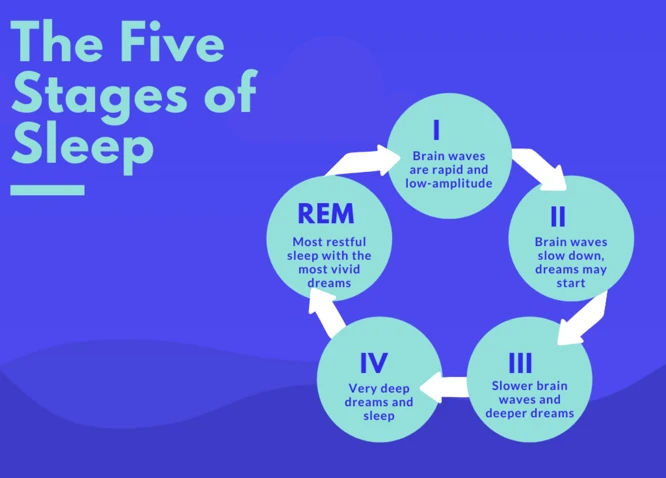
Dreams have long been a source of fascination and intrigue for humans throughout history. They are often seen as glimpses into the subconscious mind, providing insights into our thoughts, emotions, and desires. One approach to understanding dreams is through the cognitive lens, which focuses on the mental processes involved in dream formation and interpretation. By analyzing dreams through the cognitive approach, we can uncover hidden meanings, explore the role of perception and memory, and decode the symbolism that our minds create during sleep. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the key concepts of dream interpretation, explore various techniques for analyzing dreams, discuss the interpretations of common dream symbols, highlight the benefits of analyzing dreams from a cognitive perspective, examine real-life case studies, and address the challenges that arise in the interpretation of dreams. So, prepare to embark on a journey through the mysterious landscape of dreams, as we unravel their secrets through the cognitive approach.
The Cognitive Approach to Dream Analysis

The Cognitive Approach to Dream Analysis focuses on understanding dreams through the lens of cognitive processes and mental functions. According to this approach, dreams are seen as products of the mind, influenced by various cognitive factors such as perception, memory, and reasoning. By studying these cognitive processes, researchers aim to decipher the meaning and significance of dreams. One key concept of the cognitive approach is that dreams are not random or meaningless, but rather reflect the individual’s beliefs, experiences, and emotions. The role of perception and memory is also crucial in dream analysis, as dreams often incorporate elements from the dreamer’s waking life and past experiences. Additionally, cognitive processes play a significant role in the creation of dream symbols, as the mind transforms experiences and emotions into symbolic representations during sleep. This approach emphasizes the importance of understanding the cognitive mechanisms at play in order to unravel the complexities of dream content and meaning. To delve deeper into dream analysis, it is worth exploring other related approaches such as Jungian dream analysis and symbolic dream interpretation.
Key Concepts of Dream Interpretation
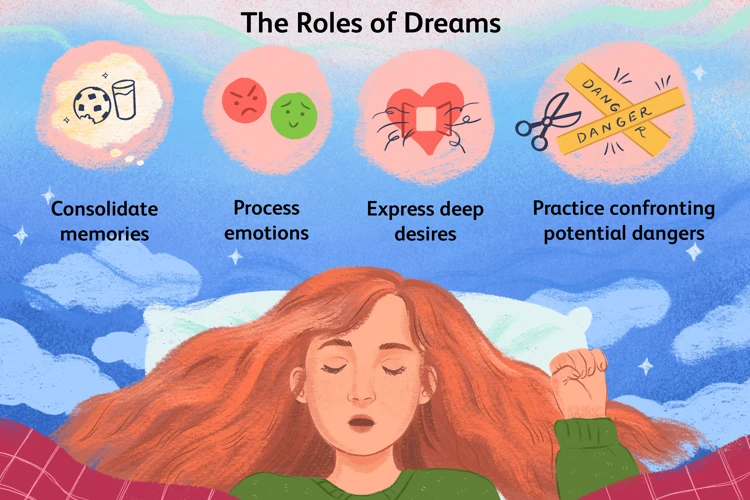
Dream interpretation is a complex process that involves several key concepts to uncover the hidden meanings within our dreams. The first concept revolves around the idea that dreams are products of the mind, influenced by our thoughts, emotions, and experiences. This means that interpreting dreams requires an understanding of the dreamer’s personal context and subjective perspective. Secondly, the role of perception and memory is crucial in dream analysis. Dreams often incorporate elements from our waking lives and past experiences, providing clues to their symbolic significance. Lastly, cognitive processes play a significant role in the interpretation of dream symbols. By understanding how our minds transform experiences into symbolic representations during sleep, we can gain deeper insights into the underlying meaning of our dreams. To further enhance our understanding of dreams, exploring techniques like lucid dreaming can provide valuable insights and potential for conscious exploration within the dream realm.
