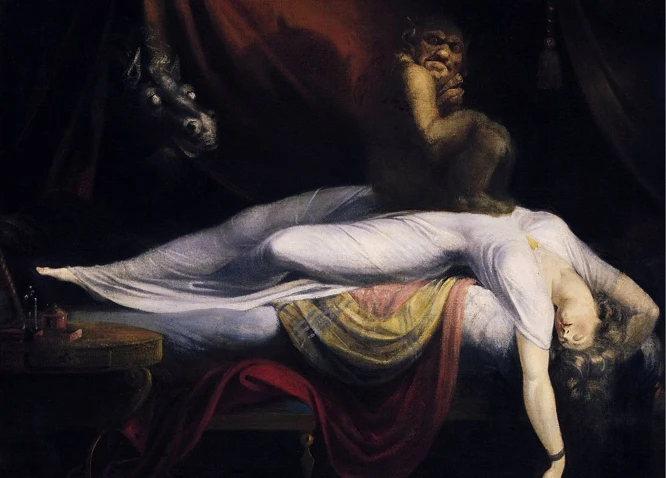
Why do nightmares haunt us in our sleep? What significance do they hold in different cultures and historical periods? In this article, we will delve into the cultural and historical perspectives on nightmares, exploring how they have been interpreted and understood throughout time. From ancient civilizations to modern societies, nightmares have played a role in shaping beliefs, psychological theories, and mental well-being. We will also examine the various methods used to manage and overcome these haunting dreams. Join us on a journey through the intricacies of nightmares, as we unravel their cultural, historical, and psychological significance.
The Role of Nightmares in Different Cultures

Nightmares have held a significant role in different cultures around the world, shaping beliefs, traditions, and understanding of the subconscious mind. These haunting dreams have been seen as more than mere nighttime terrors; they have been regarded as valuable messages or warnings from the spiritual realm. In many ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Greeks, nightmares were believed to be the result of demonic or supernatural forces, often indicating a disruption in the natural order of things. These cultures often turned to elaborate rituals and ceremonies to appease the spirits and protect themselves from the influence of nightmares.
In Indigenous beliefs, nightmares are seen as a connection to the spirit world and an opportunity for introspection and healing. Some Native American tribes view nightmares as a manifestation of unresolved conflicts within relationships or even a reflection of the collective struggles of the community. Dream catchers, woven web-like talismans, are commonly used to filter out negativity and ensure peaceful and restful sleep.
Eastern traditions, such as those found in Hinduism and Buddhism, interpret nightmares as a result of karma, past actions, and unresolved emotions. These cultures believe that nightmares offer an opportunity for spiritual growth and enlightenment. Practices such as meditation and dream analysis are utilized to gain insights into the subconscious mind and alleviate the negative effects of nightmares.
Through exploring the role of nightmares in different cultures, we can gain a deeper understanding of the diverse interpretations and beliefs surrounding these unsettling dreams. Each culture’s perspective offers a unique lens to examine the profound impact that nightmares have on the human psyche and our collective consciousness.
1. Nightmares in Ancient Civilizations
In ancient civilizations, nightmares held a prominent place in the collective beliefs and fears of the people. The Egyptians, for instance, believed that nightmares were the work of evil spirits and demons. They associated these haunting dreams with disruptions in the natural order of the world, often considering them a foretelling of impending doom or misfortune. To combat the influence of nightmares, the Egyptians engaged in elaborate rituals and ceremonies to ward off evil spirits and seek protection. They believed that by appeasing the spirits through offerings and religious practices, they could alleviate the occurrence of nightmares and restore harmony.
Similarly, in ancient Greece, nightmares were believed to be a result of supernatural beings such as the Mares. These malevolent entities were thought to sit on the chests of sleeping individuals, causing them to experience terrifying dreams. The Greeks developed various rituals and practices to dispel these nightmares, including the use of charms and amulets. They also sought guidance from oracles and priests who could help interpret the symbolic messages hidden within these unsettling dreams.
Nightmares played a significant role in the ancient civilizations, shaping their worldview and influencing their actions. The understanding of nightmares as more than mere dreams displayed the deep-rooted belief in the spiritual and supernatural forces that governed their lives. These cultural perspectives provide a fascinating glimpse into the intricate ways in which different societies interpreted and dealt with the phenomenon of nightmares.
