Nightmares in children can be a perplexing and concerning experience for both the child and their parents. These unsettling dreams during sleep can cause distress, anxiety, and disrupt a child’s overall well-being. Understanding the causes, effects, and coping strategies for nightmares is crucial in helping children manage and overcome these nighttime terrors. This article explores the various factors that contribute to nightmares in children, delves into the potential effects they can have, and provides practical strategies to cope with and alleviate these distressing dreams. Whether your child is experiencing occasional nightmares or frequent ones, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to help them navigate their dream world and achieve restful nights.
Causes of Nightmares in Children

Nightmares in children can have various causes, triggering these unsettling experiences during sleep. Understanding these underlying factors can help parents and guardians provide appropriate support and guidance to their children. One of the main causes is anxiety and stress. Children who are experiencing high levels of stress, such as changes in their environment, school pressures, or family conflicts, may be more prone to nightmares. Traumatic events, such as accidents, loss, or witnessing something distressing, can also lead to frequent nightmares. Additionally, certain sleep disorders like sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome can contribute to nightmares in children. By identifying the causes, parents can take proactive steps to address these issues and minimize the occurrence of nightmares.
1. Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress are significant contributors to nightmares in children. When children are experiencing high levels of anxiety or stress, their minds can become overwhelmed during sleep, leading to vivid and distressing dreams. Anxiety may stem from various sources, such as changes in routine, school pressures, social interactions, or family conflicts. These stressors can create a state of heightened arousal and emotional tension, making it difficult for children to fully relax and have peaceful sleep. The emotional turmoil experienced during the day can carry over into their dreams, manifesting as nightmares. It is important for parents and caregivers to identify and address the underlying causes of anxiety and stress in children, promoting a supportive and nurturing environment to help alleviate the occurrence of nightmares. Implementing stress-reducing activities, such as engaging in calming exercises or seeking professional help, if necessary, can be beneficial in minimizing the impact of anxiety and stress on a child’s sleep and overall well-being. For a deeper understanding of fear in dreams and the science behind nightmares, you can refer to the science behind nightmares: understanding fear in dreams.
2. Traumatic Events
Children who have experienced traumatic events may be at a higher risk of experiencing nightmares. Traumatic events can include accidents, natural disasters, physical or emotional abuse, witnessing violence, or the loss of a loved one. These distressing experiences can leave a lasting impact on a child’s psyche and manifest in their dreams during sleep. Nightmares related to traumatic events often involve re-experiencing the event, which can intensify feelings of fear, helplessness, and anxiety. It is crucial for parents and caregivers to provide a safe and supportive environment for the child to express their emotions and feelings related to the traumatic event. Engaging in open and honest conversations, offering reassurance and comfort, and seeking professional help if needed can aid in the healing process. Creating a sense of security and stability can help reduce the frequency of nightmares associated with traumatic events. Additionally, incorporating relaxation techniques and implementing a consistent bedtime routine can contribute to better sleep and minimize the occurrence of nightmares. For more tips on preventing nightmares, you can refer to this helpful guide. Exploring techniques such as lucid dreaming may also offer potential solutions for managing nightmares. Learn more about lucid dreaming as a possible approach to nightmares in children by checking out this informative article: The Science Behind Lucid Dreaming.
3. Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders can be a contributing factor to nightmares in children. Conditions such as sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, and insomnia can interfere with the quality and duration of a child’s sleep, increasing the likelihood of experiencing nightmares. Sleep apnea, characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep, disrupts the normal sleep cycle and can lead to vivid and distressing dreams. Restless leg syndrome, which causes uncomfortable sensations in the legs, can also disturb sleep patterns and contribute to nightmares. Insomnia, the inability to fall asleep or stay asleep, can result in fragmented sleep and an increased vulnerability to nightmares. Addressing and treating these sleep disorders, often with the help of medical professionals, can greatly improve a child’s sleep quality and reduce the frequency of nightmares. It is important for parents to recognize the signs of sleep disorders and take the necessary steps to seek appropriate medical intervention to alleviate their child’s sleep-related issues.
Effects of Nightmares on Children

Nightmares can have diverse effects on children, impacting their overall well-being and daily functioning. Understanding these effects is crucial in providing the necessary support and guidance to children who experience frequent nightmares. One of the primary effects is disturbed sleep. Nightmares can disrupt a child’s sleep patterns, leading to difficulty falling asleep, frequent waking during the night, and feelings of fatigue during the day. This can negatively impact their ability to concentrate, learn, and engage in daily activities. Additionally, nightmares can have a profound emotional impact on children. They may experience fear, anxiety, and a sense of helplessness, which can lead to mood changes, irritability, and even symptoms of depression. Nightmares can cause behavioral changes in children. They may try to avoid sleep, become clingy, or develop new fears and phobias. By recognizing these effects, parents can take proactive measures to address and mitigate the impact of nightmares on their children’s well-being.
