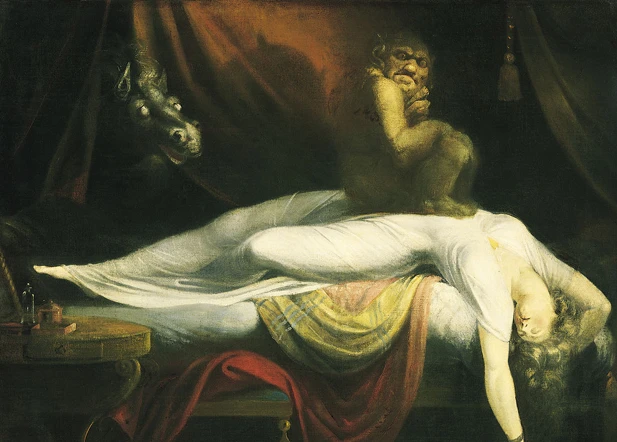
Introduction

Sleep paralysis is a perplexing phenomenon that has been experienced and interpreted differently across various cultures and belief systems. It is a state of temporary muscle paralysis that occurs upon waking up or falling asleep, during which individuals may also experience vivid hallucinations and a sense of being unable to move or speak. While sleep paralysis is primarily considered a medical condition in Western cultures, it holds deeper cultural, spiritual, and supernatural significance in Eastern and Indigenous cultures. Understanding the diverse interpretations and coping mechanisms associated with sleep paralysis in different cultures can shed light on the intriguing intersection between science, folklore, and spiritual beliefs.
What is sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a mysterious and often unsettling experience characterized by a temporary inability to move or speak while transitioning between sleep and wakefulness. This phenomenon typically occurs during two moments in the sleep cycle: as individuals are falling asleep (known as hypnagogic or predormital sleep paralysis) or as they are awakening (known as hypnopompic or postdormital sleep paralysis). During these episodes, individuals may also experience hallucinations, which can be visual, auditory, or tactile in nature. Some people report seeing shadowy figures or supernatural beings, feeling pressure on their chest, or hearing strange noises. Despite its alarming nature, sleep paralysis is usually harmless and lasts only a few seconds or minutes. However, the experience can be quite distressing and even terrifying for those who encounter it. If you want to learn more about sleep paralysis, you can read our article on the Understanding Sleep Paralysis page. It is important to note that sleep paralysis is often associated with other sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy, sleep apnea, or insomnia. To get a better understanding of the link between sleep paralysis and other sleep disorders, you can refer to our article on the Link Between Sleep Paralysis and Other Sleep Disorders page. If you or someone you know experiences sleep paralysis and would like some helpful tips for coping with it, you can check out our article on the Tips for Coping with Sleep Paralysis page.
Sleep Paralysis in Western Cultures
Sleep paralysis in Western cultures is a phenomenon that has been explored from various perspectives, including folklore, mythology, and scientific explanations. In terms of folklore and mythology, sleep paralysis has often been attributed to supernatural beings or entities, such as demons, witches, or spirits. These stories have been passed down through generations and have contributed to the fear and uneasiness associated with sleep paralysis. From a scientific standpoint, Western cultures have sought to understand sleep paralysis through physiological and psychological explanations. It is believed to be a result of the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle being disrupted, causing a temporary state of muscle atonia. Additionally, factors such as stress, sleep deprivation, and sleep disorders have been identified as potential triggers for sleep paralysis. Coping mechanisms in Western cultures typically involve reassurance, education about the condition, and implementing good sleep hygiene practices to reduce the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
1. Folklore and Mythology
Folklore and mythology often provide intriguing explanations and interpretations for sleep paralysis in Western cultures. Throughout history, various supernatural entities have been associated with this phenomenon. One such example is the “Old Hag” or “Night Hag” from European folklore. According to the tales, this malevolent creature would sit or crouch on the chest of the sleeping individual, causing the feeling of being pinned down. Another common explanation in folklore is that sleep paralysis is the result of demonic or evil spirits attempting to possess or torment the person. This belief can be found in different cultures worldwide, with variations in the names and descriptions of the entities involved. In addition to these supernatural explanations, some myths suggest that sleep paralysis is a punishment for sinful behavior or a sign of impending doom. These cultural beliefs and mythologies have shaped the way sleep paralysis is understood and perceived in Western societies, often adding an element of fear and mystery to the experience.
