrological interpretations, using constellations as symbolic tools to understand themselves and the world around them. Whether one fully believes in astrology or not, the spiritual and astrological interpretations of constellations hold a place in the tapestry of human beliefs and understanding of the universe.
Constellations Across Different Cultures
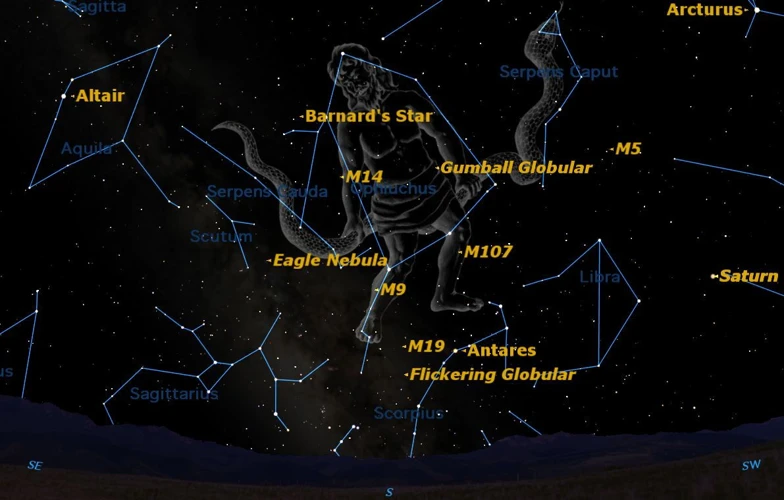
Constellations have been observed and interpreted by various cultures throughout history, each incorporating their own unique perspectives and mythologies. Greek and Roman civilizations had a significant influence on modern Western constellations, with famous figures and heroes immortalized in the night sky. The Chinese Zodiac and its celestial animals offer a different cultural perspective, representing a twelve-year cycle with each year associated with a specific animal. Indigenous cultures around the world have their own constellation stories, passing down knowledge and wisdom through generations. For example, the Aboriginal people of Australia have a rich celestial lore, connecting the stars with their Dreamtime stories. These diverse interpretations highlight the universality of human fascination with the night sky and the creative ways in which constellations are woven into the fabric of different cultures. Exploring the constellations across different cultures allows us to appreciate the richness of our global heritage and the interconnectedness of our human experience.
1. Greek and Roman Constellations
Greek and Roman constellations play a significant role in the study of astronomy and mythology. These ancient civilizations had a profound impact on the development of constellations as we know them today. In Greek mythology, many constellations are associated with gods, heroes, and legendary creatures. For example, the constellation Orion is linked to the mythological hunter Orion, known for his strength and prowess. The constellation Ursa Major, meaning “Great Bear,” is linked to the story of Callisto, a nymph who was transformed into a bear by the goddess Hera. Other notable Greek constellations include Pegasus, the winged horse, and Andromeda, the princess saved by Perseus from a sea monster.
The Romans adopted many of the Greek constellations but also added their own interpretations. For instance, the constellation Gemini represents the twin brothers Castor and Pollux, known for their bravery and loyalty. The constellation Hercules, depicting the mighty hero known for his twelve labors, also has roots in Roman mythology. The Romans also associated their emperors with constellations, connecting them to divine figures. For example, the constellation Aquila, meaning “eagle,” was linked to the Roman Empire and symbolized power and authority.
To help navigate and track time, ancient Greeks and Romans created celestial maps and star catalogs that included these constellations. They believed that the movements of the constellations could influence events on Earth. The legacy of Greek and Roman constellations can still be seen today, as many of these ancient names and stories have been passed down through generations. They continue to inspire and captivate astronomers, stargazers, and lovers of mythology alike. Whether it’s Orion’s Belt, the Pleiades, or the constellation of Leo, the influence of Greek and Roman constellations on our understanding of the night sky is immeasurable.
2. Chinese Zodiac and Celestial Animals
The Chinese Zodiac is a widely recognized and celebrated system that assigns an animal to each year in a repeating twelve-year cycle. These animal signs are associated with specific personality traits and characteristics, believed to influence the lives of those born in their respective years. The origins of the Chinese Zodiac can be traced back to ancient Chinese mythology and astrology. According to legend, the Jade Emperor organized a great race among animals to determine their order in the zodiac. The twelve animals that crossed the river in the order they arrived became the representatives of each year in the cycle.
Each animal in the Chinese Zodiac possesses its own unique symbolism and significance. For example, the Rat is considered clever and resourceful, while the Ox is known for its strength and determination. The Tiger represents courage and bravery, and the Rabbit symbolizes kindness and gentleness. The Dragon, a mythical creature in Chinese culture, is associated with power and good fortune.
