The ancient origins of the zodiac have fascinated cultures around the world for centuries, as they sought to understand the celestial influence on human lives. From the mysterious connections between the stars and earthly events to the symbolic representations of animals and mythological figures, the zodiac holds a rich tapestry of history and symbolism. In this article, we will delve into the influence of ancient cultures on the development of the zodiac, exploring its roots in Mesopotamia, the impact of Egyptian astrology, the Greek connection to mythology, and the diverse perspectives from the East. Join us on this journey of discovery as we unravel the secrets and complexities that lie within the ancient origins of the zodiac.
The Origins of the Zodiac
The origins of the zodiac can be traced back to ancient civilizations that sought to interpret and make sense of the movements of the stars and their influence on human affairs. One of the earliest connections to the zodiac can be found in Mesopotamia, where the Babylonians developed a system of astrology based on the twelve constellations along the ecliptic known as the “Zodiac of Twelve.” This system served as the foundation for astrology in various cultures, including the Egyptians who incorporated their own mythological symbolism into the zodiac. The zodiac later gained prominence in ancient Greece, where Hellenistic astrologers expanded upon the Babylonian and Egyptian interpretations. The zodiac, especially in Greek culture, became intertwined with mythology, with each sign associated with various gods and goddesses. As astrology spread to the East, it took on different forms, such as the Chinese zodiac with its animal symbolism and the Vedic astrology of ancient India. The ancient cultures’ influence on the zodiac can be seen in the rich symbolism and diverse interpretations that have shaped its significance through the ages. To explore further connections between the zodiac and other astrological aspects, you can learn about the role of zodiac signs in personality traits, the connection between zodiac and elements, or even delve into the mysteries of the astrological houses.
The Mesopotamian Connection
The Mesopotamian connection to the zodiac is a significant chapter in its history. Mesopotamia, the cradle of civilization, gave birth to the earliest known astrological practices. The ancient Babylonians, who inhabited this fertile land, developed a system of astrology based on the relationship between celestial bodies and earthly events. They divided the sky into twelve sections known as the “Zodiac of Twelve.” Each section corresponded to a specific constellation along the ecliptic, marking the path of the Sun throughout the year. The Babylonians believed that the movements of these constellations had a profound impact on human lives and the course of world events. They meticulously observed and recorded astronomical data, laying the groundwork for future astrological traditions. The Mesopotamians also associated each sign of the zodiac with a specific deity, infusing the celestial realm with divine significance. This connection between the zodiac and the divine is a thread that weaves throughout many ancient cultures, including the Mesopotamians. Through their observations and interpretations, the Mesopotamians established an enduring link between the zodiac and humanity, setting the stage for the astrological practices that would follow in the centuries to come.
The Egyptian Influence
The Egyptian influence on the zodiac is a fascinating aspect of its ancient origins. In Egyptian astrology, the twelve zodiac signs were associated with specific deities and had deep connections with their mythology and religious beliefs. One notable connection is the alignment of the zodiac signs with different gods and goddesses. For example, Aries, the Ram, was associated with the god Amun-Ra, the supreme deity in ancient Egyptian religion. Taurus, the Bull, was linked to the goddess Hathor, who represented love, beauty, and fertility. The lion-headed goddess Sekhmet was associated with Leo, representing power and protection. These connections served as a way for the ancient Egyptians to interpret and understand the qualities and characteristics of individuals born under each zodiac sign. Additionally, the ancient Egyptians believed in the concept of soul and the afterlife, and the zodiac played a significant role in their funerary rituals and beliefs. They believed that the position of the stars at the time of a person’s birth could influence their destiny and journey in the afterlife. The influence of the Egyptian zodiac extended beyond astrology, as it also influenced Egyptian art and symbolism. The animal symbols of the zodiac signs could often be found in the hieroglyphs, artwork, and temple decorations of ancient Egypt, further emphasizing the cultural significance of the zodiac in Egyptian society. The Egyptian influence on the zodiac is a testament to the deep connection between celestial observations and the spiritual beliefs and practices of this ancient civilization.
