For many of us, nights can be fraught with strange, haunting visions that disrupt the serene peace of sleep. But what are these terrifying experiences, and why do they occur? To unravel the science behind nightmares, we must delve into the enigmatic world of REM sleep. This deep slumber state is characterized by rapid eye movement, vivid dreams, and intricate brain activity that remains elusive to comprehension. By exploring the intricate processes that occur during REM sleep and understanding the implications of nightmares, we can gain valuable insights into the inner workings of our minds. So, prepare to embark on a mysterious journey as we uncover the secrets behind these unsettling nocturnal experiences.
The Basics of REM Sleep
REM sleep, short for rapid eye movement sleep, is a fascinating and essential stage of the sleep cycle. During this stage, our eyes move rapidly beneath our closed eyelids as if following the images of our dreams. The brain becomes highly active, almost as active as when we’re awake. It is during REM sleep that we experience the most vivid and memorable dreams. This stage typically occurs multiple times throughout the night, with each cycle lasting about 90-120 minutes. REM sleep is just one of the several stages of sleep, which also include non-REM stages. Within non-REM sleep, there are different levels of depth, from light to deep sleep, which play a crucial role in our overall sleep quality. However, it is during REM sleep that our dreams take center stage, capturing our minds with a myriad of colorful and sometimes unsettling scenarios. These dreams can be influenced by various factors, including daily experiences, emotions, and even our subconscious fears. Whether it’s facing common nightmare themes like falling or being chased, or unique scenarios that leave us pondering their meaning, the dreams we experience during REM sleep have a significant impact on our well-being. To comprehend the mysteries of nightmares and their effects on our daily lives, we must first unravel the science behind REM sleep and its connection to our dreamscapes.
1. Defining REM Sleep
Defining REM sleep is key to understanding its role in our sleep cycle. REM, or rapid eye movement, sleep is a stage characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and vivid dreaming. It is named after the distinctive eye movements that occur during this phase. During REM sleep, our muscles are in a state of temporary paralysis, likely as a protective measure to prevent us from physically acting out our dreams. This stage is also associated with other physiological changes, such as increased heart rate and irregular breathing. As mentioned earlier, REM sleep occurs multiple times throughout the night, with each cycle lasting about 90-120 minutes. It is important to note that REM sleep is just one component of the sleep cycle, and each stage plays a unique role in our overall sleep architecture. Understanding the characteristics of REM sleep allows us to delve into the fascinating world of dreams and their impact on our well-being. Whether we find ourselves embarking on thrilling adventures or facing common nightmare themes like being chased or falling, the dreams experienced during REM sleep offer vital insights into our subconscious mind. So, let us explore further as we unravel the science behind REM sleep and its intriguing connection to our dreamscapes.
2. Stages of Sleep
In order to understand the intricacies of REM sleep, it’s important to familiarize ourselves with the various stages of sleep. Sleep can be roughly divided into two main categories: REM (rapid eye movement) and non-REM sleep. Non-REM sleep is further divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3.
N1, also known as light sleep, occurs when we first drift off into slumber. During this stage, our brain transitions from wakefulness to sleep, and our muscles begin to relax. It is common to experience brief and fleeting dreams or thoughts during N1, but they are typically not as vivid or memorable as those experienced during REM sleep.
N2, the second stage of non-REM sleep, is characterized by a deeper level of sleep. Our brain waves slow down, and our body temperature drops. This stage makes up a significant portion of our overall sleep time and plays a crucial role in recharging our bodies and minds.
N3, also known as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep, is the stage where our body undergoes restorative processes. Our brain waves slow down even further, and it becomes challenging to wake us up. During this stage, our body repairs tissues, boosts the immune system, and releases growth hormones.
Finally, we reach REM sleep, which is often associated with the most vivid and memorable dreams. REM sleep typically occurs after cycling through the N1, N2, and N3 stages. It is characterized by increased brain activity, rapid eye movement, and temporary paralysis of our voluntary muscles. REM sleep is essential for cognitive function, learning, and emotional processing.
Understanding the different stages of sleep helps us comprehend the significance of REM sleep and its role in the grand scheme of our sleep cycles. Each stage serves a unique purpose and contributes to our overall well-being and mental health. Whether it’s the subtle flickers of dreams in N1 or the intense emotional landscapes of REM sleep, the stages of sleep work in harmony to ensure we have restful and rejuvenating nights. For tips on preventing nightmares and promoting restful sleep, you may find this guide helpful.