2. Scientific Explanations
Scientific explanations for sleep paralysis revolve around understanding the physiological and neurological factors that contribute to this phenomenon. Here are some key scientific explanations for sleep paralysis:
- Sleep Disruptions: Sleep paralysis often occurs when there is a disruption in the normal sleep-wake cycle. It is closely associated with rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, the stage of sleep where dreams occur. During REM sleep, the brain sends signals to inhibit muscle movement, preventing us from acting out our dreams. In sleep paralysis, this mechanism malfunctions, causing temporary muscle paralysis while the mind remains awake.
- Sleep Deprivation: Lack of quality sleep and chronic sleep deprivation can increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis. This can occur due to irregular sleep patterns, such as insomnia, or sleep disorders like sleep apnea, which interrupt the normal sleep cycle.
- Stress and Anxiety: Emotional stress and anxiety have been linked to the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes. These factors can disrupt sleep patterns and contribute to the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
- Neurochemical Imbalances: Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, have been suggested as potential contributors to sleep paralysis. These imbalances may affect the regulation of REM sleep and the inhibition of muscle movement during sleep.
It is important to note that while these scientific explanations provide valuable insights into the physical mechanisms behind sleep paralysis, they do not account for the cultural and spiritual interpretations that have historically been associated with this phenomenon. Understanding the interplay between scientific explanations and cultural beliefs is essential for a comprehensive understanding of sleep paralysis.
3. Coping Mechanisms
Coping with sleep paralysis can be challenging, especially for individuals who experience it frequently or find it particularly distressing. Fortunately, there are various coping mechanisms that can help alleviate the fear and discomfort associated with sleep paralysis episodes.
1. Education and Awareness: Gaining knowledge about sleep paralysis can be empowering and help individuals understand that it is a relatively common and harmless condition. Learning about the science behind sleep paralysis and its connection to the sleep cycle can provide reassurance and reduce anxiety when experiencing an episode.
2. Sleep Hygiene: Practicing good sleep habits and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can contribute to overall sleep quality and potentially reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, avoiding stimulating substances like caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can all positively impact sleep.
3. Stress Management: Stress and anxiety often exacerbate sleep paralysis episodes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help reduce overall stress levels, potentially minimizing the frequency or intensity of sleep paralysis experiences.
4. Sleep Position: Some individuals find that adjusting sleep positions can help prevent sleep paralysis. Sleeping on the side instead of the back is commonly suggested as a way to reduce the likelihood of experiencing an episode.
5. Seeking Emotional Support: Sharing experiences with others who have also experienced sleep paralysis can provide a sense of validation and support. Online communities or support groups dedicated to sleep disorders can offer a safe space for individuals to discuss their experiences and gain insights into coping strategies.