1. Dreams as Products of the Mind
Dreams as Products of the Mind hold a central position in the cognitive approach to dream analysis. According to this concept, dreams are not random occurrences but rather a reflection of the inner workings of the mind. They are shaped by an individual’s thoughts, emotions, memories, and experiences. As one sleeps, the brain continues to process information and thoughts, creating a rich tapestry of imagery and narratives known as dreams. These dreams often draw upon the dreamer’s subconscious desires, fears, conflicts, and aspirations. The cognitive approach believes that dreams serve various psychological functions, such as memory consolidation, emotional processing, and problem-solving. By analyzing dreams as products of the mind, dream interpreters can gain insights into a person’s deeper thoughts, motivations, and unresolved issues. It is through this lens that dream symbols and narratives are explored, uncovering the hidden layers of the dreamer’s psyche. Understanding dreams as products of the mind brings an appreciation for their complexity and underscores the significance of decoding their underlying meanings.
2. The Role of Perception and Memory
The Role of Perception and Memory in dream analysis is a significant aspect of understanding the cognitive processes behind dreaming. When we dream, our perception and memory play a crucial role in shaping the content and meaning of our dreams. Perception refers to the way we interpret and make sense of sensory information from the external world. In dreams, our perception is often influenced by past experiences and emotions, leading to the incorporation of real-life elements and events into the dream narrative. Our memories, both conscious and subconscious, become an integral part of dream formation. Dreams may contain fragments of memories, allowing us to revisit and process past events or emotions. Sometimes, dreams also involve the memory consolidation process, where the mind consolidates and strengthens newly acquired information during sleep. Memory retrieval can occur during dreams, bringing forward forgotten experiences or unresolved issues. The cognitive approach recognizes the powerful influence of perception and memory in shaping the dream world and highlights the need to analyze these factors when interpreting dreams.
3. Cognitive Processes and Dream Symbols
Cognitive processes and dream symbols are intricately linked within the realm of dream analysis. Dreams are not simply random collections of images and events; they are shaped by the cognitive processes that occur during sleep. These processes include perception, memory, attention, and reasoning, all of which influence the creation and interpretation of dream symbols.
Perception plays a crucial role in dream formation. Our experiences and sensory stimuli from waking life are often assimilated and integrated into dreams. For example, if you have recently visited a beach, you might dream of the sound of crashing waves or the feeling of sand between your toes. These perceptual elements are transformed into symbolic representations during the dream state.
Memory also contributes to the generation of dream symbols. Dreams often draw upon past experiences and memories, interweaving them with current emotions and concerns. Aspects of our everyday lives may resurface in disguised or distorted forms within our dreams. For instance, a childhood memory of playing with a beloved pet may emerge as a dream symbol representing affection or companionship.
Additionally, cognitive processes influence the interpretation of dream symbols. Our minds categorize and make associations between ideas, emotions, and experiences. These associations shape the symbolic meaning attributed to various dream elements. For example, the image of a snake in a dream may be interpreted differently depending on the individual’s personal experiences and cultural background. While some may see it as a symbol of transformation or rebirth, others may view it as a representation of danger or deceit.
Understanding the cognitive processes involved in dream formation and symbolization is essential for accurate dream analysis. By delving into the cognitive aspects of dreams, we can gain deeper insights into the hidden meanings and subconscious messages that dreams convey.