2. Nightmares in Indigenous Beliefs
In Indigenous beliefs, nightmares hold a significant place and are seen as more than just terrifying dreams. These cultures often view nightmares as a connection to the spirit world and believe that they provide an opportunity for introspection and healing. One common belief among Native American tribes is that nightmares reflect unresolved conflicts within relationships.
Nightmares are seen as reflections of the collective struggles within the community and are considered messages that need to be understood and addressed. Instead of fearing nightmares, these cultures embrace them as a means of personal and communal growth. The process of understanding these dreams involves deep reflection and interpretation.
Dream catchers are commonly used in Indigenous cultures as a means of protection against negative dreams. These woven talismans are believed to filter out negativity and allow only positive and peaceful dreams to pass through. By hanging dream catchers near the bed, individuals hope to create a safe and restful sleeping environment.
By recognizing the role of nightmares in Indigenous beliefs, we can appreciate how these cultures approach and interpret these unsettling dreams. The emphasis on the connection between nightmares and unresolved conflicts within relationships highlights the significance placed on maintaining harmonious connections within communities. Understanding nightmares from this perspective can provide valuable insights into the power of dreams in addressing emotional and psychological challenges.
3. Nightmares in Eastern Traditions
Nightmares hold a unique place in Eastern traditions, such as Hinduism and Buddhism, where they are seen as more than just unsettling dreams. In these cultures, nightmares are believed to be connected to karma, past actions, and unresolved emotions. They are seen as an opportunity for spiritual growth and enlightenment.
In Hinduism, nightmares are often interpreted as a reflection of one’s past actions and the consequences of negative karma. It is believed that nightmares serve as a reminder to individuals to rectify their behavior and make amends for any wrongdoings. Through introspection and self-reflection, Hindus seek to find the underlying cause of their nightmares and work toward spiritual purification.
Buddhism also acknowledges the significance of nightmares in its teachings. Nightmares are seen as a product of the mind’s attachment to worldly desires and attachments, which perpetuate the cycle of suffering. Buddhist practitioners are encouraged to observe the content of their nightmares without judgment, using them as a catalyst for self-awareness and understanding. By recognizing the impermanence and illusory nature of the dream state, individuals can transcend the fears and anxieties associated with nightmares.
Practices such as meditation and dream analysis are integral to exploring nightmares in Eastern traditions. Meditation helps individuals develop mindfulness and awareness, allowing them to observe the thoughts and emotions associated with nightmares without getting carried away by them. Dream analysis, on the other hand, involves examining the symbolism and deeper meanings within nightmares to gain insights into one’s psychological and spiritual well-being.
By understanding nightmares in the context of Eastern traditions, we can appreciate the emphasis placed on self-reflection, personal growth, and the pursuit of spiritual enlightenment. These perspectives offer valuable insights into the human experience and provide tools for individuals to navigate the realm of nightmares and their potential impact on mental and emotional well-being.
Nightmare Interpretations throughout History
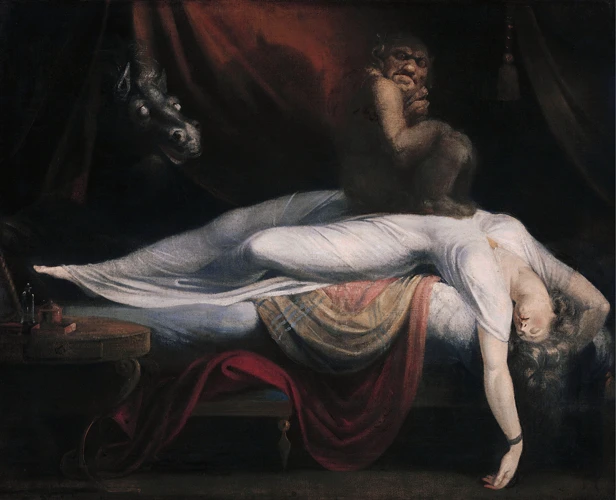

- Medieval Superstitions and Symbolism: During the Middle Ages, nightmares were often attributed to supernatural entities, such as demons or witches. They were seen as malevolent spirits that would enter a person’s body during sleep, causing disturbing dreams. Many superstitions and protective practices emerged to ward off these evil influences. The interpretation of nightmares was highly symbolic, with images and elements in the dream being associated with specific meanings. For example, dreaming of falling from a great height was believed to represent a fear of failure or a loss of control.