3. The Role of REM Sleep
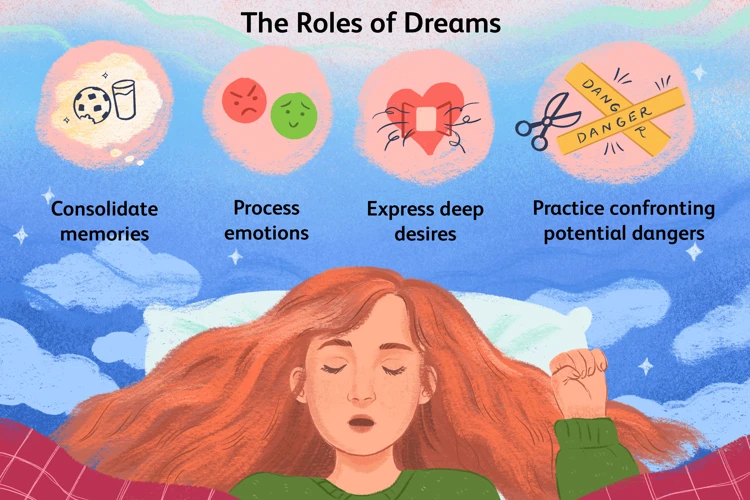
The role of REM sleep goes beyond just providing us with vivid dreams. It plays a vital role in various aspects of our physical and cognitive well-being. One significant function of REM sleep is memory consolidation. During this stage, the brain processes and consolidates information we’ve learned throughout the day, helping to solidify memories and improve our ability to retain information. Research shows that REM sleep specifically enhances the consolidation of emotionally charged memories, leading to a greater emotional understanding and resilience. Additionally, REM sleep is believed to be crucial for emotional regulation. It helps regulate and balance our emotions by facilitating the processing and integration of emotional experiences from the day. This explains why emotions are often a central aspect of our dreams during REM sleep. Nightmares, in particular, can serve as a way for our minds to process and confront fears, anxieties, and unresolved emotions. By exploring common nightmare themes, such as being chased or falling (/common-nightmare-dream-themes/), we can gain insight into the underlying emotional challenges we might be facing. Understanding the role of REM sleep and its impact on our emotional well-being (/nightmare-dreams-impact-on-well-being/) allows us to appreciate the importance of nurturing healthy sleep habits and effectively managing our dreamscape.
4. REM Sleep and Dreams
REM sleep and dreams are deeply intertwined, with REM sleep being the stage where dreams are most vivid and memorable. Dreams during REM sleep can range from mundane to fantastical, and their content can be influenced by multiple factors. This stage is characterized by intense brain activity, similar to when we are awake. The brain’s emotional and memory centers, such as the amygdala and hippocampus, play a significant role in shaping the content of dreams during REM sleep. In fact, studies have shown that emotional experiences from the previous day can influence the emotional themes of dreams. Additionally, REM sleep allows the brain to process and consolidate memories, helping us make sense of the events and information we have encountered. Dreams may serve as a simulation or rehearsal of real-life situations, enabling us to practice and prepare for different scenarios. This may explain why we sometimes dream about situations that we have experienced or situations that we fear. Understanding the intricate connection between REM sleep and dreams is crucial in unraveling the mysteries of our subconscious mind and gaining insights into our emotions, thoughts, and fears. By exploring the science behind REM sleep and the dynamics of dreaming, we can begin to comprehend the complex relationship between our sleeping minds and the vivid experiences that unfold within them.