Astrology in Ancient Greece
Astrology played a significant role in ancient Greece, where it was deeply intertwined with the beliefs and practices of the civilization. Hellenistic astrologers further developed the Babylonian and Egyptian systems of astrology, introducing new concepts and interpretations. They viewed celestial bodies as powerful influences on human lives, shaping personalities and determining destinies. Greek mythology also left an indelible mark on astrology, with each zodiac sign associated with mythological figures and their attributes. For example, Aries was linked to the mythical ram that carried Phrixus and Helle to safety, while Taurus was connected to the powerful bull that Zeus transformed into to abduct Europa. These mythological connections added depth and symbolism to the understanding of the zodiac. The ancient Greeks recognized the complexity and nuances of astrology, creating a lasting legacy that influences astrological practices to this day.
The Role of Hellenistic Astrologers
The role of Hellenistic astrologers in the development of the zodiac was immensely significant. During the Hellenistic period, astrology experienced a major resurgence and underwent significant advancements. Hellenistic astrologers played a crucial role in refining and expanding upon the Babylonian zodiac system. They developed techniques such as horoscopic astrology, which involved constructing astrological charts based on the specific time and location of an individual’s birth. These astrologers believed that the positions of the planets and stars at the time of birth could provide insights into a person’s character, destiny, and future events. They developed a system of interpreting the zodiac signs and their alignments in relation to planetary movements, known as the “aspects.” The Hellenistic astrologers also introduced the concept of rulership, assigning each sign a ruling planet based on specific qualities and characteristics associated with the planet. This played a crucial role in understanding the significance of the zodiac signs in relation to one another and in predicting future events. The contributions of these Hellenistic astrologers laid the groundwork for astrology as we know it today, influencing the practices and beliefs of subsequent cultures and civilizations.
The Connection to Greek Mythology
Greek mythology plays a significant role in the connection to the zodiac, as each zodiac sign is associated with various gods and goddesses. Here is a breakdown of the zodiac signs and their corresponding mythological figures:
- Aries: Aries is associated with the mythological figure of the Golden Ram, who saved Phrixus and Helle by flying them to safety. This ram is believed to have been sacrificed by Phrixus, and its Golden Fleece became the focus of the famous story of Jason and the Argonauts.
- Taurus: Taurus is connected to the mythological figure of the Bull, including Zeus taking the form of a bull to abduct Europa, a Phoenician princess. The Bull is also associated with the story of the Minotaur, a half-man, half-bull creature imprisoned in the Labyrinth.
- Gemini: Gemini is associated with the mythological twins Castor and Pollux, also known as the Dioscuri. These twin brothers were revered as protectors of sailors and travelers. Gemini symbolizes their unbreakable bond.
- Cancer: Cancer is connected to the myth of the giant crab that attacked Hercules during his battle with the Hydra. The goddess Hera sent the crab to distract Hercules, but he quickly dispatched it.
- Leo: Leo is associated with the mythological figure of the Nemean Lion, a beast that was invulnerable to mortal weapons. Hercules eventually killed the lion by strangling it with his bare hands, and it became one of his most famous feats.
- Virgo: Virgo is connected to the mythological figure of Persephone, the goddess of harvest and fertility. Persephone’s abduction and subsequent return from the underworld are intertwined with the changing of the seasons.
- Libra: Libra is associated with the scales of justice and is often connected to the goddess Themis, the personification of divine order and law. Themis is also associated with the Oracle at Delphi and played a crucial role in Greek mythology.
- Scorpio: Scorpio is connected with the mythological creature Scorpius, the giant scorpion that was sent by Gaia to kill Orion. Orion and Scorpius were placed in the sky as constellations, forever separated in the heavens.
- Sagittarius: Sagittarius is associated with the mythological figure of the Centaur, specifically Chiron, the wise and knowledgeable centaur. Chiron was a healer and teacher who mentored several heroes in Greek mythology.
- Capricorn: Capricorn is connected to the myth of the Sea-Goat, a creature with the upper body of a goat and the lower body of a fish. This mythological creature represents the blending of land and sea, as well as ambition and resourcefulness.