- Victorian Era’s Psychological Theories: In the 19th century, psychological theories started to emerge as a way to understand nightmares. Sigmund Freud, a prominent figure in this era, believed that dreams, including nightmares, were a manifestation of repressed desires and unresolved conflicts. According to Freud, nightmares provided a window into the unconscious mind, often revealing suppressed emotions or traumatic experiences. This perspective marked a shift towards analyzing the psychological significance of nightmares and their potential connection to mental well-being.
- Freud’s Psychoanalytic Perspective: Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective on nightmares has had a lasting impact. He believed that nightmares were symbolic representations of unconscious desires, fears, and conflicts. Freud introduced the concept of dream analysis, suggesting that exploring the hidden meanings behind nightmares could provide insight into an individual’s psyche. This approach influenced the field of psychology and has been widely debated and expanded upon by subsequent theorists.
The interpretation of nightmares throughout history reflects the evolving understanding of the human mind and the significance placed on dreams. From medieval superstitions to Freud’s psychoanalytic theories, each era has offered its own lens to explore the hidden meanings and psychological implications of nightmares. By examining these historical perspectives, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex nature of dreams and their impact on our psychological well-being.
1. Medieval Superstitions and Symbolism
During the medieval period, nightmares were heavily influenced by superstitions and symbolism. It was believed that nightmares were a result of demonic or evil spirits tormenting a person during their sleep. People in this time period regarded nightmares as ominous and foretelling of impending doom or misfortune. Nightmares were often seen as a punishment for sins or as a sign of being possessed by the devil.
Symbolism played a significant role in interpreting nightmares during the medieval era. Dreams and their associated symbols were believed to hold hidden meanings and messages. For example, dreaming of snakes was seen as a warning of betrayal or deceit, while dreaming of fire symbolized impending danger or punishment. These interpretations were rooted in the religious beliefs and cultural traditions of the time.
People in medieval times turned to various rituals and practices to ward off nightmares and protect themselves from the associated dangers. These included carrying protective amulets, reciting prayers before sleep, and using herbal remedies believed to ward off evil spirits. Nightmares were not only seen as personal experiences but also as a reflection of the broader social and spiritual dynamics of the time.
By understanding the medieval superstitions and symbolism surrounding nightmares, we gain insight into how people in that era navigated the unknown and sought to protect themselves from the perceived malevolent forces at play. It serves as a reminder of the profound impact that cultural beliefs and historical contexts have on shaping our understanding and interpretation of nightmares.
2. Victorian Era’s Psychological Theories
During the Victorian Era, psychological theories emerged to explain the significance of nightmares. Sigmund Freud, a prominent figure in this era, delved into the interpretation of dreams and their connection to the unconscious mind. Freud believed that nightmares were symbolic representations of repressed desires and unresolved conflicts within one’s psyche.
Victorian psychologists also explored the impact of trauma on the occurrence of nightmares. The horrors of war, industrialization, and social upheaval during this time led to an increased focus on the connection between trauma and disturbed sleep. Nightmares were seen as a manifestation of unresolved emotional turmoil and the mind’s attempt to process traumatic experiences.
In addition to trauma, Victorian psychological theories attributed nightmares to various other factors, such as anxiety, guilt, and sexual repression. These theories emphasized the importance of analyzing the symbolism and hidden meanings within nightmares to gain insights into the inner workings of the human mind.
The Victorian Era’s psychological theories marked a shift towards understanding nightmares from a more scientific and psychological perspective. This period laid the foundation for future studies and theories surrounding the interpretation and analysis of dreams, providing a framework for understanding the complex relationship between nightmares and the human psyche.
3. Freud’s Psychoanalytic Perspective
In the realm of nightmare interpretations throughout history, Sigmund Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective holds a prominent place. Freud believed that nightmares were a gateway to the unconscious mind, expressing repressed desires, fears, and unresolved conflicts. According to Freud, nightmares often stemmed from traumatic experiences and unfulfilled wishes. He theorized that the symbolic imagery found in nightmares served as a mechanism for the mind to process and protect itself from distressing thoughts and emotions.
Freud introduced the concept of dream analysis as a way to decipher the hidden meanings behind nightmares. He believed that by interpreting the symbols within the dream, one could gain insight into their deep-seated anxieties and suppressed desires. This process involved analyzing elements such as objects, people, and actions present in the nightmare, as well as exploring the dreamer’s personal experiences and associations.
Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective on nightmares revolutionized the field of psychology and paved the way for the exploration of the subconscious mind. His theories provided a framework for understanding the psychological significance of nightmares and their potential connection to unresolved traumas or conflicts. Today, Freud’s ideas continue to influence the practice of dream analysis and offer valuable insights into the human psyche’s intricate workings.
Cultural Variations in Understanding Nightmares

The understanding of nightmares varies greatly across different cultures, influenced by their unique belief systems and societal norms. One prominent concept that emerges from cultural perspectives is the idea of the collective unconscious and archetypes. Coined by psychologist Carl Jung, the collective unconscious refers to the shared reservoir of knowledge and symbols that reside within every individual’s psyche. It is believed that nightmares can tap into this collective unconscious, revealing universal symbols and themes that resonate across cultures.
In many cultures, nightmares are seen as symbolic experiences rather than literal events. The interpretation of these symbols often depends on the cultural context and personal experiences of the dreamer. For example, a common archetype found in nightmares is the shadow figure, representing suppressed aspects of the self. In some cultures, this may be viewed as an omen or warning, while in others, it may be seen as an opportunity for self-reflection and growth.
Modern cultural influences have also played a role in shaping the understanding of nightmares. The rise of technology and media has introduced new fears and anxieties into people’s lives, which can manifest in nightmares. Additionally, cultural taboos and stigmatizations may impact the way nightmares are viewed and discussed within a society.
By exploring these cultural variations in understanding nightmares, we can gain a broader appreciation for the complexities of these nocturnal experiences. Understanding how different cultures interpret and respond to nightmares can enhance our own understanding of the human psyche and the significance of these haunting dreams.
1. Collective Unconscious and Archetypes
The concept of the collective unconscious, introduced by Swiss psychologist Carl Jung, offers a fascinating perspective on the role of nightmares. According to Jung, the collective unconscious is a shared reservoir of archetypes, universal symbols and themes that are present across cultures and time periods. Nightmares, in this framework, are seen as a manifestation of these archetypes and a reflection of the collective human experience. Jung believed that nightmares provide a window into the deeper layers of the psyche, tapping into the primal fears and desires that connect us all.
Archetypes are recurring patterns or symbols that exist in the collective unconscious. These archetypes often appear in nightmares, representing fundamental aspects of human existence. For example, the shadow archetype represents the repressed or unacknowledged aspects of the self, and it may manifest in nightmares as a menacing figure or an ominous presence. Other archetypes that commonly appear in nightmares include the anima/animus (representing the opposite gender within ourselves), the trickster, and the hero/heroine.
Exploring the collective unconscious and archetypes sheds light on the universal nature of nightmares, transcending cultural and historical boundaries. It reveals the deep-rooted connections we share as human beings and the symbolic language through which our subconscious communicates with us in the realm of dreams.
2. Modern Cultural Influences
Modern cultural influences have also shaped our understanding of nightmares and the significance we attribute to them. In many Western societies, nightmares are often associated with psychological factors rather than spiritual or supernatural forces. The field of psychology and psychiatry has played a crucial role in analyzing and interpreting nightmares from a scientific standpoint.
With the advancement of technology and the rise of global media, popular culture has further influenced our perception of nightmares. Movies, books, and television shows often depict nightmares as a source of horror and fear, perpetuating the idea that they are inherently negative experiences.
Additionally, trauma and unresolved conflicts within relationships have been identified as modern influences on the occurrence of nightmares. Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one, financial difficulties, or a difficult breakup, can trigger nightmares as the mind tries to process and cope with the emotional turmoil.
It is crucial to recognize and consider these modern cultural influences when studying nightmares, as they shape our understanding and the ways in which we approach their management and interpretation.
Effects of Nightmares on Mental Health
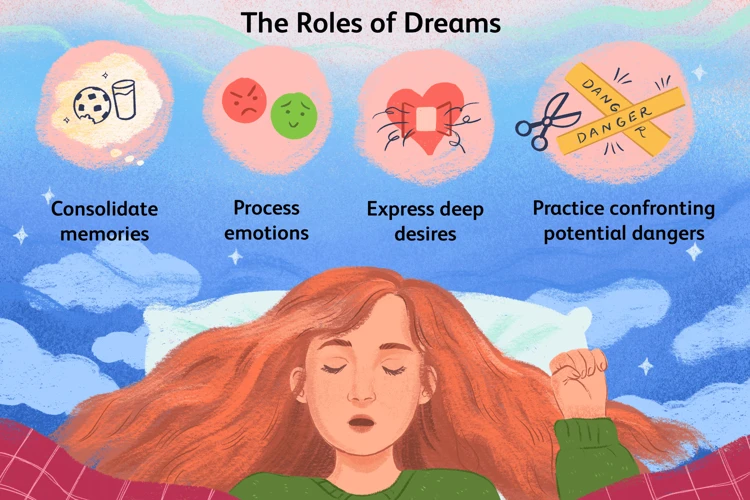
Nightmares can have profound effects on mental health, impacting both the individual and their overall well-being. For some individuals, recurring nightmares can lead to the development of nightmare disorders, such as nightmare disorder and sleep-related eating disorder. These disorders can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to sleep deprivation and fatigue, which in turn can contribute to cognitive impairment, mood disturbances, and decreased overall functioning.