It is important to note that while coping mechanisms can be beneficial, consulting with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist is still recommended, especially if sleep paralysis is causing significant distress or interfering with daily life. A professional can provide support, guidance, and potential treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Sleep Paralysis in Eastern Cultures
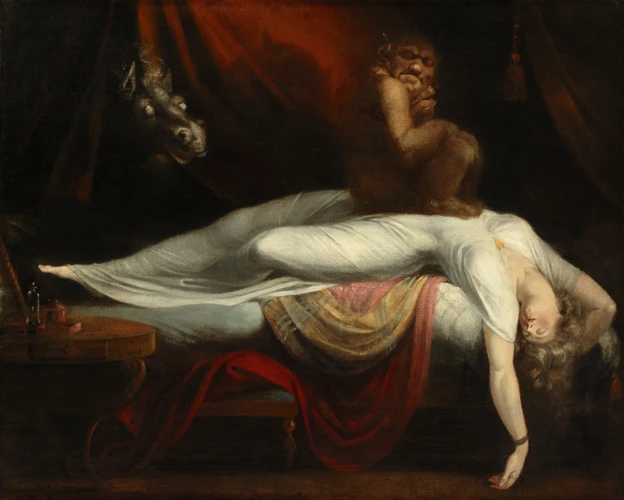

Sleep paralysis holds cultural significance and is interpreted differently in Eastern cultures, reflecting the deep-rooted beliefs and superstitions of these societies. In many Eastern cultures, sleep paralysis is commonly attributed to spiritual and supernatural causes rather than mere physiological factors. It is often seen as a potential encounter with evil spirits or malevolent entities, believed to be responsible for the immobilizing sensation and hallucinations. These entities are thought to be more active during the night, making sleep paralysis a terrifying experience associated with ghostly encounters. Eastern cultures may consider sleep paralysis as a sign of spiritual awakening or heightened intuition, indicating a connection with the spiritual realm. In some belief systems, it is linked to the concept of astral projection or out-of-body experiences, where the soul is believed to travel beyond the physical body during sleep. Practices like meditation, prayer, and protective rituals are often employed to ward off negative energies and ensure spiritual protection during sleep. The cultural beliefs surrounding sleep paralysis in Eastern cultures provide a fascinating insight into their rich folklore, spiritual traditions, and the complex relationship between the physical and metaphysical realms.
1. Cultural Beliefs and Superstitions
Cultural beliefs and superstitions surrounding sleep paralysis vary across different Eastern cultures. In many Asian cultures, sleep paralysis is often attributed to the presence of malevolent spirits or supernatural entities. Some believe that these spirits sit on the chest of the person, leading to the sensation of being pinned down. In Japan, this phenomenon is known as “kanashibari,” which translates to “bound or fastened in metal.” It is believed to be caused by a type of spirit called “kanashibari-oni.” In Chinese culture, sleep paralysis is linked to the concept of “gui ya,” which means “ghost pressure.” It is believed that the soul temporarily leaves the body during sleep, making it susceptible to evil spirits or ghosts. Similar beliefs exist in Thai folklore, where sleep paralysis is attributed to a ghost called “Phi Am.” It is believed that Phi Am sits on the chest of the person, causing the paralysis. In some cultures, specific rituals or talismans are used to ward off these malevolent spirits or protect against sleep paralysis. These cultural beliefs and superstitions demonstrate the rich tapestry of interpretations surrounding sleep paralysis in Eastern cultures.
2. Spiritual and Supernatural Explanations
In Eastern cultures, sleep paralysis is often attributed to spiritual and supernatural explanations. These beliefs stem from the idea that during sleep paralysis, individuals are vulnerable to otherworldly entities or spirits. In some cultures, it is believed that during this state, a person’s soul or consciousness becomes detached from their physical body, allowing them to enter the realm of spirits or the supernatural. This interpretation often leads to the belief that the hallucinations experienced during sleep paralysis are actually encounters with these entities. In some cases, it is believed that sleep paralysis is a result of malevolent spirits or even demonic possession. These supernatural explanations can be deeply ingrained in cultural beliefs and may influence how individuals cope with or perceive sleep paralysis. For instance, individuals may seek spiritual interventions, such as prayers, rituals, or protective amulets, to ward off negative entities or to seek guidance and protection from benevolent forces. It is important to note that these interpretations and practices may vary greatly among different Eastern cultures and religious traditions. While some view sleep paralysis as a spiritual or supernatural encounter, others may attribute it to other factors, such as karma, past lives, or imbalances of energy.
3. Healing Practices
Healing practices associated with sleep paralysis in Eastern cultures vary widely, reflecting the diverse spiritual and cultural beliefs prevalent in these regions. Some common approaches to healing include:
1. Spiritual Cleansing: In certain Eastern cultures, it is believed that sleep paralysis is caused by negative energy or spiritual disturbances. To counteract these influences, individuals may seek spiritual cleansing rituals. These rituals often involve the use of herbs, prayers, and incense to purify the body and environment, creating a protective barrier against negative entities.