Unraveling the Mystery of Nightmares

Nightmares, those dark and unsettling dreams that can send chills down our spines, have fascinated and perplexed us for centuries. Understanding nightmares is essential for unraveling the intricate workings of our subconscious minds. These vivid and distressing dreams often involve experiencing intense fear, anxiety, or a sense of impending doom. Although nightmares can occur during any stage of sleep, they are most commonly associated with REM sleep. REM sleep is believed to play a crucial role in the consolidation of memories and emotional processing, which may explain why nightmares are more prevalent during this stage. To truly grasp the mystery of nightmares, we must explore the brain’s involvement in their creation. The amygdala, a key player in processing emotions, becomes highly active during REM sleep, potentially contributing to the intensity of nightmares. Additionally, the activation of the prefrontal cortex, responsible for logical thinking and decision-making, is diminished during this stage, leading to a more unbridled and chaotic dream experience. As we delve deeper into the psychological aspects of nightmares, it becomes clear that they can provide a window into our deepest fears, anxieties, and unresolved traumas. Unraveling the mystery of nightmares entails not only understanding their neurological and emotional underpinnings but also exploring the influence of trauma on these haunting dreams. Studying the frequency and content of nightmares can offer valuable insights into the effects of trauma on our subconscious mind. Whether it involves reliving past traumatic experiences or serving as a coping mechanism, nightmares can be both an unsettling and powerful manifestation of our innermost struggles. By unraveling the mystery of nightmares, we can gain a deeper understanding of the human psyche and potentially identify ways to cope with and overcome their disruptive effects on our psychological well-being.
1. Understanding Nightmares
Understanding nightmares is a crucial step in unraveling the science behind these haunting nighttime experiences. Nightmares are vivid, distressing dreams that often evoke intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, or sadness. They can wake us up abruptly, leaving us feeling unsettled and disturbed. While nightmares can occur at any age, they are most common in children and tend to decrease in frequency as we reach adulthood. The content of nightmares can vary widely, and each individual may have their own unique recurring themes. Common nightmare themes include being chased or attacked, falling from great heights, being trapped or paralyzed, or experiencing the loss of loved ones. Nightmares can stem from a variety of factors, including stress, trauma, anxiety, medication side effects, or even certain sleep disorders. They can also be influenced by our daily experiences and emotions. Understanding the underlying causes and triggers of nightmares is essential in developing effective coping strategies and promoting restful sleep.
2. The Brain’s Involvement
2. The Brain’s Involvement:
When it comes to the realm of dreams and nightmares, the brain takes center stage as the main actor in this nocturnal production. During REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active, with various regions working together to create the rich tapestry of our dreams. One key area involved is the amygdala, which plays a central role in processing emotions. This region becomes particularly active during REM sleep, leading to the intense emotional experiences often felt in dreams. Additionally, the hippocampus is responsible for memory consolidation, and it also plays a crucial role during REM sleep, linking fragments of memories together to form dream narratives. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for logical reasoning and decision-making, is relatively less active during REM sleep, which may help explain why dreams often defy logical boundaries. Other areas of the brain, such as the visual cortex and motor cortex, also contribute to the vivid imagery and movements experienced during dreams. As the brain orchestrates these complex processes, it weaves together fragments of memories, emotions, and perceptions to create the sometimes bizarre and surreal landscapes of our dreams. Through its intricate involvement, the brain unlocks the door to the realm of dreams, inviting us into a world of endless possibilities and untamed imagination.
3. Emotional Processing in Dreams
Emotional processing in dreams is a remarkable aspect of REM sleep that offers a glimpse into the depths of our psyche. During this stage, our brains actively engage in the processing and integration of emotions that we experience while awake. Dreams serve as a platform for the exploration and examination of these emotions, allowing us to confront and make sense of our feelings on a subconscious level. This emotional processing can be incredibly vivid and impactful, as dreams have the ability to evoke intense emotions such as fear, joy, sadness, and even love. Interestingly, research has shown that the emotional content of dreams mirrors our waking life experiences, with emotionally challenging or traumatic events often manifesting in distorted or symbolic ways. This suggests that dream experiences serve a vital function in regulating and managing our emotional well-being. By allowing us to process and confront emotions in the safety of our dreams, REM sleep plays a critical role in maintaining our psychological equilibrium. Understanding the intricate relationship between emotions and dreams can provide valuable insights into our own mental and emotional states. It can help us unravel the hidden complexities of our minds and foster a deeper understanding of ourselves. To learn more about how emotional processing unfolds in dreams and its profound impact on our overall well-being, we can delve further into the science behind REM sleep and the mysteries it holds within.