In addition to the immediate effects on sleep, nightmares can also have long-lasting psychological consequences. People who experience frequent nightmares may develop symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Nightmares related to traumatic experiences can serve as distressing reminders of past events and contribute to the development or exacerbation of PTSD symptoms. These nightmares can be particularly challenging as they may be vivid and realistic, causing significant emotional distress and difficulty in coping with the trauma.
Unresolved conflicts within relationships can also be manifest in nightmares, leading to emotional distress and strained interpersonal dynamics. Nightmares that revolve around themes of betrayal, abandonment, or unresolved issues with loved ones can create tension and impact mental well-being. Couples or families experiencing these types of nightmares may benefit from open communication, therapy, or mediation to address and resolve underlying conflicts.
While the exact causes of nightmares and their effects on mental health can vary depending on individual circumstances, it is clear that they can significantly impact overall well-being. Seeking professional help from therapists, psychologists, or sleep specialists can be beneficial in managing and addressing the psychological effects of nightmares, allowing individuals to regain control of their mental health and quality of life.
1. Nightmare Disorders and PTSD
Nightmare disorders and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) are two conditions that can significantly impact an individual’s mental health. Nightmare disorders, also known as dream anxiety disorders, involve recurrent nightmares that cause distress or impairment in daily life. These nightmares often revolve around themes of danger, harm, or personal threats, and can lead to sleep disturbances and anxiety upon waking.
PTSD, on the other hand, is a psychiatric disorder that can develop after a person experiences or witnesses a traumatic event. Nightmares are one of the hallmark symptoms of PTSD, with individuals frequently experiencing vivid and disturbing dreams related to the traumatic event. These nightmares can be intrusive, causing intense fear and emotional distress.
The effects of nightmare disorders and PTSD extend beyond the realm of sleep. The distress caused by recurrent nightmares can lead to difficulties in falling asleep, staying asleep, and getting restorative rest. This can result in fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and overall impaired functioning in various areas of life.
It’s worth noting that the impact of nightmares on mental health can be influenced by cultural factors. For example, in cultures where collective trauma or historical events have occurred, nightmares related to these events can have a profound impact on individuals and even whole communities. The emotional and psychological toll of such nightmares can contribute to a sense of shared trauma and ongoing distress.
Understanding the connection between nightmare disorders, PTSD, and cultural influences is crucial to developing effective treatment approaches. By addressing the underlying trauma or anxiety that gives rise to these nightmares, individuals can find relief and regain control over their sleep and overall mental well-being.
To learn more about the impact of diet and lifestyle on the occurrence of nightmares, click here.
2. Cultural Factors Impacting Mental Well-being
Cultural factors play a crucial role in shaping an individual’s mental well-being, and this includes the impact on nightmares. The way different cultures perceive and interpret nightmares can influence how individuals experience and cope with these unsettling dreams. Let’s explore some of the cultural factors that can impact mental well-being in relation to nightmares:
- Belief Systems: Cultural belief systems and religious practices can significantly influence how nightmares are understood and dealt with. For example, in certain cultures, nightmares may be seen as spiritual experiences or encounters with supernatural entities. This belief system may lead to different coping mechanisms, such as seeking spiritual guidance or engaging in specific rituals to protect against negative dreams.
- Social Support: The social support and cultural norms within a community can affect an individual’s mental well-being in relation to nightmares. In cultures where open discussions about dreams are encouraged and support systems are in place, individuals may feel more comfortable sharing their nightmares and seeking help or guidance from others. Conversely, cultures that discourage the acknowledgment of dreams may leave individuals feeling isolated or ashamed, negatively impacting their mental health.