2. Energy Healing: Energy healing techniques, such as Reiki or Qi Gong, are utilized in certain Eastern cultures to address sleep paralysis. These practices involve the transfer of healing energy from the practitioner to the individual experiencing sleep paralysis. By balancing and harmonizing the body’s energy system, these healing modalities aim to alleviate the symptoms and prevent further occurrences of sleep paralysis.
3. Meditation and Mindfulness: Meditation and mindfulness practices are commonly employed in Eastern cultures to promote overall well-being and balance. They can also be beneficial for individuals experiencing sleep paralysis. Regular meditation practices help calm the mind and reduce stress, potentially reducing the frequency and intensity of sleep paralysis episodes.
4. Herbal Remedies: Traditional herbal remedies are often utilized in Eastern cultures to address sleep-related issues, including sleep paralysis. These remedies may include the use of specific herbs, such as valerian root or chamomile, known for their calming and sleep-inducing properties. Herbal teas or supplements are commonly consumed to promote a more restful sleep and potentially reduce the occurrence of sleep paralysis episodes.
5. Seeking guidance from spiritual healers or shamans: In some Eastern cultures, individuals experiencing sleep paralysis may consult spiritual healers or shamans. These spiritual guides offer guidance, prayers, rituals, and sometimes even herbal remedies to address the underlying spiritual causes of sleep paralysis.
It is important to note that while these healing practices may hold cultural and spiritual significance, seeking professional medical advice is always recommended to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to sleep paralysis.
Sleep Paralysis in Indigenous Cultures
Sleep paralysis holds deep cultural significance in Indigenous cultures around the world, where it is often intertwined with spiritual beliefs and practices. In these cultures, sleep paralysis is seen as a gateway to the spirit world, offering opportunities for spiritual encounters and communication with ancestors or guardian spirits. Shamanism plays a significant role in understanding and interpreting sleep paralysis in Indigenous cultures, as shamans are believed to have the ability to navigate between the physical and spiritual realms. Rituals and ceremonies are conducted to protect individuals from negative spiritual influences during sleep paralysis episodes and to harness the potential spiritual insights that can be gained from these experiences. The cultural understanding of sleep paralysis in Indigenous communities underscores the interconnectedness between the human and spiritual dimensions of existence, offering a unique perspective on this enigmatic phenomenon.
1. Shamanism and Spiritual Encounters
Shamanism and spiritual encounters play a significant role in the interpretation of sleep paralysis in many indigenous cultures. In these cultures, sleep paralysis is often regarded as a supernatural experience rather than a medical condition. Shamans, who are the spiritual leaders and healers in these communities, are believed to have the ability to communicate with the spirit world. In the context of sleep paralysis, it is believed that during these episodes, the individual’s soul leaves their body and interacts with the spiritual realm. The paralysis is seen as a necessary safeguard to prevent the physical body from acting out the individual’s experiences in the spiritual realm. Some indigenous cultures also view sleep paralysis as a sacred initiation or a rite of passage, where the person is being tested or chosen by the spirits. The encounters during sleep paralysis are often seen as opportunities for communication with ancestors, guardian spirits, or other spiritual entities. Depending on the specific beliefs of the culture, these encounters can be seen as positive or negative, with some individuals seeking guidance and protection from these spiritual encounters, while others may fear them. The role of shamans in these cultures is crucial in helping individuals navigate and make sense of these experiences, providing spiritual guidance, and offering rituals or ceremonies to heal and protect against negative spiritual encounters. The interpretation of sleep paralysis as a spiritual encounter in indigenous cultures highlights the rich and diverse ways in which different belief systems understand and explain this phenomenon.
2. Rituals and Ceremonies
Rituals and ceremonies hold significant importance in many indigenous cultures when it comes to dealing with sleep paralysis. These rituals and ceremonies are often performed by shamans or spiritual leaders who possess the knowledge and connection to the spiritual realm. In some cultures, specific rituals are conducted to cleanse the affected individual’s energy and to protect them from negative entities that may be causing the sleep paralysis episodes. These rituals can involve the use of sacred herbs, incense, or smudging ceremonies to purify the space and the individual’s energy field. Shamanic drumming or chanting may also be employed to create a sacred and protective atmosphere. Additionally, some indigenous cultures believe in the power of dreamcatchers to ward off evil spirits and prevent sleep paralysis. Dreamcatchers are often hung near the individual’s sleeping area to capture and filter any negative energies or spirits that may be causing the episodes. The belief is that these rituals and ceremonies help restore balance and harmony within the affected individual, providing spiritual protection and alleviating the experiences of sleep paralysis.