Techniques for Analyzing Dreams

When it comes to analyzing dreams, there are various techniques that can be employed. One popular technique is content analysis, which involves closely examining the elements and themes present in a dream to gain insight into its meaning. Content analysis may involve keeping dream journals, recording the details of dreams upon waking, and looking for patterns or recurring symbols. Another technique is psychoanalysis and dreamwork, which seeks to uncover the hidden meanings of dreams by exploring the unconscious mind. This approach, popularized by Sigmund Freud, involves analyzing the latent content of a dream, the underlying desires and conflicts, and connecting them to the manifest content, the actual images and events experienced in the dream. Lastly, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can also be utilized in dream analysis, focusing on identifying and challenging cognitive distortions or negative thought patterns that may be reflected in dreams. Each of these techniques offers a unique perspective and set of tools for understanding the intricate world of dreams, providing valuable insights into our innermost thoughts, emotions, and experiences.
1. Content Analysis
Content analysis is a valuable technique used in dream analysis to examine the various elements and themes present in a dream. This method involves systematically breaking down the components of the dream, such as characters, settings, actions, and emotions, and analyzing their symbolic meanings and significance. By studying the content of a dream, analysts can identify patterns and recurring themes that may offer insights into the dreamer’s subconscious thoughts and emotions. Key elements to consider during content analysis include the people or characters featured in the dream, their relationships, the locations or settings, and the actions or events that unfold. By examining these aspects, analysts can identify underlying emotions, conflicts, and desires that may be represented in the dream. Gender, age, and cultural factors may also be considered when interpreting the content of a dream, as these can influence the symbolism and meaning attached to specific elements. Content analysis is a powerful tool that helps unravel the rich tapestry of dream imagery and provides a deeper understanding of the dreamer’s subconscious mind.
2. Psychoanalysis and Dreamwork
Psychoanalysis and dreamwork are important techniques used in the analysis of dreams. Developed by Sigmund Freud, psychoanalysis explores the unconscious mind and its influence on behavior. In the context of dream analysis, Freud believed that dreams serve as a means for the unconscious mind to express repressed thoughts, desires, and conflicts. Dreamwork refers to the method by which the unconscious material is transformed into dream content. Freud identified several mechanisms of dreamwork, including condensation, displacement, symbolism, and secondary revision. Condensation involves combining multiple thoughts or experiences into a single dream image, while displacement involves the shifting of emotional significance from one element to another. Symbolism, a common feature in dreams, represents hidden meanings and desires. Lastly, secondary revision is the process by which the mind organizes and reshapes the dream content to make it more coherent and acceptable. Such techniques aim to uncover the latent content of the dream, which is the true underlying meaning. Psychoanalysis and dreamwork remain influential in dream analysis, offering insights into the unconscious mind and providing a deeper understanding of the individual’s psychodynamic processes.
3. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a powerful technique for analyzing dreams from a cognitive perspective. This therapeutic approach focuses on examining the connections between thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, with the aim of identifying and modifying unhelpful patterns of thinking and behavior. When applied to dream analysis, CBT looks at how cognitive distortions and irrational beliefs may be influencing the content and meaning of dreams. One technique commonly used in CBT for analyzing dreams is cognitive restructuring. This involves challenging and replacing negative or irrational thoughts in order to create more positive and realistic interpretations of dream events. Another technique used in CBT is behavior activation, which focuses on identifying and changing behavioral patterns that may be contributing to distressing or recurring dreams. By understanding the cognitive processes underlying dream formation and utilizing CBT techniques, individuals can gain greater insight into their dreams and develop strategies for coping with any negative emotions or experiences that arise during sleep.
Common Dream Symbols and their Interpretations

Common Dream Symbols and their Interpretations provide insights into the hidden meanings and symbolism behind certain recurring elements in dreams. Understanding these symbols can help unravel the messages and emotions embedded in our dreams. Here are a few examples:
1. Falling: Falling in dreams often represents a sense of insecurity, loss of control, or fear of failure in waking life. It can also symbolize a need for grounding or a desire for change.
2. Flying: The ability to fly in dreams is often associated with freedom, liberation, and empowerment. It can represent the desire for independence, escape from limitations, or a sense of achievement and control.
3. Being Chased: Being chased in a dream typically signifies feelings of anxiety, pressure, or avoidance in real life. It may reflect unresolved conflicts or the need to confront and overcome challenges.