1. Disturbed Sleep
Disturbed sleep is one of the effects that nightmares can have on children. When children experience nightmares, their sleep can be disrupted, leading to difficulty in falling asleep or frequent awakenings throughout the night. This can result in excessive daytime sleepiness and an overall decrease in the quality of their sleep. The interrupted sleep caused by nightmares can leave children feeling tired, irritable, and less focused during the day.
Disturbed sleep can impact a child’s physical health. Lack of quality sleep can weaken the immune system, making children more susceptible to illnesses and infections. It can also affect their growth and development, as sleep is crucial for the body to repair and rejuvenate.
In addition to the physical effects, disturbed sleep due to nightmares can also impact a child’s mental and emotional well-being. Children may experience anxiety, fear, and negative emotions associated with their nightmares, making it challenging for them to relax and feel at ease when it’s time to sleep. This can create a cycle of fear and anxiety around bedtime, leading to even more disrupted sleep.
In order to address the effects of disturbed sleep caused by nightmares, it is important for parents and guardians to establish a consistent bedtime routine that promotes relaxation and comfort. Creating a calming sleep environment, encouraging open communication about dreams and fears, and teaching relaxation techniques can all help alleviate the negative impact of nightmares on a child’s sleep.
2. Emotional Impact
The emotional impact of nightmares on children can be significant, affecting their overall well-being and daily functioning. When children experience distressing and vivid nightmares, it can leave them feeling fearful, anxious, and overwhelmed. These intense emotions may linger even after they wake up, making it difficult for them to go back to sleep or feel secure during waking hours. The recurring nature of nightmares can also lead to a constant state of fear and anticipation, creating a heightened sense of anxiety and unease in children. Nightmares can have a lasting impact on a child’s emotional development, influencing their self-confidence, resilience, and overall emotional stability. It is essential for parents and caregivers to provide a supportive and understanding environment for children to express their feelings and emotions related to their nightmares. By acknowledging and validating their emotions, parents can help children process their experiences, build resilience, and reduce the emotional impact of nightmares.
3. Behavioral Changes
The occurrence of nightmares in children can result in significant behavioral changes that can be observed during their waking hours. These changes may manifest in various ways, affecting their daily routines and interactions. Here are some common behavioral changes that children may exhibit as a result of nightmares:
1. Resistance to bedtime: Children who experience frequent nightmares may develop a reluctance to go to bed, fearing the recurrence of unsettling dreams. They may become anxious or exhibit signs of distress as bedtime approaches.
2. Sleep disturbances: Nightmares can disrupt a child’s sleep, leading to difficulties in falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. As a result, they may experience daytime drowsiness, fatigue, or have difficulties concentrating.
3. Changes in mood: Nightmares can have an emotional impact on children, resulting in changes in their overall mood and behavior. They may become irritable, moody, or exhibit signs of anxiety, sadness, or fear.
4. Regression: Some children may revert to earlier behaviors such as bedwetting, separation anxiety, or clinginess as a response to the emotional distress caused by nightmares.
5. Avoidance of triggers: Children may actively avoid situations, places, or people that they associate with their nightmares. They may express a heightened sense of fear or anxiety when exposed to these triggers.
6. Changes in social interactions: Nightmares can impact a child’s social interactions, leading to withdrawal from activities or decreased interest in socializing with peers. They may become more reserved or display changes in their play patterns.
It is important for parents and caregivers to observe and address these behavioral changes appropriately. Providing a supportive and understanding environment, engaging in open communication, and incorporating coping strategies can help children navigate the effects of nightmares on their behavior and overall well-being.
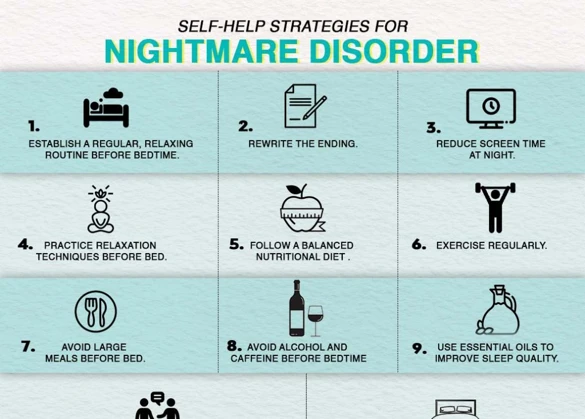
Coping Strategies for Nightmares in Children
When it comes to coping with nightmares in children, there are several effective strategies that can help alleviate their distress and promote better sleep. Here are some coping strategies for nightmares in children:
1. Maintain a Consistent Bedtime Routine: Establishing a consistent bedtime routine can help create a sense of security and stability for children, reducing their anxiety before sleep.
