Have you ever experienced the sensation of being aware that you are dreaming while you are still asleep? This phenomenon, known as lucid dreaming, has captured the fascination of humans for centuries. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to consciously navigate and manipulate their dreams, blurring the line between imagination and reality. However, the ethical and moral implications of this extraordinary ability raise profound questions about the boundaries of our unconscious minds. In this article, we will delve into the enigmatic world of lucid dreaming, examining its definition, scientific research, and exploring the ethical dimensions, societal considerations, as well as the benefits and perceived dangers associated with this phenomenon. Join us as we venture into the depths of the human mind, wrestling with its complexities and pondering the profound implications of lucid dreaming.
Understanding Lucid Dreaming

Lucid dreaming is a remarkable phenomenon in which an individual becomes consciously aware of being in a dream state while still asleep. Unlike a regular dream, in which the dreamer remains unaware of the dream’s illusory nature, during lucid dreaming, individuals possess the ability to recognize and identify the dream as a creation of their own mind. This awareness grants them the opportunity to actively participate in and manipulate the dream’s unfolding events. The experience of lucid dreaming varies from person to person, with some individuals experiencing it spontaneously, while others develop the skill through practice and technique. The defining characteristic of lucid dreaming is the presence of self-awareness and cognitive control within the dream environment, empowering individuals to engage with and shape their dreams in unexpected and exciting ways.
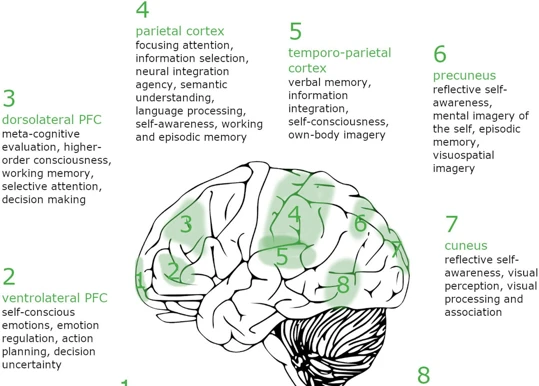
Scientific interest in lucid dreaming has grown significantly in recent years, leading to a better understanding of this intriguing phenomenon. Researchers have conducted various studies using neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), to examine the brain activity associated with lucid dreaming. These studies have revealed distinct patterns of brain activation during lucid dreaming, particularly in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions such as self-awareness, decision-making, and introspection. These findings indicate that lucid dreaming is a unique and identifiable state of consciousness, separate from both waking and regular dreaming states. Additionally, research has explored the potential therapeutic applications of lucid dreaming, such as treating nightmares, enhancing creativity, and aiding in self-reflection and personal growth.
Usefull links:
- Famous Lucid Dreamers in History
- Lucid Dreaming: Benefits and Challenges
- Lucid Dreaming and Self-Reflection: Exploring the Subconscious Mind
Definition and Characteristics
Lucid dreaming is defined as the state of being aware that one is dreaming while the dream is still in progress. It is a unique occurrence where the dreamer becomes a conscious participant in their dream world. This awareness allows individuals to have a level of control over their dreams, enabling them to manipulate the dream environment, interact with dream characters, and even influence the course of events.
One of the distinctive features of lucid dreaming is the ability to differentiate between the dream world and reality. Dreamers often report a sense of heightened clarity, vividness, and sensory perception within their dreams. They may notice details that are usually overlooked in regular dreams, such as the texture of objects, the taste of food, or the feeling of the wind on their skin. This enhanced awareness can create a sense of awe and wonder within the dream, as well as a feeling of empowerment and freedom.
While the prevalence of lucid dreaming varies among individuals, research suggests that it is a relatively common experience. Surveys have indicated that approximately 55% of people have had at least one lucid dream in their lifetime, with some individuals experiencing them more frequently. It is worth noting that lucid dreams can occur spontaneously, but there are also techniques and practices that individuals can employ to increase their likelihood of having lucid dreams, such as reality checks, dream journaling, and meditation.
Lucid dreaming is a fascinating state of consciousness that offers unique opportunities for self-exploration, creativity, and personal growth. The ability to be fully conscious and engaged in the dream world opens up a realm of possibilities and raises intriguing questions about the nature of our consciousness and the boundaries of our minds.