4. Teeth Falling Out: Dreams involving teeth falling out can be related to feelings of vulnerability, insecurity, or a fear of aging and loss. They can also highlight concerns about communication, self-image, or a lack of confidence.
It is important to note that dream symbols can have different interpretations based on personal experiences and cultural background. Exploring the symbolism within dreams can provide valuable insights into our subconscious thoughts and emotions, helping us gain a deeper understanding of ourselves and our lives.
1. Falling
Falling is a common dream symbol that often elicits a sense of fear or unease. In the cognitive approach to dream analysis, the interpretation of falling dreams focuses on the underlying emotions and cognitive processes associated with this experience. Rather than taking a literal interpretation, psychologists believe that falling dreams represent a sense of lack of control or instability in one’s waking life. The dreamer may be grappling with feelings of insecurity, uncertainty, or a fear of failure. The sensation of falling in dreams can mirror the feeling of losing control or being overwhelmed by circumstances in reality. It is important to consider the context and personal experiences of the dreamer when analyzing falling dreams, as the emotional response and interpretation can vary. For some, falling dreams may indicate a need for support or a desire for stability, while for others, it may highlight the need to take risks or face challenges head-on. Understanding the individual’s unique cognitive processes and emotional landscape is crucial in uncovering the true meaning behind falling dreams.
2. Flying
Flying is a common dream symbol that often evokes feelings of freedom, empowerment, and liberation. When analyzing dreams that involve flying, it is important to consider the specific context and emotions associated with the dream. Flying dreams can have various interpretations depending on the individual’s personal experiences and beliefs.
1. Sense of Freedom: One interpretation of flying dreams is that they represent a desire for liberation or a sense of freedom. Flying in a dream may symbolize the dreamer’s longing for independence or the need to break free from restrictions and limitations in their waking life.
2. Power and Control: Flying dreams can also symbolize a sense of power and control. When soaring through the skies, individuals may experience a heightened sense of control and mastery over their own lives. This interpretation suggests that the dreamer is feeling confident and capable of overcoming obstacles and challenges.
3. Escaping or Avoidance: In some cases, flying dreams may reflect a desire to escape from a difficult situation or avoid facing certain emotions or responsibilities. The act of flying can represent a retreat or evasion from reality, allowing the dreamer to temporarily detach themselves from their daily struggles.
4. Elevated Perspective: Flying dreams often provide a unique perspective, allowing the dreamer to view the world from a higher vantage point. This interpretation suggests a need for a broader perspective or a desire to gain a clearer understanding of one’s life circumstances.
It is important to note that the interpretation of flying dreams can vary greatly depending on the individual’s personal associations and experiences. It is crucial to consider the specific details and emotions within the dream to unlock its deeper meaning.
3. Being Chased
When it comes to dream symbols, few are as common and anxiety-inducing as the experience of being chased. In dreams, being chased represents a sense of fear, vulnerability, or a desire to escape from something in our waking lives. The cognitive approach offers insights into the possible interpretations of this dream symbol. It suggests that being chased may symbolize unresolved conflicts or challenges that we are avoiding or running away from. It could be an indication of stress or pressure in our daily lives, where we feel pursued by responsibilities or expectations. Alternatively, being chased in a dream may reflect a lack of control or powerlessness in a particular situation. It can symbolize the need to confront our fears, face challenges head-on, and regain a sense of control over our lives. This dream can also provide an opportunity for self-reflection, prompting us to examine the source of our anxieties and take steps towards resolving them. It is important to note that the interpretation of dreams is highly subjective and context-dependent, so each individual’s experience and emotions should be considered.
4. Teeth Falling Out
One common dream symbol that many people experience is the sensation of their teeth falling out. This dream can be quite unsettling and often leaves individuals feeling puzzled and concerned. In the cognitive approach to dream analysis, the interpretation of this dream symbol can vary based on individual experiences and beliefs.
From a cognitive perspective, teeth falling out may represent feelings of powerlessness or a loss of control. This dream could reflect a situation in waking life where the dreamer feels overwhelmed or unable to assert themselves. It might also indicate anxieties related to appearance, self-image, or communication. The sensation of teeth falling out could symbolize a fear of rejection or the fear of losing one’s ability to express oneself effectively.