- Aquarius: Aquarius is associated with the mythological figure of Ganymede, the cupbearer of the gods. Ganymede was a mortal who was abducted by Zeus to become the cupbearer on Mount Olympus, symbolizing youth and service.
- Pisces: Pisces is connected to the mythological tale of Aphrodite and her son Eros transforming into fish to escape the monster Typhon. The fish later became a symbol of their divine connection.
The connection to Greek mythology adds a layer of depth and storytelling to the zodiac signs, making their symbolism more vibrant and engaging. It highlights the ancient Greeks’ fascination with the stars and their belief in the influence of the gods and goddesses on human lives.
Eastern Perspectives on Astrology
Eastern cultures have their own unique perspectives on astrology, bringing a different flavor to the ancient practice. In China, astrology is deeply rooted in the Chinese zodiac, also known as Shengxiao, which is based on twelve animal signs that each correspond to a year in a twelve-year cycle. These animal signs are believed to represent different personality traits and characteristics. The Chinese zodiac is also influenced by the five elements – Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water – which further add layers of complexity and symbolism to the astrological system. Similarly, in ancient India, Vedic astrology holds great significance. Vedic astrology, or Jyotish, is a complex system that incorporates the positions of celestial bodies at the time of a person’s birth to determine various aspects of their life. It encompasses not only personal predictions but also provides guidance on important life events such as marriage, career, and wealth. The Eastern perspectives on astrology offer a unique lens through which to view the influence of the celestial bodies and their impact on human existence.
The Chinese Zodiac
The Chinese Zodiac, also known as Shengxiao, is a system that assigns animal signs to each year in a 12-year cycle. This system has a rich history dating back to ancient China and holds great significance in Chinese culture. Each animal sign in the Chinese Zodiac represents certain characteristics and traits that are believed to influence the personality and destiny of individuals born under that sign. The 12 animal signs are the Rat, Ox, Tiger, Rabbit, Dragon, Snake, Horse, Sheep, Monkey, Rooster, Dog, and Pig. These animal signs are further associated with five elements – Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, and Water, creating a 60-year cycle of zodiac signs. The Chinese Zodiac plays a vital role in various aspects of Chinese culture, including compatibility, fortune telling, and even in determining auspicious dates for important events. People born under a specific animal sign are believed to inherit the qualities and characteristics associated with that sign, shaping their personalities, relationships, and overall life path. Whether it’s understanding your own Chinese Zodiac sign or exploring the compatibility between different signs, the Chinese Zodiac offers a fascinating perspective on astrology and its impact on individual lives.
The Vedic Astrology Connection
Vedic astrology, also known as Jyotish, has a deep connection to the zodiac. In the Vedic tradition, the zodiac is divided into twelve equal parts, each corresponding to a specific constellation or star cluster. The Vedic astrologers use these divisions, known as Rashis, as a fundamental part of their system. Each Rashi is associated with a ruling planet, indicating its influence on the individual’s life and personality traits. The Vedic zodiac differs slightly from the Western zodiac, as it is based on the sidereal year, which accounts for the slight shift in the positions of the stars over time.
In Vedic astrology, the birth chart, or Kundli, is derived from the precise moment and place of an individual’s birth. This chart maps the positions of the planets and their relationship to each other, providing insights into various aspects of one’s life, such as career, relationships, and spiritual growth. The zodiac signs play a crucial role in Vedic astrology, reflecting the characteristics and tendencies of individuals based on their birth dates.
Vedic astrologers consider the zodiac signs along with other factors, such as planetary aspects, house placements, and the influence of planetary periods, known as dashas, to make predictions and offer guidance. The Vedic astrology connection to the zodiac provides a comprehensive understanding of individuals’ lives and their potential paths. It offers insights into their strengths, weaknesses, and karmic influences, emphasizing the importance of destiny and the interconnectedness of cosmic energies.
