The southern hemisphere is adorned with celestial gems that captivate the imagination and awe of stargazers. These magnificent constellations have rich histories, mythology, and symbolism that make them a captivating sight in the night sky. In this article, we take a close look at some of the most beautiful southern constellations, delving into their legends, notable features, and best viewing opportunities. From the iconic Southern Cross to the majestic Centaurus and the colorful Pavo, each constellation has its unique allure. So, let us embark on a journey through the southern skies and explore the wonders that await us.
The Southern Cross
The Southern Cross, also known as Crux, is one of the most iconic and recognizable constellations in the southern hemisphere. This compact and distinctive pattern of stars is steeped in legends and holds significant cultural symbolism for many indigenous cultures in the region. The Southern Cross is composed of four bright stars that form a cross shape, with the fifth star adding to its beauty. Legends and mythology surrounding the constellation vary among different cultures, with stories often associating it with navigation, guidance, and spiritual significance. Notable features of the Southern Cross include its position as a prominent symbol on the flags of several southern hemisphere countries, including Australia and New Zealand. It is also a helpful navigational tool, pointing towards the South Celestial Pole, making it a useful guide for observers in the southern hemisphere. To explore more about the mythology and symbolism behind the Southern Cross, you can visit the mythology of southern constellations down under.
1. Legends and Mythology
Legends and mythology surrounding the Southern Cross have captivated cultures throughout history. In Australian Aboriginal Dreamtime stories, the Southern Cross represents an old woman, and the four brighter stars are her daughters who are being chased by a man represented by the fifth star. In Māori mythology, the constellation is known as “Te Punga” and is associated with a celestial anchor that connects the sky to the land. It is believed that once the anchor is lowered, it can be used as a means to ascend to the heavens. The Tupi people of Brazil have a different interpretation, seeing the Southern Cross as a celestial bird who acts as a guide to the Sun at sunrise. These captivating legends highlight the cultural diversity and rich symbolism associated with the Southern Cross. To delve deeper into the fascinating world of southern constellations and their mythology, you can explore the resource on exploring southern sky constellations.
2. Notable Features
Notable features of the Southern Cross constellation are what make it a standout in the night sky. Firstly, the four main stars that form the cross shape are remarkably bright and easily visible, even in urban areas with moderate light pollution. These stars, known as Alpha, Beta, Gamma, and Delta Crucis, are all hot and massive blue stars, adding to the dazzling display of the constellation. The fifth star, known as Epsilon Crucis, is slightly fainter but still adds to the beauty of the cross shape. Another notable feature of the Southern Cross is its significance in celestial navigation. By drawing an imaginary line from the long axis of the cross to the South Celestial Pole, one can determine true south. This makes the Southern Cross an essential guide for sailors, pilots, and navigators in the southern hemisphere. To further delve into the awe-inspiring patterns of the night sky, you can explore the breathtaking starry cosmos via the unveiling of southern star patterns.
3. Viewing Tips
To enhance your viewing experience of the Southern Cross, here are some helpful tips to keep in mind. Firstly, finding a location with minimal light pollution is crucial for optimal visibility. Look for areas away from city lights and try to choose a clear night with minimal cloud cover. Once you’ve found a suitable spot, give your eyes some time to adjust to the darkness. This process, known as dark adaptation, allows you to see fainter stars more clearly. It usually takes around 20-30 minutes for your eyes to fully adjust. Once your eyes have adapted, look towards the southern sky to locate the Southern Cross. The constellation can be found relatively low on the horizon for observers in southern latitudes, so make sure to have a wide, unobstructed view. The Southern Cross is an excellent guide to finding the South Celestial Pole, which is near the star Sigma Octantis. By drawing an imaginary line through the long axis of the cross and extending it roughly four to five times its length, you can locate the Southern Celestial Pole. This will help you orient yourself to the southern skies and explore other constellations in the region. Remember to pack warm clothing, a comfortable chair or blanket, and perhaps a star chart or mobile app to assist you in identifying other celestial objects. With these tips in mind, you are ready to embark on your journey to admire the splendor of the Southern Cross and the other stunning celestial sights of the southern hemisphere.