Additionally, this dream symbol may tap into deeper psychological themes. For instance, losing teeth in dreams has been linked to issues of self-esteem and concerns about aging. It may also reflect underlying feelings of insecurity or vulnerability.
It’s important to note that while this interpretation provides a general framework, individual experiences and personal contexts play a crucial role in dream analysis. For some, the experience of teeth falling out may have different meanings based on their unique mindset and life circumstances. It is recommended to explore the dream symbol in the broader context of the individual’s life experiences and emotions.
Understanding the symbolic significance of teeth falling out in dreams provides an opportunity for self-reflection and gaining insight into one’s subconscious thoughts and emotions. Whether it represents a fear of losing control or reflects deeper issues of self-esteem and vulnerability, the cognitive approach to dream analysis encourages individuals to explore the personal significance of this symbol in order to gain a deeper understanding of themselves and their psychological well-being.
Benefits of Analyzing Dreams from a Cognitive Perspective
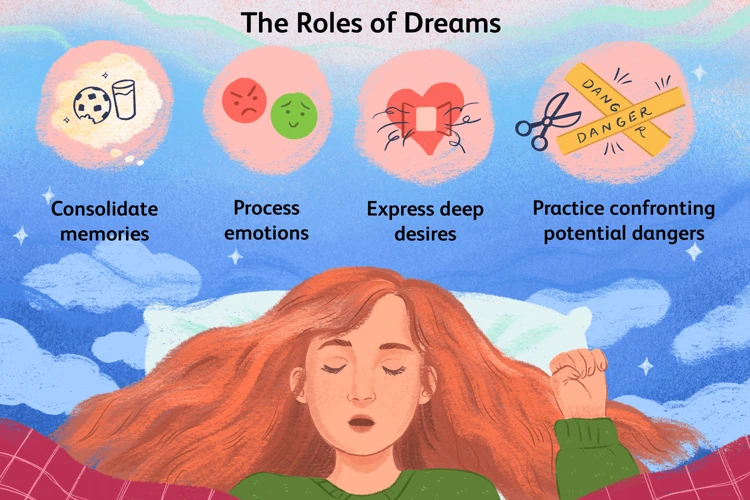
Analyzing dreams from a cognitive perspective offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly enhance self-awareness and personal growth. One of the key advantages is gaining insight into one’s thoughts, emotions, and desires that may be operating at a subconscious level. By examining the cognitive processes involved in dream formation, individuals can uncover patterns, themes, and recurring motifs that shed light on their innermost concerns and aspirations. This awareness can lead to a deeper understanding of oneself and promote personal development.
Analyzing dreams from a cognitive perspective can assist in problem-solving and decision-making. Dreams often present situations, conflicts, or dilemmas that mirror real-life challenges. By examining these dream scenarios, individuals can evaluate different perspectives, explore possible solutions, and gain new insights into their waking life predicaments.
Another benefit is the potential for emotional healing and resolution. Dreams sometimes serve as a platform for processing unresolved emotions and traumas. Through cognitive dream analysis, individuals can identify emotional patterns, confront repressed feelings, and potentially find closure or healing through dream exploration. This can contribute to improved overall mental well-being and emotional resilience.
Additionally, examining dreams from a cognitive perspective can foster creativity and innovation. Dreams have long been associated with inspiration and problem-solving breakthroughs. By studying the cognitive processes at play in dreams, individuals may be able to access their subconscious creativity and tap into unconventional ways of thinking. This can be particularly beneficial for artists, writers, and anyone seeking fresh perspectives or new ideas.
Lastly, analyzing dreams from a cognitive perspective can deepen the connection between the conscious and unconscious mind. Dreams offer a window into the hidden recesses of the psyche, allowing individuals to bridge the gap between their waking and dreaming selves. This integration can promote self-integration, leading to a greater sense of wholeness and alignment within oneself.
The benefits of analyzing dreams from a cognitive perspective are numerous and encompass personal insight, problem-solving, emotional healing, creativity, and self-integration. By embracing this approach, individuals can unlock the transformative power of their dreams and harness its potential for personal growth and self-discovery.