Vedic astrology’s connection to the zodiac enhances our understanding of how ancient cultures interpreted and incorporated celestial influences into their systems of divination and guidance. It showcases the vast and intricate web of astrological knowledge passed down through generations, offering a unique perspective on the zodiac and its ongoing relevance in modern times.
Ancient Cultures and Zodiac Symbolism

Ancient cultures played a significant role in shaping the symbolism associated with the zodiac. One of the key aspects of this symbolism lies in the connection between the zodiac and animal representations. Each zodiac sign is associated with a specific animal, and this animal symbolism carries deep cultural and spiritual significance. For example, the ram represents Aries, the bull represents Taurus, and so on. These animal associations can be traced back to ancient mythologies and belief systems, where animals held special meanings and characteristics attributed to them. Additionally, cultural iconography also played a role in shaping the symbolism of the zodiac. In ancient Egypt, for instance, the zodiac signs were depicted as human figures with animal heads, reflecting the fusion of human and animal symbolism. The ancient cultures’ interpretation and depiction of zodiac symbolism have shaped our understanding and appreciation of the zodiac today, providing us with a rich tapestry of cultural heritage to explore and unravel.
The Zodiac and Animal Symbolism
The Zodiac and Animal Symbolism have been intricately linked throughout the ages, with each zodiac sign associated with a specific animal. This connection between the zodiac and animals can be observed in various ancient cultures and holds significant meaning. In Western astrology, for example, Aries is represented by the ram, Taurus by the bull, and Leo by the lion. The choice of these animals is not arbitrary; rather, it reflects the characteristics and qualities attributed to each zodiac sign. The ram symbolizes determination and assertiveness, while the bull represents strength and stubbornness. The lion embodies leadership and courage.
In Eastern astrology, the Chinese zodiac takes animal symbolism even further, with each year being associated with a particular animal and its characteristics. For instance, the Year of the Rat is believed to bring resourcefulness and intelligence, while the Year of the Ox signifies hard work and perseverance. This rich animal symbolism adds depth and nuance to the interpretation of the zodiac signs and allows individuals to connect with their corresponding animals on a symbolic level.
The use of animal symbolism in the zodiac extends beyond the characteristics attributed to the animals themselves. It also draws upon cultural beliefs, folklore, and mythology associated with these animals. For instance, the ancient Egyptians believed that the god Horus took the form of a falcon, which influenced their association of the zodiac sign Scorpio with this bird. Similarly, in Chinese astrology, the dragon is revered as a symbol of power, luck, and protection, leading to its representation in the zodiac.
The animal symbolism within the zodiac serves to enhance the understanding of each zodiac sign’s traits and qualities. It provides a visual and relatable representation that allows individuals to connect with their zodiac signs on a deeper level. Whether it’s the determination of the ram, the loyalty of the dog, or the adaptability of the chameleon-like Gemini, animal symbolism brings the zodiac to life and adds a layer of intrigue and fascination to the ancient system of astrology.
The Zodiac and Cultural Iconography
Throughout history, the zodiac has played a significant role in shaping cultural iconography, incorporating its symbolism into various art forms, architecture, and cultural practices. One of the most notable examples can be found in ancient Egypt, where the zodiac signs were often depicted in the artwork and hieroglyphics found within temples and tombs. The Egyptian civilization closely associated certain animals with specific zodiac signs, such as the lion with Leo and the ram with Aries. These symbols were not only representations of the zodiac but also held deeper cultural and religious significance.
Moving from Egypt to ancient Greece, we see the influence of cultural iconography in their depiction of the zodiac. Greek mythology and gods played a crucial role in associating certain mythological figures with specific zodiac signs. For instance, Aries, the ram, was linked to the myth of the Golden Fleece and the hero Jason, while Taurus, the bull, was connected to the myth of Zeus and Europa. These mythological connections added richness and depth to the representations of the zodiac, making it more than just a celestial system, but a reflection of cultural beliefs and stories.