In addition to the twelve animal signs, Chinese astrology also incorporates celestial animals, which are mythological creatures with symbolic meanings. These celestial animals include the Azure Dragon, the Vermilion Bird, the White Tiger, and the Black Tortoise. Each of these animals is associated with cardinal directions and elements, and they are believed to have a profound influence on Feng Shui, Chinese astrology, and traditional Chinese medicine.
The Chinese Zodiac and the celestial animals hold great cultural and spiritual importance in Chinese society. They are used for various purposes, including horoscope predictions, compatibility assessments, and auspicious date selections for significant events such as weddings and business ventures. The Chinese New Year celebrations, based on the lunar calendar, are marked by colorful festivities with each year corresponding to a specific animal sign. The Chinese Zodiac and celestial animals continue to be cherished elements of Chinese culture, representing a unique blend of mythology, astrology, and symbolism.
3. Indigenous Constellation Stories
Indigenous cultures around the world have their own unique and captivating constellation stories, passed down through generations to preserve their rich cultural heritage. These stories often reflect the deep connections between indigenous peoples and the natural world. For example, in Australian Aboriginal culture, the constellation known as the “Emu in the Sky” represents the Emu, a significant animal in their mythology. The pattern of stars in the sky mirrors the shape of an Emu as it stands tall on Earth. In the Navajo tradition, the “Black God” constellation represents the Dark Cloud of the Sacred Mountain, and it is believed that this constellation guides people to safety during times of darkness. The Inuit people of North America have their own celestial stories, such as the constellation of “Amarok,” which represents the Great Wolf and is seen as a protective force. These indigenous constellation stories go beyond mere astronomical observations—they carry spiritual, moral, and practical lessons for the communities that uphold them. They serve as a reminder of the deep connection between indigenous peoples and their surrounding natural environments.
The Modern Understanding of Constellations
As our knowledge of the universe has expanded, so too has our modern understanding of constellations. Scientific classification and naming methods have provided a systematic approach to categorizing and identifying these celestial patterns. Astronomers use specific criteria to define constellations, taking into account the shape, size, and arrangement of the stars within each grouping. This scientific understanding has allowed for clearer communication and collaboration among astronomers worldwide. Constellations serve practical purposes in the modern age, such as aiding in navigation and space exploration. Technology has enabled us to study and observe constellations in greater detail, providing insights into stellar evolution and the broader workings of the universe. From ancient cultural symbols to scientific tools, constellations continue to captivate our imagination, reminding us of humanity’s enduring fascination with the cosmos.
1. Scientific Classification and Naming
Scientific classification and naming play a crucial role in our modern understanding of constellations. Astronomers have developed a systematic approach to categorize and identify different celestial formations. One method of classification is based on the International Astronomical Union (IAU)’s constellation boundaries. The night sky is divided into 88 official constellations, each encompassing a specific region of the celestial sphere. These boundaries help astronomers pinpoint the location of stars within a particular constellation and facilitate communication within the scientific community.
Stars within constellations are often named using a combination of Greek letters and the genitive form of the constellation name. For instance, stars in the Orion constellation are identified as “Alpha Orionis,” “Beta Orionis,” and so on. This nomenclature system makes it easier to refer to specific stars and study their characteristics. Additionally, prominent stars within constellations are sometimes given proper names, like Betelgeuse or Sirius, adding a more recognizable and memorable element to their identification.
Astronomers also employ the use of symbols to represent each constellation. These symbols are derived from the ancient Greek tradition of connecting stars to form shapes and figures. For example, the constellation Ursa Major is represented by a bear, and its symbol resembles the outline of the animal. These symbols simplify the representation of constellations in star charts and assist amateur astronomers in identifying and locating constellations in the night sky.
Through scientific classification, naming conventions, and symbolic representation, our understanding of constellations has been refined and made accessible to both professional astronomers and enthusiasts. This approach ensures a standardized way of referring to and studying these celestial formations, contributing to the ongoing exploration and appreciation of the wonders of the cosmos.
2. Modern Uses of Constellations
In addition to their historical and cultural significance, constellations serve various practical and scientific purposes in the modern world. Let’s explore some of the key modern uses of constellations:
1. Navigation and Global Positioning System (GPS): Constellations are integral to navigation, both on land and sea. The alignment and positions of specific stars within constellations help mariners and explorers navigate and determine their precise location. Similarly, the Global Positioning System (GPS) relies on a network of satellites that form their own set of artificial constellations in space. These satellites utilize precise measurements of time and signal transmission to accurately determine positions on Earth.
2. Space Exploration and Astronomical Research: Constellations continue to play a crucial role in space exploration and astronomical research. Scientists and astronomers utilize constellations to map the visible universe, identify and study celestial objects such as stars, galaxies, and nebulas, and track the motion of objects in space. Observatories around the world use telescopes and advanced imaging technology to capture and analyze the light emitted by these celestial bodies, providing insights into their composition, behavior, and evolution.