Orion the Hunter
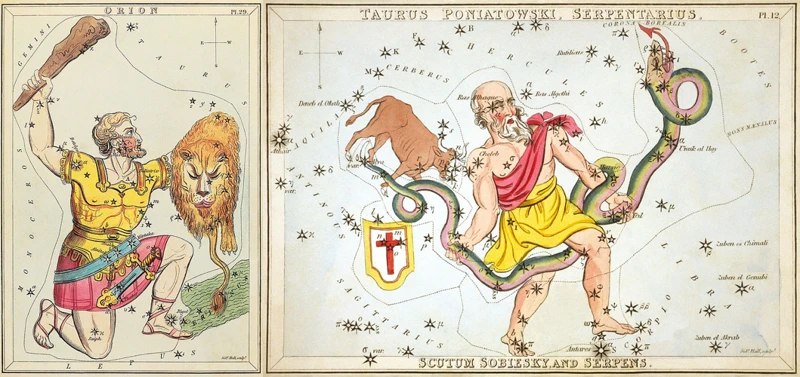
Orion the Hunter is a prominent and captivating constellation that can be observed in both the northern and southern hemispheres, but it is particularly celebrated in the southern skies. Steeped in history and significance, Orion has fascinated cultures throughout the ages. This constellation is named after Orion, a mighty hunter from Greek mythology. A standout feature of Orion is the group of three bright stars that form Orion’s Belt, which is unmistakable in the night sky. Other notable features of Orion include the brilliant star Betelgeuse, known for its distinct reddish color, and the stunning Orion Nebula, a celestial cloud of gas and dust where new stars are born. Observing Orion in the night sky is a delight for stargazers, as it provides a treasure trove of celestial wonders to explore. Whether you spot it in the northern or southern hemisphere, Orion’s charm and splendor will leave you in awe. If you’re interested in exploring more about the southern sky constellations, you can read our article on exploring southern sky constellations.
1. History and Significance
The history and significance of Orion the Hunter are deeply rooted in ancient mythology and cultural symbolism. Throughout history, this constellation has been recognized and revered by various civilizations around the world. In Greek mythology, Orion was a mighty hunter and the son of the sea god Poseidon. He was known for his exceptional strength and skill with a bow and arrow. According to the myth, Orion’s story ended tragically when he was stung to death by a Scorpion, represented by the neighboring constellation Scorpius. However, the gods were so impressed by Orion’s abilities and character that they immortalized him in the night sky as a constellation.
The significance of Orion extends beyond Greek mythology. In ancient Egyptian culture, Orion was closely associated with Osiris, the god of the afterlife and resurrection. The alignment of Orion’s belt with the Great Pyramid of Giza has led to speculation that the pyramids were constructed in reference to this sacred constellation.
Orion holds cultural significance in many other societies as well. Indigenous Australian Aboriginal cultures have rich oral traditions and Dreamtime stories that involve Orion. In Māori culture, Orion is known as Te Taura Whiri a Tāne, representing the rope that Tāne Mahuta, the god of forests and birds, used to ascend to the heavens.
Today, Orion remains one of the most easily recognizable constellations in the night sky. Its distinct pattern of three stars in a row, representing Orion’s belt, makes it a popular celestial feature for stargazers. Its visibility in both the northern and southern hemispheres ensures that people all over the world can appreciate its beauty and significance. Whether you’re observing Orion from a dark countryside or a bustling city, its captivating presence continues to inspire wonder and awe in those who gaze upon it.
2. Key Features
The Southern Cross, a constellation of the southern hemisphere, boasts several unique and noteworthy features. One of its standout characteristics is its distinctive shape. Composed of four bright stars that form a cross pattern, with the fifth star adding to its allure, the Southern Cross is instantly recognizable in the night sky. The stars that comprise this constellation are Alpha Crucis, Beta Crucis, Gamma Crucis, Delta Crucis, and Epsilon Crucis. Alpha Crucis, also known as Acrux, is the brightest star in the constellation, while Beta Crucis, also called Mimosa, shines with a vibrant blue-white hue. Gamma Crucis, also known as Gacrux, is an intriguing red giant star that adds a splash of color to the constellation. These stars, along with Epsilon Crucis, create a remarkable visual spectacle that has captivated skywatchers for centuries. By observing these key features, stargazers can appreciate the beauty and significance of the Southern Cross in all its celestial glory.