In addition to ancient Egypt and Greece, cultural iconography related to the zodiac can be found in various other civilizations. In Chinese culture, the zodiac signs are often depicted in traditional artwork and are deeply embedded in the cultural fabric of the country. Each Chinese zodiac sign is associated with a specific animal, and these symbols are frequently used in art, embroidery, and even on buildings and temples. The Chinese New Year celebrations also incorporate these animal symbols, with each year dedicated to a different zodiac sign.
The influence of the zodiac on cultural iconography continues to be seen in modern times as well. From jewelry adorned with zodiac symbols to zodiac-themed tattoo art, the zodiac has become a popular inspiration for artistic expression. The connection between the zodiac and cultural iconography serves as a testament to the enduring fascination and influence of this ancient system on human culture and creativity.
The Evolving Zodiac
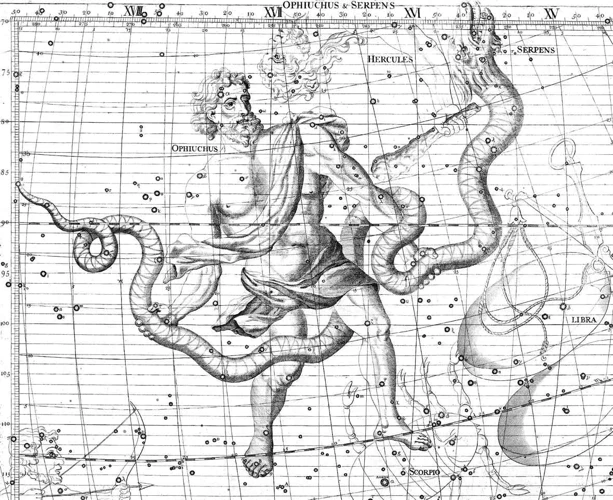
The zodiac, throughout its ancient history, has undergone various changes and evolutions. One notable development is the addition of a thirteenth sign known as Ophiuchus, which exists along the ecliptic, but has been historically overlooked in traditional astrology. Ophiuchus, represented by a serpent bearer, has led to debates and controversies among astrologers and zodiac enthusiasts, as it disrupts the traditional understanding of the twelve signs. While some have embraced Ophiuchus as a significant addition, others argue that it undermines the integrity of the zodiac system. These disagreements highlight the evolving nature of the zodiac and the ongoing exploration and reinterpretation of astrological symbolism. As the zodiac continues to capture the imagination of people across the world, it is likely that its evolution will continue, challenging and expanding our understanding of astrology and its connection to human lives.
The Addition of Ophiuchus
The Addition of Ophiuchus to the zodiac is a topic that has sparked much controversy and discussion in recent times. Ophiuchus, also known as the Serpent Bearer, is a constellation that lies along the ecliptic and was recognized by the ancient Greeks. However, it was not included in the original twelve zodiac signs. This constellation gained attention in 2011 when reports emerged that NASA had announced the addition of a thirteenth zodiac sign. According to this claim, Ophiuchus would be inserted between Scorpio and Sagittarius, shifting the dates of the other signs. However, it is important to note that this addition is not universally accepted by astrologers and is not recognized in traditional Western astrology. The controversy surrounding the inclusion of Ophiuchus revolves around the impact it would have on individuals’ zodiac signs and astrological interpretations. While some argue that it adds a new dimension and accuracy to astrology, others criticize it as a deviation from centuries-old tradition. It is worth mentioning that the zodiac and its signs are based on the position of the Sun as observed from Earth and are not affected by the existence of additional constellations. As a result, whether or not Ophiuchus is included, the traditional twelve zodiac signs continue to be widely used in astrology and horoscopes, as they have been for centuries.