Interpreting Dreams: Case Studies

Interpreting Dreams: Case Studies presents real-life examples that illustrate the application of dream analysis from a cognitive perspective. These case studies offer valuable insights into the complexities of dreams and the diverse interpretations that can arise. One such case study involves a recurring nightmare, where a person experiences unresolved fears in their dreams. Through cognitive analysis, it is possible to identify the underlying fears and work towards resolving them. Another case study focuses on lucid dreaming, where individuals gain control over their dreams and can actively participate in them. This highlights the potential for harnessing control and exploring one’s consciousness during sleep. Lastly, the symbolic journey case study delves into dreams that are laden with unconscious desires and motivations. By examining the symbols and narratives within these dreams, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their hidden desires and aspirations. These case studies demonstrate the richness and complexity of dream interpretation, showcasing how the cognitive approach can provide profound insights into the human mind and behavior.
1. The Recurring Nightmare: Unresolved Fears
The Recurring Nightmare: Unresolved Fears. One common type of dream that individuals experience is the recurring nightmare. These nightmares often involve themes of fear, anxiety, and distress, and they can occur repeatedly over an extended period of time. Analyzing these recurring nightmares through the cognitive approach can provide valuable insights into the dreamer’s unresolved fears and anxieties. The repetition of the nightmare indicates that there is an underlying issue that the dreamer has not yet resolved or come to terms with in their waking life. The cognitive interpretation of these nightmares posits that they reflect the mind’s attempt to process and confront these unresolved fears. The content of the nightmare may symbolically represent the fear or anxiety that the dreamer is experiencing. For example, recurring nightmares about being chased may represent a persistent feeling of being pursued or threatened in daily life. By exploring the emotions, events, and symbols within the recurring nightmare, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of their unresolved fears and work towards resolving them. This self-reflection and introspection can lead to personal growth and the alleviation of anxiety and distress associated with the recurring nightmare.
2. The Lucid Dream: Harnessing Control
The phenomenon of lucid dreaming is a fascinating topic within the realm of dream analysis. In a lucid dream, the dreamer becomes aware that they are dreaming while the dream is still occurring. This awareness grants the dreamer a unique opportunity to consciously interact with and manipulate the dream environment. Lucid dreams provide a sense of control and agency, allowing individuals to shape the narrative, explore different scenarios, and even engage in activities that may not be possible in waking life. This concept of harnessing control in a lucid dream has captured the attention of researchers and individuals alike.
One technique often employed to achieve lucidity in dreams is reality testing. This involves performing regular checks throughout the day to confirm whether one is in a dream or reality. By continuously questioning the nature of their surroundings, individuals create a habit of mindfulness that carries over into their dream state. This heightened awareness increases the likelihood of recognizing the dream state when it occurs, leading to the ability to exert control.
Once lucidity is achieved, dreamers can experiment with different techniques to influence the dream’s content. They can manifest their desires by actively interacting with dream characters and objects or altering the dream’s environment. Some individuals use visualization techniques to summon specific dream scenarios or engage in activities that they find fulfilling or exciting.
Harnessing control in lucid dreams can offer a range of benefits. It provides an avenue for personal growth, enabling individuals to confront fears, practice skills, and explore the depths of their imagination. Lucid dreaming also has therapeutic potential, as it allows individuals to engage in vivid simulations that can help address anxieties, traumas, and unresolved issues.
With the increasing interest and research in lucid dreaming, individuals are discovering ways to enhance their lucid dream experiences. Techniques such as keeping dream journals, practicing reality checks, and utilizing lucid dreaming supplements are gaining popularity. By harnessing control in lucid dreams, individuals can unlock a realm of endless possibilities within their subconscious minds, leading to a deeper understanding of the self and the power of the dreaming mind.