2. Create a Safe and Comfortable Sleeping Environment: Ensure that the child’s sleep environment is conducive to relaxation and comfort. This can include having a night light, a favorite stuffed animal, or soothing music.
3. Encourage Open Communication: Create a safe space for your child to express their fears and worries. Encouraging open communication can not only help them process their emotions but also build trust and reassurance.
4. Teach Relaxation Techniques: Teach your child various relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or visualization to help them calm themselves before bed and manage their anxiety.
5. Seek Professional Help if Needed: If nightmares persist or significantly impact your child’s well-being, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare professional or a pediatric sleep specialist.
By implementing these coping strategies, parents and caretakers can support their children in overcoming nightmares and improve their overall sleep quality and emotional well-being.
1. Maintain a Consistent Bedtime Routine
Maintaining a consistent bedtime routine is essential when it comes to managing nightmares in children. By establishing a regular pattern of activities before bed, you can create a sense of security and relaxation for your child. Here are some key strategies to implement for a consistent bedtime routine:
- Establish a regular sleep schedule: Set a consistent bedtime and wake-up time for your child, even on weekends or holidays. This helps regulate their internal body clock and promotes better sleep quality.
- Create a calming pre-bedtime routine: Encourage activities that help your child wind down, such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or practicing gentle stretches. Avoid stimulating activities like screen time or rough play close to bedtime.
- Create a soothing sleep environment: Ensure that your child’s bedroom is quiet, dark, and at a comfortable temperature. Consider using a nightlight or a favorite stuffed animal for added comfort.
- Limit food and drinks before bed: Avoid giving your child sugary or caffeinated foods and drinks close to bedtime, as these can interfere with sleep. Opt for a light and healthy snack if needed.
- Encourage relaxation techniques: Teach your child relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation. These techniques can help reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm before sleep.
By consistently following a bedtime routine, your child will associate these activities with sleep, creating a sense of predictability and security. This can help minimize the occurrence of nightmares and promote better overall sleep quality.
2. Create a Safe and Comfortable Sleeping Environment
Creating a safe and comfortable sleeping environment for children is essential in reducing the likelihood of nightmares. This involves setting up a space that promotes relaxation and feelings of security. Here are some tips to achieve this:
1. Choose the right bedding: Opt for soft and cozy bedding materials that your child finds comfortable. Ensure that the mattress and pillows provide adequate support for their growing bodies.
2. Keep the bedroom dark and quiet: Use blackout curtains or blinds to block out external light sources that may disrupt your child’s sleep. Minimize noise by using earplugs or a white noise machine if necessary.
3. Regulate temperature: Maintain a comfortable temperature in the bedroom, neither too hot nor too cold. Use appropriate clothing and bedding to ensure your child stays cozy throughout the night.
4. Remove distractions: Eliminate any distractions that may disturb your child’s sleep, such as electronic devices, bright lights, or excessive clutter in the bedroom.
5. Ensure safety measures: Install safety gates on stairs, secure furniture to the walls, and keep potentially dangerous objects out of reach. This will help create a worry-free environment, promoting a sense of security for your child.
6. Use nightlights or comforting objects: If your child feels uneasy in the dark, consider using a nightlight or providing a comforting object, like a stuffed animal or blanket, for them to hold onto during sleep.
By implementing these strategies, you can establish a safe and comfortable sleeping environment that promotes peaceful and restorative sleep for your child, reducing the likelihood of nightmares.
3. Encourage Open Communication
Encouraging open communication is a crucial strategy in addressing nightmares in children. By creating a safe and supportive environment, parents can facilitate open discussions about their child’s fears, anxieties, and experiences during sleep. It’s important to actively listen to your child without judgment and offer reassurance. Letting them know that it is normal to have nightmares and that they can share their dreams can help alleviate their anxiety. Encourage them to express their feelings and thoughts about their nightmares, allowing them to release any pent-up emotions. Validate their emotions and let them know that you understand and are there to support them. This can help build trust and strengthen the parent-child relationship. Emphasize that nightmares are not a reflection of reality and provide comforting and factual information to help ease their fears. By promoting open communication, parents can empower their children to express themselves and navigate their dream world with confidence.