Controversies Surrounding the New Zodiac
Controversies surrounding the new zodiac have stirred debate and discussion among astrologers and enthusiasts alike. One major source of controversy arose in 2011 when an astronomer introduced the concept of a 13th zodiac sign, Ophiuchus, which would disrupt the traditional 12-sign system. This revelation created a significant uproar, as it meant that individuals previously identified with a specific zodiac sign may now find themselves belonging to a different sign. Opponents of the inclusion of Ophiuchus argue that it undermines the established astrological system and creates confusion among zodiac followers. Skeptics question the scientific basis for the inclusion of Ophiuchus, highlighting discrepancies between astronomy and astrology. Despite the controversy, many astrologers and enthusiasts continue to adhere to the traditional 12-sign system, while others embrace the idea of Ophiuchus as a welcome addition to the zodiac. The debate surrounding the new zodiac highlights the dynamic and evolving nature of astrology, sparking discussions about the accuracy, relevance, and interpretation of astrological systems in the modern era.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the exploration of the influence of ancient cultures on the zodiac reveals a fascinating and intricate tapestry of history, symbolism, and astrology. From the Mesopotamian origins in the Zodiac of Twelve to the Egyptian incorporation of mythological symbolism, the zodiac has undergone a constant evolution. Greek culture expanded upon these foundations, intertwining the zodiac with captivating tales of gods and goddesses. The East also contributed its unique perspectives, with the Chinese zodiac incorporating animal symbolism and the Vedic astrology of ancient India providing its own insights. Throughout history, the zodiac has served as a tool for understanding and interpreting the celestial influences on human lives. It continues to captivate our imagination, offering a lens through which we can explore our own personalities, relationships, and destinies. Whether viewed as a guide or a source of entertainment, the ancient cultures’ influence on the zodiac ensures that it remains a significant and enduring aspect of human culture. So, as we look up at the stars and ponder the mysteries of the cosmos, let us remember the ancient origins that have shaped the zodiac into the fascinating and complex system we know today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the zodiac in ancient cultures?
The zodiac held great significance in ancient cultures as it was believed to connect the celestial realm with human life. It provided a framework for understanding the influence of the stars and planets on various aspects of existence, including personality traits, destiny, and even agricultural cycles.
How did Mesopotamian astrology contribute to the development of the zodiac?
The Mesopotamians were among the first to develop a systematic approach to astrology, assigning meanings to the twelve constellations along the ecliptic. This formed the basis for the zodiac system that later spread to other civilizations.
What role did Greek mythology play in the interpretation of the zodiac?
Greek mythology played a significant role in the interpretation of the zodiac. Each zodiac sign was associated with a mythological figure or deity, adding a layer of symbolism and meaning to the astrological system.
How does the Chinese zodiac differ from Western astrology?
The Chinese zodiac is based on a twelve-year cycle, with each year represented by an animal sign. Unlike Western astrology, which primarily focuses on the position of the sun at the time of birth, Chinese astrology incorporates both the lunar calendar and the alignment of the five elements.
What is Vedic astrology and how does it relate to the zodiac?
Vedic astrology, also known as Jyotish, is an ancient Indian system of astrology. It incorporates the zodiac signs but places greater emphasis on the positions of the planets and their influence on an individual’s life.
How are animals connected to the zodiac?
In many cultures, animals are associated with the zodiac signs. These connections often stem from the characteristics and traits associated with specific animals, which are believed to correspond to the qualities of individuals born under each zodiac sign.
What is the significance of zodiac symbolism in art and iconography?
Zodiac symbolism has inspired countless works of art throughout history. The zodiac signs and their associated symbols are often depicted in paintings, sculptures, and other forms of visual art as a way to convey astrological concepts and beliefs.
How did the addition of Ophiuchus impact the zodiac?
The inclusion of Ophiuchus, a thirteenth constellation, sparked controversy and debate in the astrological community. While some astrologers embraced the addition as an opportunity for new insights, others rejected it, arguing that it disrupted the traditional system and interpretations of the zodiac.
What controversies surround the new zodiac?
The addition of Ophiuchus to the zodiac sparked debates regarding the validity of astrology as a whole. Skeptics argue that the inclusion of a new constellation undermines the credibility of traditional astrological systems, while proponents see it as an expansion of knowledge and possibilities.
How has the zodiac evolved over time?
The zodiac has undergone changes and adaptations throughout history. The interpretations, associations, and even the number of constellations included in the zodiac have varied across different cultures and time periods, reflecting the evolving understanding and beliefs about the stars and human existence.