4. Trauma and Nightmares
Trauma can leave a deep and lasting impact on our psychological well-being, and nightmares can often be a manifestation of that impact. Those who have experienced trauma, such as physical or emotional abuse, accidents, or combat exposure, are more likely to suffer from nightmares. The nightmares may replay the traumatic event or incorporate elements from the experience. These distressing dreams can intensify feelings of fear, anxiety, and helplessness, leading to disrupted sleep and impaired daytime functioning. Trauma-related nightmares can be highly vivid, evoking strong emotions and physical sensations. They can be so distressing that individuals may develop a fear of falling asleep or experiencing these nightmares, leading to further sleep disturbances. It is important to note that nightmares alone are not indicative of trauma, as they can occur for other reasons as well. However, when nightmares are accompanied by other symptoms of trauma, such as flashbacks, avoidance behaviors, and hyperarousal, seeking professional help and support becomes crucial. Therapy modalities such as trauma-focused therapy and cognitive-behavioral therapy for nightmares can help individuals process and cope with traumatic events, reducing the frequency and intensity of trauma-related nightmares.
The Biological Processes at Play

Understanding the biological processes at play during REM sleep and nightmares can shed light on the intricate workings of our minds. During REM sleep, the brain experiences neural activation, with certain areas becoming highly active while others exhibit decreased activity. This neural activation is crucial for the formation and recall of dreams. The amygdala, known for its role in processing emotions, becomes hyperactive during REM sleep, leading to intense emotional experiences in dreams. Additionally, the prefrontal cortex, responsible for logical thinking and decision-making, shows reduced activity during REM sleep, which may explain the irrational and bizarre nature of dreams. Research suggests that nightmares serve a purpose in emotional processing, allowing the brain to consolidate and make sense of distressing experiences. By replaying and confronting threatening scenarios in dreams, the brain can potentially desensitize itself to fear and reduce anxiety in waking life. However, for some individuals, nightmares can become excessive, leading to nightmare disorders or other sleep disturbances. These conditions may require further intervention and treatment. Understanding the biological processes involved in REM sleep and nightmares provides valuable insights into the complex relationship between our dreams and mental well-being. By comprehending these processes, we can potentially develop strategies to manage nightmares and enhance the quality of our sleep.
1. Neural Activation during REM Sleep
During REM sleep, a remarkable process unfolds within the brain, characterized by intense neural activation. Studies have shown that the brain’s activity during this stage closely resembles the patterns observed while we are awake. The neocortex, which is responsible for higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception and thought processes, becomes highly active during REM sleep. This heightened neural activity is believed to be the reason behind the vivid and detailed nature of our dreams. Another notable aspect of REM sleep is the inhibition of the motor neurons in the brainstem. This temporary paralysis prevents us from acting out our dreams, ensuring that we stay safe and immobile during this active sleep stage. It is worth noting that this inhibition does not extend to all muscles. Essential muscles responsible for vital functions like respiration and eye movement remain active, explaining the rapid eye movements that give REM sleep its name. This intricate interplay of neural activity and muscular inhibition during REM sleep is crucial for maintaining a harmonious balance between an immersive dream world and the physical safety of our bodies.
2. The Function of Nightmares
The Function of Nightmares:
1. Emotional Release: Nightmares may serve as a mechanism for emotional release and processing. When we experience intense emotions such as fear or anxiety during a nightmare, our brain is actively working to process and understand these emotions. This can help us cope with challenging experiences or repressed emotions that we may not be addressing in our waking lives.
2. Threat Simulation: Nightmares may also have an evolutionary purpose of simulating threatening situations to prepare us for potential dangers in real life. By experiencing these distressing scenarios in our dreams, our brain can rehearse how to react and potentially develop strategies to overcome similar threats in waking life.
3. Memory Consolidation: Research suggests that nightmares play a role in memory consolidation. During REM sleep, our brain consolidates and stores memories, helping us retain important information. Nightmares may enhance this process by prioritizing emotionally charged memories and improving our ability to recall and learn from them.
4. Problem Solving: Nightmares can act as a channel for problem-solving and creativity. Some individuals report having nightmares that ultimately help them find solutions to real-life challenges. These dream experiences force the brain to think outside the box and approach difficult situations from different angles.
5. Symbolic Communication: Nightmares often contain symbolic elements that can represent deeper meanings or psychological conflicts. Analyzing and interpreting these symbols can provide insights into our subconscious thoughts, desires, and fears, allowing us to gain a better understanding of ourselves.