3. Observing Orion
Observing Orion is a rewarding experience for stargazers in the southern hemisphere. Here are some tips and techniques to enhance your viewing of this magnificent constellation:
– Find a Dark Location: To fully appreciate Orion, it is best to observe from a dark location away from city lights. This will ensure a clearer view of the stars and allow you to see the fainter details of the constellation.
– Look for Orion’s Belt: Orion is most easily identified by its three bright stars that form a straight line, known as Orion’s Belt. These stars, Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka, are an excellent starting point for locating the rest of the constellation.
– Discover Orion’s Sword: Hanging from Orion’s Belt, you will find a fainter group of stars known as Orion’s Sword. This region contains the famous Orion Nebula, a stellar nursery where new stars are born. Using binoculars or a telescope, you can witness the intricate details of this celestial marvel.
– Seek out Betelgeuse and Rigel: Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star that marks Orion’s right shoulder, while Rigel is a bright blue supergiant star that represents his left foot. These stars add a captivating element to the constellation and can be easily spotted.
– Don’t Forget the Surrounding Stars: While Orion’s Belt, Sword, and prominent stars capture much attention, take the time to explore the surrounding stars and the patterns they create. Initiating constellations, such as Taurus the Bull and Canis Major, can be seen in close proximity to Orion.
– Capture the Beauty: Consider photographing Orion to preserve its beauty. With long exposure photography, you can capture stunning images of the constellation and its surroundings, revealing intricate details not visible to the naked eye.
Observing Orion allows us to connect with its rich history, mythology, and the wonders of the universe. So, venture out under the southern skies, armed with these tips, and immerse yourself in the celestial splendor of Orion.
Pavo, the Peacock

Pavo, the Peacock, is a remarkable constellation that graces the southern skies with its colorful brilliance. This celestial gem has its origins in Greek mythology, with its feathers symbolizing the eyes on the tail of the mythical peacock. Pavo is known for its standout characteristics, such as its distinctive shape and vibrant stars that represent the peacock’s feathers. One of the noteworthy features of Pavo is its impressive globular star cluster, NGC 6752, which is one of the brightest in the sky. This cluster adds to the allure of Pavo and makes it a captivating sight for stargazers. To catch a glimpse of Pavo’s splendor, it is best observed from the southern latitudes during the late southern hemisphere winter. So, venture into the southern skies and be mesmerized by the celestial majesty of Pavo, the Peacock.
1. Origins and Symbolism
The origins and symbolism of the constellation Pavo, the Peacock, are fascinating and deeply rooted in ancient mythology. In Greek mythology, the Peacock was associated with the goddess Hera, who placed the magnificent eyes of the bird’s feathers as markings on the peacock. This association with Hera symbolized immortality and the all-seeing eyes of the goddess. The name “Pavo” itself comes from the Latin word for peacock, emphasizing the significance of this celestial bird. In Hindu mythology, the Peacock is associated with the god Kartikeya, who is often depicted riding a peacock. The Peacock constellation also holds significance in indigenous Australian Dreamtime stories, where it is said that the bird’s sparkling feathers represent the creation of the Milky Way. With its graceful shape and bright stars, Pavo is truly a symbol of beauty and divinity in the southern skies. Its mythical origins and various cultural associations make it a compelling constellation to explore and admire.
2. Standout Characteristics
The constellation Pavo, also known as the Peacock, boasts several standout characteristics that make it a captivating sight in the southern hemisphere’s night sky. Here are some notable features of this celestial gem:
1. Brilliant Peacock Star: At the heart of Pavo lies the captivating star known as Peacock. This remarkable star, formally called Alpha Pavonis, is a blue-hued supergiant that shines brightly with its luminosity. Its mesmerizing and vibrant color adds to the allure of the constellation, making it easily recognizable.
2. Distinctive Shape: Pavo is distinctive in its appearance, resembling a majestic peacock with its outstretched tail feathers. The constellation’s main stars form a graceful pattern that loosely resembles the tail feathers of a peacock, symbolizing elegance and beauty.