3. The Symbolic Journey: Unconscious Desires
The symbolic journey in dream analysis is a fascinating exploration of the dreamer’s unconscious desires. Dreams often present themselves as metaphoric narratives or symbolic representations that can offer deep insights into one’s hidden desires, fears, and unresolved conflicts. Through the cognitive approach, we can unravel the layers of symbolism embedded in these dreams and unearth their underlying meanings. The symbolic journey can take various forms, such as embarking on a quest, traveling through different landscapes, or encountering enigmatic characters. Each element in the dream holds significance and represents aspects of the dreamer’s psyche. For example, dreaming of a long and treacherous journey might mirror the dreamer’s personal struggles or aspirations. Similarly, encountering certain symbols, like a locked door or an unreachable destination, can symbolize obstacles or unattainable goals in one’s waking life. By delving into the symbolic journey within dreams, we gain access to the realm of the unconscious and gain valuable insights into our deepest desires and motivations. Understanding these unconscious desires can help individuals gain self-awareness and work towards personal growth and fulfillment.
Common Challenges of Dream Interpretation
Interpreting dreams is a fascinating endeavor, but it comes with its fair share of challenges. One common challenge in dream interpretation is the subjectivity and personal context of dreams. Dreams are deeply personal experiences, influenced by an individual’s unique life circumstances, beliefs, and emotions. This subjectivity makes it essential to consider the dreamer’s personal experiences and perspective when deciphering dream symbols and meanings. Another challenge is the symbolic ambiguity often present in dreams. Symbols in dreams can have multiple interpretations, making it difficult to pinpoint a definitive meaning. Dream symbols can also vary in significance across different cultures, adding another layer of complexity. Lastly, cultural variations pose a challenge in dream interpretation. Cultural beliefs and symbols can significantly influence dream content, requiring an understanding of cultural contexts to accurately interpret dreams. Despite these challenges, with careful analysis and understanding, dream interpretation can provide valuable insights into the inner workings of the mind.
1. Subjectivity and Personal Context
Subjectivity and personal context are common challenges encountered when analyzing dreams. Due to the highly individual nature of dreams, their interpretation is subjective and influenced by the dreamer’s personal experiences, beliefs, and emotions. Each person has unique associations with symbols and events, which can greatly impact the meaning and significance attributed to their dreams. What may be seen as a positive symbol for one person could hold a negative connotation for another. For example, dreaming about snakes might be interpreted as a symbol of transformation and renewal in one cultural context, while in another culture, it may represent danger and deceit. The interpretation of a dream also depends on the dreamer’s personal experiences and memories. A person with a fear of heights may interpret a dream about falling quite differently than someone who enjoys bungee jumping. It is crucial to consider the subjectivity and personal context of the dreamer when analyzing their dreams. By taking into account the individual’s unique background and experiences, dream interpretations can be more accurate and meaningful.
2. Symbolic Ambiguity
2. Symbolic Ambiguity
Symbolic ambiguity is a common challenge faced in the interpretation of dreams. Dreams often contain symbols that have multiple possible meanings, making it difficult to determine the exact significance intended by the dreamer’s subconscious. The same symbol can hold different interpretations based on personal experiences, cultural context, and individual associations. For example, water can symbolize purification and renewal for some, while representing uncertainty and emotional turmoil for others. This ambiguity requires dream analysts to approach dream interpretation with caution and open-mindedness. It is crucial to consider the dreamer’s personal background, beliefs, and emotions to uncover the most accurate interpretation.
To navigate through symbolic ambiguity, dream analysts often rely on various techniques. One such technique is free association, where the dreamer is encouraged to brainstorm and express their immediate thoughts and feelings related to the dream symbols. This can provide valuable insights and help unravel the personal meanings attached to ambiguous symbols. Another technique is maintaining a dream journal, which allows the dreamer to record recurring symbols and themes over time. By analyzing patterns and connections between symbols, analysts can gain a deeper understanding of the dreamer’s unique symbolic language.
In some cases, symbolic ambiguity can become an opportunity for exploration and self-discovery. The rich and diverse interpretations of dreams allow for introspection and the exploration of different layers of meaning. Dream analysts must acknowledge that dreams are highly personal and that the true interpretation lies within the dreamer’s subjective experience. By embracing the ambiguity and using it as a catalyst for discussion and reflection, analysts can uncover profound insights and facilitate personal growth.