While nightmares can be distressing, understanding their potential functions can help us contextualize these experiences. Recognizing the underlying purposes of nightmares can encourage us to explore their meanings and extract valuable insights from our dreamscapes. By embracing and actively engaging with our nightmares, we have the opportunity to leverage their benefits for personal growth and self-discovery.
3. Nightmare Disorders and Sleep Disorders
Nightmare disorders and sleep disorders often go hand in hand, as disturbed sleep patterns can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares and vice versa. When nightmares become frequent and significantly disrupt a person’s sleep and overall well-being, they may be diagnosed with a nightmare disorder. Nightmare disorders are characterized by recurring and distressing dreams that lead to significant distress or impairment during waking hours. These nightmares often evoke intense emotions such as fear, anxiety, or sadness. Sleep disorders, on the other hand, refer to disruptions in the normal sleep pattern. Conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and narcolepsy can disrupt the sleep cycle and increase the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Additionally, there is a bidirectional relationship between trauma and nightmares. Trauma can lead to nightmares, and nightmares can exacerbate symptoms of trauma-related disorders such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Understanding the complex interplay between nightmare disorders and sleep disorders is crucial in diagnosing and treating individuals who suffer from disrupted sleep patterns and frequent nightmares. By addressing the underlying sleep issues and employing therapeutic interventions, individuals can find relief from both the distressing dreams and the sleep disturbances that often accompany them. Making sleep a priority and seeking professional help when needed can significantly improve the quality of life for those struggling with nightmare disorders and sleep disorders.
Managing Nightmares and Enhancing Sleep
Nightmares can be distressing and disrupt our overall sleep quality, impacting our well-being and daily functioning. Fortunately, there are strategies available to help manage nightmares and promote restful sleep. Here are some tips:
1. Coping Strategies for Nightmares:
- Journaling: Keeping a dream journal can help gain insights into recurring themes or triggers of nightmares. Writing down the details of your dreams can also provide a sense of relief and validation.
- Imagery Rehearsal Therapy: This technique involves rewriting the script of your nightmare. By actively imagining a more positive and empowering ending, you can gradually modify the content of your dreams.
- Relaxation Techniques: Practicing relaxation exercises such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation before bed can help alleviate anxiety and promote calmness, reducing the likelihood of nightmares.
- Seeking Support: Speaking with a therapist or joining a support group can provide a safe space to discuss your nightmares and receive guidance in managing them effectively.
2. Promoting Healthy Sleep Habits:
- Establishing a bedtime routine: Engaging in relaxing activities before bed, such as reading a book or taking a warm bath, signals to your body that it’s time to wind down and prepare for sleep.
- Create a sleep-friendly environment: Ensure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding and invest in a supportive mattress and pillows.
- Avoid stimulants: Limit or avoid caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol, especially close to bedtime, as they can disrupt your sleep patterns.
- Stick to a regular sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at consistent times helps regulate your body’s internal clock, optimizing the quality of your sleep.
By implementing these strategies and incorporating healthy sleep habits into your routine, you can manage nightmares more effectively and enhance the overall quality of your sleep. Remember that everyone is unique, and it may take some experimentation to find what works best for you. Persistent nightmares or sleep disturbances should be discussed with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and support. Restful, rejuvenating sleep is within reach, and by taking proactive steps, you can unlock the potential for vibrant and peaceful nights.
1. Coping Strategies for Nightmares
When it comes to coping with nightmares, there are several strategies that can help alleviate the distress and improve overall sleep quality. One effective approach is to establish a relaxing bedtime routine that promotes a sense of calm and serenity before sleep. This can include activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing mindfulness exercises. Additionally, creating a comfortable sleep environment that is free from distractions and promotes relaxation can also contribute to reducing the likelihood of nightmares. Some individuals find it helpful to keep a dream journal by their bedside to record and analyze their dreams, which can provide insights into underlying emotions and themes. Another coping strategy is practicing lucid dreaming, where individuals develop the ability to be aware that they are dreaming and can exert control over the dream content. While this may not completely eliminate nightmares, it empowers individuals to actively steer the dream in a more positive direction. Seeking support from a therapist or counselor who specializes in sleep disorders and nightmares can also be beneficial. They can provide guidance, techniques, and cognitive-behavioral therapy to address fears and anxieties that may be contributing to nightmares. Additionally, implementing stress management techniques, such as regular exercise, meditation, and relaxation exercises, can help reduce overall stress levels and improve sleep quality. By adopting these coping strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing and reducing the impact of nightmares, ultimately leading to restful and rejuvenating sleep.