- Perception of Dreams: Cultural attitudes and perceptions of dreams can also influence how nightmares are perceived and their impact on mental well-being. Cultures that view dreams as meaningful messages or opportunities for personal growth may approach nightmares with a more positive mindset, using them as a tool for self-reflection and exploration. On the other hand, cultures that dismiss dreams as insignificant may overlook the potential psychological impact of nightmares on individuals.
It is essential to recognize and consider these cultural factors when examining the relationship between nightmares and mental well-being. By understanding how cultural beliefs, social support, and perceptions shape individuals’ experiences, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive environment to address the mental health implications of nightmares.
Methods to Manage and Overcome Nightmares
Many cultures have developed rituals and talismans to manage and overcome nightmares. Dream catchers, as mentioned earlier, are one such example. Originating from Native American cultures, dream catchers are believed to catch and filter out negative dreams, allowing only positive dreams to pass through and reach the sleeper. The intricate web-like design of the dream catcher symbolizes the interconnectedness of all things and acts as a protective barrier against bad dreams. By hanging a dream catcher near the sleeping area, individuals hope to minimize the occurrence of nightmares and promote restful sleep.
In modern times, various therapeutic approaches have been developed to help individuals manage and overcome nightmares. One such approach is imagery rehearsal therapy (IRT), which involves rewriting the content of the nightmare during wakefulness and practicing the new, positive version. This technique aims to change the emotional response associated with the recurring nightmare, reducing its frequency and intensity. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is another commonly used treatment that focuses on identifying and challenging negative thoughts and beliefs associated with nightmares. Through techniques such as cognitive restructuring and exposure therapy, individuals can learn to reframe their thoughts and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
While rituals and therapeutic approaches can be helpful, it is important to address the underlying causes of nightmares, such as trauma or unresolved conflicts. Seeking professional help from psychologists or counselors can provide valuable support in understanding and processing the root causes of nightmares. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a regular sleep schedule, managing stress, and avoiding stimulants before bed, can contribute to a better overall sleep experience and potentially reduce the occurrence of nightmares.
1. Rituals and Dream Catchers
Rituals and dream catchers have long been utilized as methods to manage and overcome nightmares in various cultures around the world. These practices aim to create a sense of safety and protection during sleep, allowing individuals to have more peaceful and restful nights.
In many indigenous cultures, including Native American tribes, the use of dream catchers is prevalent. These intricately woven webs, traditionally made from sinew, feathers, and beads, are believed to trap negative dreams and thoughts, allowing only positive ones to pass through and reach the dreamer. This filtering process helps to alleviate nightmares and promote a sense of security during sleep.
Additionally, rituals play a significant role in dealing with nightmares in numerous cultures. These rituals can vary widely, ranging from simple bedtime routines to elaborate ceremonies. For example, some individuals may engage in calming activities before sleep, such as taking a warm bath, practicing deep breathing exercises, or listening to soothing music. These actions help create a peaceful environment and set the stage for a more positive dream experience.
In other cultures, rituals may involve spiritual or religious practices to combat nightmares. These can include prayer, meditation, or the burning of incense or herbs with soothing aromas. The aim is to cleanse the energy surrounding the dreamer and provide a sense of spiritual protection against negative influences.
By incorporating rituals and dream catchers into their nighttime routines, individuals can create a sanctuary for themselves, free from the disturbances of nightmares. These practices not only offer comfort and reassurance but also allow individuals to gain a sense of control over their dreams and ultimately their subconscious mind.
2. Therapeutic Approaches
When it comes to managing and overcoming nightmares, various therapeutic approaches have been developed to help individuals navigate through the distressing experiences. These approaches aim to provide support, alleviate anxiety, and promote better sleep patterns. Here are a few therapeutic methods commonly used:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I is a type of therapy that focuses on addressing the thoughts, behaviors, and emotions that contribute to sleep disturbances. It involves identifying and challenging negative thoughts related to sleep and nightmares, implementing relaxation techniques, and establishing healthy sleep habits.
- Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR): EMDR is a therapy primarily used for individuals who have experienced trauma. It involves guided eye movements or other forms of bilateral stimulation to process distressing memories and reduce the emotional impact associated with nightmares and other trauma-related symptoms.
- Hypnotherapy: Hypnotherapy is a therapeutic approach that utilizes guided relaxation, intense concentration, and focused attention to achieve a heightened state of awareness. It can help individuals explore the root causes of their nightmares, gain insights, and develop alternative narratives or coping mechanisms.