4. Teach Relaxation Techniques
Teaching relaxation techniques to children can be a valuable tool in managing and reducing nightmares. These techniques aim to promote a sense of calmness and relaxation, helping children unwind before bedtime and creating a peaceful sleep environment. One effective relaxation technique is deep breathing exercises. Encourage your child to take slow, deep breaths, inhaling through their nose and exhaling through their mouth. This can help slow down their heart rate and relax their body. Another technique is progressive muscle relaxation, where children systematically tense and release their muscles, starting from their toes and working all the way up to their head. This helps release tension and promotes overall relaxation. Guided imagery is another helpful technique, where children visualize a peaceful and happy place, engaging their senses to create a vivid mental image. This can distract their mind from negative thoughts and promote a sense of tranquility. Additionally, incorporating mindfulness activities such as yoga or meditation can further enhance relaxation and promote better sleep. By teaching these techniques and practicing them regularly with your child, you can empower them to manage their stress and anxiety, reducing the likelihood of nightmares and promoting healthier sleep patterns.
5. Seek Professional Help if Needed
If your child’s nightmares persist despite implementing coping strategies and providing a supportive environment, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. Consulting with a pediatrician, therapist, or sleep specialist can offer valuable insights and guidance. Professionals who specialize in children’s mental health can help assess the underlying causes of the nightmares and develop a tailored treatment plan. This may involve cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which can help children identify and challenge negative thought patterns that contribute to their nightmares. Understanding the science behind nightmares and their impact on children’s emotions can aid professionals in providing specific interventions to address the child’s needs. They may also recommend medical interventions or medications, if necessary, to manage any underlying sleep disorders or anxiety that may be contributing to the nightmares. Seeking professional help ensures that your child receives the appropriate support and interventions to alleviate the distress caused by nightmares, ultimately promoting their overall well-being and quality of sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nightmares in children can be distressing experiences that affect their overall well-being. It is important for parents and guardians to understand the causes, effects, and coping strategies associated with nightmares in order to provide the necessary support to their children. The causes of nightmares can range from anxiety and stress to traumatic events and sleep disorders. By identifying these underlying factors, parents can address the root causes and help alleviate the frequency and intensity of nightmares. The effects of nightmares on children can manifest in disturbed sleep, emotional impact, and behavioral changes. It is crucial for parents to create a safe and comfortable sleeping environment, encourage open communication, and teach relaxation techniques to help children cope with nightmares. Seeking professional help should be considered if nightmares persist and significantly impact the child’s well-being. With the right strategies and support, children can overcome nightmares and achieve restful nights of sleep, leading to improved overall mental and emotional health.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do children have nightmares?
Children can have nightmares due to a variety of reasons. Major causes include anxiety and stress, traumatic events, and sleep disorders.
2. Are nightmares common in children?
Yes, nightmares are common in children. Around 50-85% of children experience nightmares at some point in their lives.
3. At what age do nightmares typically start?
Nightmares can start as early as 2 years old, but they are most common in children aged 3-6 years.
4. Can nightmares be a sign of an underlying problem?
Nightmares can sometimes be a sign of underlying issues, such as emotional distress, fear, or trauma. It’s important to assess the child’s overall well-being and seek professional help if needed.
5. How can I help my child cope with nightmares?
There are various coping strategies you can try, including establishing a consistent bedtime routine, creating a safe sleeping environment, encouraging open communication, teaching relaxation techniques, and seeking professional help if necessary.
6. Is it normal for my child to remember their nightmares?
It is common for children to remember their nightmares, especially if they wake up during or immediately after the dream. However, their memory of nightmares may fade quickly over time.
7. Should I wake up my child after a nightmare?
If your child is visibly upset or scared, it is best to comfort them and reassure them that they are safe. However, it is generally recommended to avoid fully waking them up unless necessary, as it may disrupt their sleep further.
8. Can certain foods or activities trigger nightmares in children?
While there is no direct scientific evidence linking specific foods or activities to nightmares in children, some studies suggest that consuming heavy or spicy meals close to bedtime or engaging in stimulating activities before sleep may increase the likelihood of nightmares.
9. How long do nightmares typically last?
Nightmares typically last for a few minutes, but the impact on a child’s emotional state can linger throughout the night and even into the morning.
10. When should I seek professional help for my child’s nightmares?
If nightmares persist for an extended period or significantly impact your child’s daily life, such as causing excessive fear, affecting their sleep patterns, or resulting in behavioral changes, it may be beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional or a pediatric sleep specialist.