2. Promoting Healthy Sleep Habits
Promoting healthy sleep habits is crucial for achieving restful nights and minimizing the occurrence of nightmares. Here are some strategies that can help:
1. Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Establishing a regular sleep routine helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and maintain quality sleep. Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
3. Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment: Make your bedroom a sanctuary for sleep. Ensure the room is cool, dark, and quiet. Use blackout curtains or a sleep mask to block out any intrusive light, earplugs or a white noise machine to drown out noise, and a comfortable mattress and pillows for optimal comfort.
4. Limit Exposure to Stimulating Factors: Avoid consuming caffeine, nicotine, and alcohol close to bedtime as they can disrupt sleep patterns. Additionally, limit exposure to electronic devices, such as smartphones and tablets, as the blue light emitted by these devices can interfere with the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
5. Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise can improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety and stress levels, which can contribute to nightmares. However, it’s best to complete workouts at least a few hours before bedtime to allow your body to wind down.
6. Manage Stress and Anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can disrupt sleep and increase the likelihood of nightmares. Incorporate stress-management techniques into your daily life, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from a therapist or counselor.
By implementing these strategies and prioritizing healthy sleep habits, you can pave the way for restful nights and minimize the potential for nightmares. Remember, everyone’s sleep needs and preferences vary, so it may take some trial and error to find what works best for you.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the science behind nightmares and the role of REM sleep can provide valuable insights into the complexity of our sleep and dream cycles. REM sleep, characterized by rapid eye movement, vivid dreams, and heightened brain activity, is a crucial stage of the sleep cycle. It is during this stage that we experience the most memorable and often unsettling dreams. Nightmares, which can be influenced by various factors such as emotions, daily experiences, and even trauma, have a significant impact on our overall well-being. By delving into the biological processes at play, such as neural activation during REM sleep and the function of nightmares, we gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind these disturbing dreamscapes. Additionally, managing nightmares and promoting healthy sleep habits can help alleviate their frequency and intensity, leading to a more restful and rejuvenating sleep. Ultimately, by unraveling the mysteries behind nightmares and REM sleep, we can equip ourselves with the knowledge and strategies needed to enhance our sleep quality and overall mental well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does REM stand for?
REM stands for rapid eye movement, which is a stage of sleep characterized by rapid movement of the eyes beneath closed eyelids.
2. How long does REM sleep last?
A typical REM sleep cycle lasts around 90-120 minutes and may occur multiple times throughout the night.
3. Why is REM sleep important?
REM sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, learning, emotional processing, and overall cognitive function.
4. Can you dream during non-REM sleep?
While dreams can occur during non-REM sleep, they are typically less vivid and memorable compared to those experienced in REM sleep.
5. What happens to our body during REM sleep?
During REM sleep, our muscles become temporarily paralyzed, preventing us from acting out our dreams and potentially causing harm to ourselves or others.
6. Do all animals experience REM sleep?
Most mammals, including humans, experience REM sleep. However, the duration and frequency of REM sleep may vary among different species.
7. Are nightmares a normal part of REM sleep?
Yes, nightmares are a common occurrence during REM sleep. They can be triggered by various factors, including stress, trauma, and underlying emotional issues.
8. Can nightmares have long-term effects on our well-being?
Yes, frequent nightmares or intense, disturbing dreams can impact our well-being, leading to issues such as disrupted sleep, anxiety, and decreased quality of life.
9. Are there any ways to prevent or reduce nightmares?
While it may be challenging to completely prevent nightmares, practicing relaxation techniques, maintaining a healthy sleep routine, and addressing underlying psychological issues can help reduce the frequency and intensity of nightmares.
10. Can nightmares be a symptom of a sleep disorder?
Yes, persistent nightmares that significantly disrupt sleep and cause distress can be a symptom of nightmare disorder, a type of sleep disorder that requires professional diagnosis and treatment.