3. Globular Cluster NGC 6752: Pavo is home to the stunning globular cluster NGC 6752. This cluster contains a multitude of stars that are tightly packed together, creating a dense and mesmerizing appearance. NGC 6752 is one of the brightest and most massive globular clusters visible from Earth, making it a popular target for astronomers and amateur stargazers alike.
4. Southern Pole Perspective: One unique characteristic of Pavo is its proximity to the southern celestial pole. This means that the constellation is visible all year round for observers in the southern hemisphere. Its consistent presence in the night sky provides ample opportunities for stargazers to appreciate its beauty and learn more about its mythology and symbolism.
By exploring the standout characteristics of Pavo, we gain a deeper understanding of the distinctive features that make this constellation a celestial gem in the southern hemisphere. Its brilliant star, distinctive shape, captivating globular cluster, and southern pole perspective all contribute to its allure and make Pavo a must-see constellation for anyone interested in exploring the wonders of the southern skies.
3. Best Viewing Opportunities
Best Viewing Opportunities
When it comes to observing the Southern Cross, there are a few factors to consider for the best viewing opportunities. Here are some tips to enhance your experience:
- Location: The visibility of the Southern Cross depends on your latitude. The further south you are, the higher in the sky it will appear. Southern hemisphere countries like Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, and Chile offer excellent chances of viewing the Southern Cross.
- Time of Year: The Southern Cross is visible year-round in most southern latitudes. However, its orientation in the sky changes throughout the seasons. The best time to observe it is during the Southern Hemisphere’s winter months (June to August) when it is higher in the sky and more prominent.
- Dark Sky: To fully appreciate the beauty of the Southern Cross, it is ideal to find a location away from light pollution. Head to rural areas, national parks, or astronomical observatories for the best dark sky conditions.
- Clear Weather: Look for clear nights with minimal cloud cover to maximize your chances of seeing the Southern Cross. A cloudless sky will provide optimal viewing conditions and allow you to marvel at the constellation’s intricate pattern of stars.
- Use Stellar Apps or Star Charts: To aid in locating the Southern Cross, you can utilize stellar apps or refer to star charts that specifically highlight its position. These resources can help you identify the constellation accurately, especially if you are new to southern hemisphere stargazing.
By considering these factors and following the tips above, you’ll increase your chances of experiencing the Southern Cross in all its celestial glory. So, pack your binoculars or telescope, find a suitable location, and prepare to be mesmerized by this awe-inspiring constellation.
Centaurus, Half-Man Half-Horse
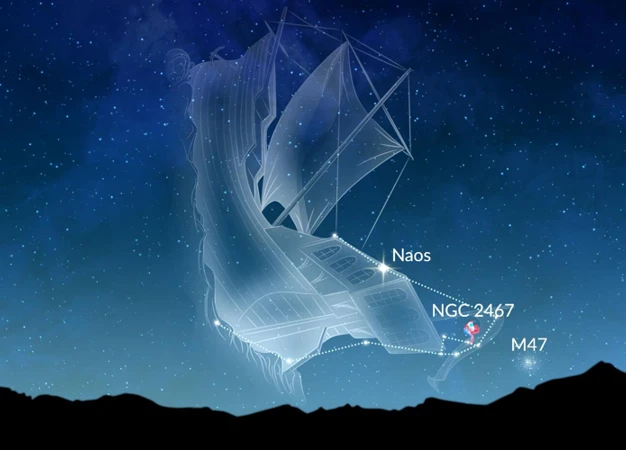
Centaurus, the Half-Man Half-Horse constellation, is a fascinating and mythical figure in the southern skies. In ancient tales and symbols, Centaurus is often associated with Chiron, a wise and renowned centaur known for his expertise in medicine and teaching. The constellation is characterized by its unique blend of both human and equine forms, with the upper half depicting a human torso and the lower half resembling a horse. Fascinating highlights of Centaurus include its position as one of the largest constellations in the night sky, spanning a vast area and hosting a plethora of bright stars, clusters, and nebulae. One standout feature is Alpha Centauri, a triple-star system and the closest star system to Earth after our Sun. Spotting Centaurus in the sky can be an exhilarating experience, especially in regions with minimal light pollution. To learn more about the captivating celestial wonders of the southern hemisphere, you can explore the extensive guide on exploring southern sky constellations.