These are just a few examples of therapeutic approaches that can assist individuals in managing and overcoming nightmares. It is important to consult with a qualified mental health professional to determine the most appropriate approach based on individual needs and circumstances.
Conclusion
The exploration of cultural and historical perspectives on nightmares provides us with valuable insights into the significance of these haunting dreams. Across different cultures, nightmares have been viewed as more than just random occurrences during sleep; they have been seen as messages from the spiritual realm, reflections of unresolved conflicts, and opportunities for spiritual growth. Ancient civilizations utilized rituals and ceremonies to protect themselves from the influence of nightmares, while Indigenous beliefs emphasized the importance of dream catchers and introspection. Eastern traditions utilized meditation and dream analysis to gain insights into the subconscious mind. By understanding these diverse perspectives, we can appreciate the profound impact that nightmares have on mental well-being and our collective understanding of the human psyche.
Furthermore, the study of nightmares throughout history allows us to trace the evolution of interpretations and theories surrounding these unsettling dreams. From medieval superstitions and symbolism to Victorian psychological theories and Freud’s psychoanalytic perspective, different eras have provided unique frameworks for understanding nightmares. This historical context reminds us that how we perceive and interpret nightmares is influenced by cultural and societal beliefs.
In conclusion, exploring cultural and historical perspectives on nightmares expands our understanding of this universal human experience. Nightmares have played prominent roles in various cultures, shaping beliefs, rituals, and approaches to mental health. They offer glimpses into the human subconscious, providing messages, warnings, and opportunities for growth. By studying the role of nightmares, we gain a richer appreciation for the complexities of the human mind and its intricate relationship with culture and history.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some common symbols or themes in nightmares across different cultures?
Nightmares often contain symbols or themes related to fears, anxieties, and unresolved conflicts. While specific symbols may vary, common themes include being chased, falling, or experiencing a sense of powerlessness.
2. Do different cultures believe that nightmares have supernatural or spiritual origins?
Yes, many cultures attribute the occurrence of nightmares to supernatural or spiritual forces. These cultures often believe that nightmares can be messages from the spirit realm or indications of a disruption in the natural order of things.
3. How do Indigenous cultures use dream catchers to combat nightmares?
Dream catchers are believed to filter out negative energies and promote peaceful sleep. In Indigenous cultures, dream catchers are often hung near the sleeping area to entangle and trap bad dreams, allowing only good dreams to pass through.
4. How do Eastern traditions interpret nightmares?
Eastern traditions view nightmares as a result of karma, past actions, and unresolved emotions. They believe that nightmares provide an opportunity for spiritual growth and enlightenment.
5. Can cultural beliefs about nightmares impact an individual’s mental well-being?
Yes, cultural beliefs about nightmares can significantly impact an individual’s mental well-being. For example, in cultures that view nightmares as negative spirits or supernatural entities, the fear associated with these beliefs can contribute to anxiety and sleep disturbances.
6. Are there any specific rituals or practices to manage nightmares?
Yes, different cultures have various rituals and practices to manage nightmares. These range from performing cleansing ceremonies, using protective talismans, engaging in meditation and dream analysis, to seeking the guidance of spiritual or religious leaders.
7. Can nightmares be a symptom of trauma?
Yes, nightmares can be a symptom of trauma, particularly in cases of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Traumatic experiences can manifest in dreams, causing repetitive or vivid nightmares related to the traumatic event.
8. How can understanding cultural perspectives on nightmares help in therapy?
Understanding cultural perspectives on nightmares is crucial in therapy as it helps mental health professionals to consider the nuances and beliefs of their clients. By acknowledging cultural interpretations, therapists can tailor treatment approaches to better fit the client’s worldview and address their specific concerns.
9. Are there any dietary or lifestyle factors that could contribute to the occurrence of nightmares?
Yes, certain dietary and lifestyle factors can contribute to the occurrence of nightmares. For example, consuming heavy meals before bedtime, excessive caffeine intake, or experiencing high stress levels can increase the likelihood of experiencing vivid or disturbing dreams.
10. Can nightmares serve a positive purpose despite their unsettling nature?
Yes, nightmares can serve a positive purpose. In many cultures and psychological theories, nightmares are seen as opportunities for growth, self-reflection, and resolving internal conflicts. They can provide insights into unresolved issues and serve as a catalyst for personal transformation.