Symbolic ambiguity poses a challenge in dream interpretation as symbols often hold multiple meanings. Dream analysts must approach these symbols with an open mind, considering personal experiences, cultural context, and individual associations. Techniques such as free association and maintaining a dream journal can assist in navigating through the complexity of symbolic ambiguity, leading to a more accurate understanding of the dreamer’s subconscious. Embracing the ambiguity allows for exploration and self-discovery, fostering personal growth and deeper insights into the intricacies of the dreaming mind.
3. Cultural Variations
Cultural variations play a significant role in dream interpretation and analysis. Different cultures have unique beliefs, values, and symbols that can significantly influence the meaning and interpretation of dreams. The cultural context in which an individual grows up shapes their understanding and perception of the world, including their dreams. The symbolism and significance attached to certain dream elements can vary widely across cultures. For example, while snakes are often associated with danger and deceit in Western cultures, they are revered as symbols of wisdom and fertility in some Indigenous cultures. Similarly, the interpretation of colors, animals, and even specific actions can vary greatly depending on cultural beliefs and traditions. It is vital to consider these cultural variations when analyzing dreams, as they provide important context for understanding the dreamer’s experiences and perspectives. By taking into account cultural influences, dream analysts can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the dreams and their significance for the dreamer.
Conclusion
In conclusion, analyzing dreams through the cognitive approach provides valuable insights into the workings of the mind during sleep. By understanding the cognitive processes involved in dream formation, such as perception, memory, and reasoning, we can unlock the hidden meanings and symbolism behind our dreams. The cognitive approach highlights the idea that dreams are not random or meaningless, but rather reflect our beliefs, experiences, and emotions. Techniques like content analysis, psychoanalysis, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) offer different approaches to interpreting dreams and gaining a deeper understanding of ourselves. Common dream symbols, such as falling, flying, being chased, and teeth falling out, can be decoded using the principles of cognitive dream analysis. While dream interpretation can present challenges due to subjectivity, symbolic ambiguity, and cultural variations, the cognitive approach provides a structured framework to navigate these complexities. Studying dreams from a cognitive perspective allows us to explore the depths of our subconscious and gain valuable insights into our thoughts, emotions, and desires. So, continue your journey of self-discovery by analyzing your dreams through the cognitive approach and unraveling the fascinating mysteries of the mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can dreams be analyzed using scientific methods?
Yes, dreams can be analyzed using scientific methods, including the cognitive approach. Researchers employ various techniques and theories to examine the cognitive processes involved in dream formation and interpret the meanings behind them.
2. Are all dreams symbolic?
No, not all dreams are purely symbolic. While symbolism is often present in dreams, some dreams may reflect more literal experiences or events from the dreamer’s daily life.
3. Can analyzing dreams help with self-discovery?
Absolutely. Analyzing dreams can provide valuable insights into one’s thoughts, emotions, and desires, offering a deeper understanding of oneself and facilitating personal growth and self-discovery.
4. Is dream analysis only useful for psychological purposes?
No, dream analysis can be beneficial for various purposes. In addition to psychological insights, analyzing dreams can aid in problem-solving, idea generation, and creative inspiration.
5. Can dreams provide solutions to real-life problems?
While dreams cannot offer direct solutions to real-life problems, they can provide subconscious perspectives and alternative viewpoints that may inspire new approaches or ideas for problem-solving.
6. Are dream interpretations universal or subjective?
Dream interpretations can be both universal and subjective. Some symbols and themes may have collective meanings across cultures, while others can be highly subjective, influenced by personal experiences and cultural backgrounds.
7. Can dreams predict the future?
Dreams are not reliable predictors of the future. They are a reflection of our current thoughts, emotions, and experiences rather than premonitions or prophetic visions.
8. Can recurring dreams have specific meanings?
Recurring dreams often indicate unresolved issues, worries, or emotions that the dreamer needs to address. Analyzing the patterns and themes in recurring dreams can provide valuable insights into underlying concerns.
9. Can external factors influence dream content?
Absolutely. External factors such as stress, daily experiences, and environmental stimuli can influence dream content. These factors can shape the symbols and scenarios that appear in dreams.
10. Is it possible to control or manipulate dreams?
Yes, it is possible to develop techniques for controlling or manipulating dreams. Practices like lucid dreaming, where the dreamer becomes aware within a dream, allow individuals to consciously influence and navigate their dreams.