1. Ancient Tales and Symbols
In ancient tales and symbols, Centaurus, the half-man half-horse constellation, has captured the imaginations of civilizations throughout history. Mythology surrounding this intriguing constellation varies among different cultures, but there are some common threads. In Greek mythology, Centaurus is linked to the story of Chiron, a wise and revered centaur who mentored numerous heroes, including Heracles and Jason. Chiron’s placement in the sky as the constellation Centaurus symbolizes his immortal and enduring wisdom. In some indigenous Australian cultures, Centaurus is associated with the Emu in the Sky. According to their legends, the Emu is a celestial creature that appears during the winter months and influences the time for hunting emus. The distinctive shape of Centaurus, resembling a centaur holding a spear, also evokes different interpretations. Some cultures see it as a hunter, while others associate it with shamanistic figures or divine beings. Centaurus is a constellation steeped in rich symbolism and ancient tales, reflecting the complexities of different cultures and their interpretations of the celestial realm.
2. Fascinating Highlights
– Centaurus, the Half-Man Half-Horse constellation, is not only visually striking but also holds great astronomical significance. One of its most remarkable features is the bright star Alpha Centauri, which is the closest star system to our solar system. It is a triple star system consisting of three stars: Alpha Centauri A, Alpha Centauri B, and Proxima Centauri. Proxima Centauri, the closest of the three, is a red dwarf star and is the nearest star to Earth apart from the Sun. This makes Centaurus a captivating constellation for astronomers and sky enthusiasts alike.
– Another standout characteristic of Centaurus is the presence of a prominent globular cluster, Omega Centauri. This cluster is one of the largest and brightest globular clusters in the Milky Way galaxy, containing millions of stars densely packed together. It is visible to the naked eye, although a pair of binoculars or a small telescope can reveal its dazzling details. The presence of Omega Centauri adds to the allure and fascination of this constellation.
– The mythology and symbolism associated with Centaurus are equally captivating. In Greek mythology, Centaurus is often associated with the legendary figure Chiron, a wise and knowledgeable centaur known for his teaching abilities. Interestingly, Centaurus is also associated with different mythologies from other cultures, such as the Khoikhoi people of Southern Africa, who see it as a celestial reed dance. This diversity of myths and stories connected to Centaurus adds a layer of cultural richness and intrigue to the constellation.
Centaurus is best observed from the southern latitudes, where it can be seen prominently in the night sky during the summer months. Its location near the Southern Cross and the Milky Way makes it an excellent addition to any stargazing session. Whether you are an astronomy enthusiast or simply appreciate the beauty of the night sky, Centaurus with its fascinating highlights is a constellation that promises to leave a lasting impression.
3. Spotting Centaurus in the Sky
Spotting Centaurus in the sky can be an exciting and rewarding experience for stargazers in the southern hemisphere. Here are some tips to help you locate this captivating celestial gem:
1. Timing: Centaurus is best seen during the winter months in the southern hemisphere when it’s highest in the sky. Look for it between late evening and early morning for optimal viewing opportunities.
2. Location: Centaurus is located in the constellation quadrant of the sky that lies between the Southern Cross and Scorpius. Look for its distinctive shape, often described as half-man half-horse, with the bright star Alpha Centauri serving as its head.
3. Guide stars: To spot Centaurus, you can use nearby guide stars as reference points. One helpful technique is to use the two bright stars Alpha and Beta Centauri, also known as Rigil Kentaurus and Hadar respectively. Start by locating these stars and then trace the outline of Centaurus from there.
4. Southern Cross alignment: Another useful method to find Centaurus is by using the alignment of the Southern Cross. Draw an imaginary line connecting the stars of the Southern Cross and extend it in the direction of the Pointers (Alpha and Beta Centauri). This line will guide you towards the general vicinity of Centaurus.
5. Dark sky conditions: As with any stargazing endeavor, finding a location away from city lights and light pollution is crucial for the best viewing experience. Head to a dark and open area with unobstructed views of the southern horizon to maximize your chances of spotting Centaurus.