3. Communication and Telecommunications: Satellites placed in specific orbits within the Earth’s atmosphere often utilize constellations to provide global communication services. These communication satellites are strategically positioned to cover large areas of the planet and ensure stable and reliable communication channels for telephones, internet connectivity, television broadcasting, and other forms of telecommunications.
4. Scientific Education and Outreach: Constellations also serve as a powerful educational tool to inspire and engage people in science. Planetariums and educational institutions use detailed star maps and presentations to explain the concept of constellations, their mythology, and their role in understanding the universe. Public stargazing events, astronomy clubs, and online resources provide opportunities for people of all ages to learn about constellations, sparking curiosity and a sense of wonder about the cosmos.
5. Cultural and Artistic Expressions: Constellations continue to inspire artists, writers, and performers in various creative endeavors. From ancient times to the present day, constellations have been the subject of paintings, sculptures, poetry, music, and literature. They symbolize unity, storytelling, and our connection with the vastness of the universe, serving as a muse for artistic expressions that capture the imagination and emotions of individuals.
The modern uses of constellations highlight their ongoing relevance and significance in our technologically advanced society. These stellar patterns not only connect us to our past but also guide us in our exploration of the present and future frontiers of science, navigation, communication, and artistic expression.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the ancient origins and symbolism of constellations showcase the profound connection humans have with the night sky. From early observations and cultural significance to the myths and stories behind them, constellations have played a crucial role in humanity’s understanding of the cosmos. The stories and legends that surround the stars have been passed down through generations, creating a rich tapestry of narratives and interpretations. Spiritual and astrological interpretations have further added to the symbolism of constellations, offering insights into personal and collective meanings. Across different cultures, constellations have taken on unique identities, such as the Greek and Roman constellations with their rich mythologies, the Chinese zodiac and celestial animals representing different years, and the indigenous constellation stories that embody the connection between land and sky. However, it is important to note that the modern understanding of constellations is rooted in scientific classification and naming methods. These advancements have allowed us to map and study the celestial bodies more accurately, leading to a deeper comprehension of the universe. Whether we gaze at the stars in awe, navigate using their guidance, or seek personal meaning in their arrangements, constellations continue to inspire and ignite our imaginations. They serve as a reminder of our place in the universe and the timeless wonder that lies beyond our reach. So next time you find yourself beneath the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the ancient history and symbolism that constellations have to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How were constellations first observed by early civilizations?
Early civilizations observed constellations by carefully observing the patterns formed by stars in the night sky. They noticed that certain groups of stars appeared to form shapes or patterns, which they then associated with objects, animals, or mythological figures.
2. What is the cultural significance of constellations?
Constellations hold cultural significance as they were used for navigation, determining seasons, and tracking time. They were also woven into the fabric of ancient myths, providing storytelling and spiritual connections for different cultures.
3. How did prehistoric societies use constellations as seasonal markers?
Prehistoric societies used constellations as seasonal markers for activities such as hunting or agriculture. They observed how the positions of specific constellations changed throughout the year, indicating the changing seasons and guiding them in their daily lives.
4. How did ancient civilizations incorporate constellations into their mythology?
Ancient civilizations incorporated constellations into their mythology by attributing stories and legends to the patterns they saw in the stars. These stories often portrayed gods, heroes, or creatures associated with the constellation, adding a mythical narrative to their understanding of the cosmos.
5. What stories and legends are associated with specific constellations?
Each culture has its own unique stories and legends associated with specific constellations. For example, the constellation Orion is associated with a mighty hunter in Greek mythology, while the constellation Ursa Major is associated with the Great Bear in various cultures around the world.
6. How are constellations interpreted spiritually and astrologically?
Constellations are often interpreted spiritually and astrologically, with different cultures finding deeper meanings and connections between the stars and human life. Astrologers believe that the positions and alignments of constellations can influence personality traits and predict future events.
7. What are some famous Greek and Roman constellations?
Famous Greek and Roman constellations include Orion, Ursa Major, Hercules, and Pegasus. These constellations played significant roles in Greek and Roman mythology and are still widely recognized and studied today.
8. How does the Chinese zodiac incorporate constellations and celestial animals?
The Chinese zodiac incorporates constellations and celestial animals as symbols for different years in their calendar cycle. Each year is associated with a specific animal, such as the rat, dragon, or tiger, which has its own characteristics and influences.
9. What are some indigenous constellation stories from different cultures?
Indigenous cultures all around the world have their own unique constellation stories. For example, in Australian Aboriginal culture, the constellation known as the Pleiades holds great cultural significance and is associated with Dreamtime stories and rituals.
10. How are constellations named and classified in modern scientific understanding?
Constellations are named and classified in modern scientific understanding using specific coordinate systems. The International Astronomical Union (IAU) sets the official names and boundaries for constellations, and astronomers use these designations to locate and study celestial objects within them.