3. Ancestors and Guardian Spirits
In Indigenous cultures, sleep paralysis is often attributed to the presence of ancestors and guardian spirits. It is believed that during sleep paralysis episodes, these entities are attempting to communicate with the individual or provide guidance. The experience is seen as a form of spiritual encounter rather than a medical condition. Indigenous cultures have long traditions of honoring and seeking guidance from their ancestors, and sleep paralysis is seen as a doorway into the spiritual realm. It is thought that the ancestors or guardian spirits may be visiting the individual to deliver important messages or warnings. In some cases, individuals may even enter into a trance-like state during sleep paralysis, allowing them to connect more deeply with the spiritual realm. This belief in the presence of ancestors and guardian spirits during sleep paralysis is deeply ingrained in Indigenous cultures and is met with reverence and respect.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep paralysis is a fascinating phenomenon that is influenced and interpreted differently across various cultures and belief systems. While Western cultures tend to view sleep paralysis primarily through a scientific lens, acknowledging the physiological and psychological factors at play, Eastern cultures often attribute supernatural or spiritual significance to these experiences. Indigenous cultures, on the other hand, associate sleep paralysis with shamanic encounters, ancestral wisdom, and rituals. The varied explanations and coping mechanisms associated with sleep paralysis highlight the intersection of science, folklore, and spirituality. Regardless of the cultural context, sleep paralysis can be a distressing experience, and understanding its different interpretations can help individuals navigate and cope with their encounters. Further research and cross-cultural studies can provide valuable insights into this enigmatic phenomenon, ultimately shedding light on the complex relationship between sleep, culture, and the human mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can sleep paralysis be dangerous?
No, sleep paralysis itself is not dangerous. While it can be a frightening experience, it is usually harmless and temporary.
2. Why does sleep paralysis occur?
The exact cause of sleep paralysis is not fully understood. It is believed to be related to disruptions in the sleep-wake cycle and the transition between different stages of sleep.
3. Is sleep paralysis a common phenomenon?
Yes, sleep paralysis is relatively common, with studies suggesting that about 20-40% of the population may experience it at least once in their lifetime.
4. Can sleep paralysis be prevented?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent sleep paralysis, adopting healthy sleep habits, managing stress levels, and creating a comfortable sleep environment may reduce the likelihood of experiencing it.
5. Is there a connection between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming?
Yes, there is a link between sleep paralysis and lucid dreaming. Some individuals may transition from sleep paralysis into a lucid dream state, where they are aware of their dream and can exert some control over it.
6. Can certain medications or substances trigger sleep paralysis?
Yes, certain medications, such as those used to treat narcolepsy or insomnia, and substances like alcohol or illicit drugs, may increase the likelihood of experiencing sleep paralysis.
7. Are there any long-term effects of sleep paralysis?
Sleep paralysis itself does not have any known long-term effects on physical or mental health. However, repeated episodes of sleep paralysis can cause distress, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
8. Can sleep paralysis be inherited?
There may be a genetic component to sleep paralysis, as studies have found a higher prevalence of the condition among individuals with a family history of sleep paralysis or related sleep disorders.
9. Can stress or sleep deprivation trigger sleep paralysis?
Yes, both stress and sleep deprivation have been associated with an increased risk of experiencing sleep paralysis. It is essential to manage stress levels and prioritize sufficient sleep for overall well-being.
10. Should I be concerned if I experience sleep paralysis frequently?
If you frequently experience sleep paralysis and it is significantly affecting your sleep quality or overall well-being, it may be helpful to consult a healthcare professional who specializes in sleep disorders for further evaluation and guidance.