Remember, patience and persistence are key when it comes to observing constellations. Take your time, allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness, and enjoy the beauty of Centaurus as it reveals itself in the southern sky.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the southern hemisphere presents stargazers with a breathtaking display of celestial gems. From the iconic Southern Cross with its legends and navigational significance, to the majestic Orion the Hunter and its rich history, each constellation holds its own unique allure. The vibrant Pavo, with its origins in mythology and its symbolism, adds a splash of color to the southern skies. And who can forget Centaurus, the half-man half-horse constellation, with its intriguing ancient tales and fascinating highlights. Exploring the southern sky allows us to connect with the wonders of the universe and unravel the mysteries of the cosmos. Whether you’re a seasoned astronomer or a novice stargazer, the southern constellations offer endless opportunities for observation and discovery. So, next time you find yourself gazing up at the night sky, take a moment to appreciate the celestial beauty that the southern hemisphere has to offer.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How did the Southern Cross become a symbol of the southern hemisphere?
The Southern Cross became a symbol of the southern hemisphere due to its visibility in the night sky and its association with navigation. The constellation’s distinctive cross shape has been used in flags, national emblems, and cultural symbols, representing pride, identity, and a connection to the southern skies.
2. Are there any other constellations that can be seen alongside the Southern Cross?
Yes, there are several constellations that can be seen alongside the Southern Cross, including Centaurus, Carina, and Musca. These neighboring constellations add to the celestial beauty of the southern hemisphere and provide stargazers with even more opportunities for exploration.
3. Can the Southern Cross be seen from the Northern Hemisphere?
No, the Southern Cross is primarily visible from latitudes in the southern hemisphere. It is located close to the South Celestial Pole, making it difficult to observe from northern latitudes. However, some parts of the Southern Cross can be glimpsed from certain areas in the northern hemisphere, particularly near the equator.
4. What is the significance of the fifth star in the Southern Cross?
The fifth star in the Southern Cross is known as Epsilon Crucis. While it may not be as bright as the other four stars, it enhances the overall beauty and shape of the constellation. Epsilon Crucis is also used as a reference point for navigational purposes, guiding observers towards the South Celestial Pole.
5. What does the Southern Cross represent in indigenous cultures?
The Southern Cross holds deep cultural significance in various indigenous cultures across the southern hemisphere. It is often associated with stories of creation, navigation, and divine guidance. Different indigenous cultures have their own unique interpretations and mythology surrounding the Southern Cross, adding to its rich cultural tapestry.
6. Can the Southern Cross be seen all year round?
No, the visibility of the Southern Cross depends on the observer’s location and the time of year. In some southern hemisphere countries, such as Australia and New Zealand, the Southern Cross is visible year-round. However, its position in the sky changes throughout the year due to the Earth’s rotation, making it more prominent during certain seasons.
7. How can I find the Southern Cross in the night sky?
Locating the Southern Cross in the night sky can be relatively easy. One method is to use the two pointer stars, Alpha Centauri and Beta Centauri, in the neighboring Centaurus constellation. These two stars can lead you to the Southern Cross, which is located nearby. Additionally, there are several stargazing apps and resources available that can help you identify and locate the Southern Cross.
8. Is the Southern Cross visible from all countries in the southern hemisphere?
Yes, the Southern Cross can be seen from all countries in the southern hemisphere, to varying degrees of visibility depending on the observer’s location. However, the further south you are, the higher the Southern Cross will be in the sky and the more prominent it will appear.
9. Can you spot the Southern Cross from Antarctica?
Yes, the Southern Cross is visible from Antarctica, as it lies within the southern polar region. Due to the remote and largely uninhabited nature of Antarctica, the Southern Cross can be observed with exceptional clarity and brightness, free from the light pollution commonly found in more populated areas.
10. Are there any significant events or festivals associated with the Southern Cross?
Yes, there are several events and festivals that celebrate the Southern Cross and the southern hemisphere’s celestial wonders. For example, in Australia, the Southern Cross is honored during the National Flag Day on September 3rd. Additionally, various stargazing festivals and astronomy events take place throughout the year, providing opportunities for people to connect with and learn more about the wonders of the night sky.