Scientific Research on Lucid Dreaming
Scientific research on lucid dreaming has shed light on the underlying mechanisms and potential benefits of this unique dream state. Neuroscientists and psychologists have utilized various methods to study and understand the phenomenon, including brain imaging techniques and self-reporting surveys.
One area of interest in scientific research is the brain activity associated with lucid dreaming. Neuroimaging studies using techniques such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have revealed distinct patterns of brain activation during lucid dreaming. These studies have shown increased activity in the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for executive functions like self-awareness, decision-making, and introspection. Understanding the neural correlates of lucid dreaming can help unravel its mechanisms and distinguish it from regular dream states.
Another aspect of scientific research on lucid dreaming is exploring the potential benefits and applications. Studies have shown that lucid dreaming can be used as a tool for enhancing creativity and problem-solving. During lucid dreaming, individuals can actively engage with their dreams, exploring different scenarios and possibilities. This creative exploration can extend beyond the dream state and be applied to real-life situations, leading to enhanced creative thinking and problem-solving skills.
Research has shown that lucid dreaming can have therapeutic benefits. For individuals suffering from nightmares or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), lucid dreaming techniques can be used to confront and overcome traumatic experiences within the safety of a dream environment. Lucid dreaming therapy has shown promising results in reducing the frequency and intensity of nightmares and providing psychological healing.
Scientific research on lucid dreaming continues to expand our understanding of this mysterious phenomenon. By uncovering the brain processes involved and exploring its potential applications, researchers are unlocking the possibilities of harnessing lucid dreaming for personal growth, creativity, and psychological well-being.
Exploring Ethical Dimensions

Ethical considerations arise when we delve into the realm of lucid dreaming, as the ability to consciously navigate and manipulate dreams raises important questions about the influence we have over our own thoughts and experiences.
- Influencing Dream Content: One ethical dimension of lucid dreaming revolves around the act of intentionally influencing the content of dreams. While this ability allows individuals to explore their fantasies or desires, it raises concerns about the potential for abuse or exploitation. Some argue that actively manipulating dream content could lead to harmful obsessions or reinforce negative behavior patterns.
- Manipulating Dream Characters: Another ethical consideration is the manipulation of dream characters within the dream world. Lucid dreamers can engage with, control, or even harm dream characters, raising questions about the moral implications of these actions. Should dream characters be treated as conscious entities with their own rights and feelings, or are they mere constructs of the dreamer’s mind?
- Moral Responsibility within Dreams: The concept of moral responsibility within dreams also enters the ethical discussion surrounding lucid dreaming. If actions in dreams have no direct consequences in waking life, some argue that ethical boundaries should be loosened or even discarded within the dream world. However, others contend that moral principles should still apply, as dreams can shape our subconscious mind and influence our behavior when awake.
- Avoiding Harm and Consent: The issue of consent plays a crucial role in the ethical exploration of lucid dreaming. Engaging in activities within dreams that involve other dream characters raises the question of whether explicit consent is necessary. Lucid dreamers must grapple with the responsibility of ensuring that their actions and interactions within their dreams do not cause harm or violate the boundaries of others.
In navigating these ethical dimensions of lucid dreaming, it becomes essential to reflect on the potential consequences of our actions within the dream world and consider the moral implications of consciously shaping our dreams.
Influencing Dream Content
In lucid dreaming, one of the key ethical considerations is the ability to influence the content of the dream itself. When individuals are aware that they are dreaming, they have the power to manipulate their dream environment, characters, and events. This newfound control over the dream world raises questions about the morality of deliberately altering the dream content. On one hand, individuals may use this ability to fulfill their fantasies, explore their desires, or experience things that are otherwise impossible in waking life. This can provide a sense of liberation, creativity, and personal growth. However, on the other hand, it presents the potential for ethical concerns. For instance, individuals may engage in activities within their dreams that they consider immoral, such as engaging in violent or harmful behavior towards dream characters. The key issue here is the blurred line between the dream world and reality – while actions within dreams may not have direct consequences in the waking world, they could still impact individuals emotionally and morally. The ethical implications of influencing dream content raise important questions about personal responsibility, empathy, and the potential psychological effects of our actions within the dreamscape.
Manipulating Dream Characters
In the world of lucid dreaming, one of the most intriguing aspects is the ability to manipulate dream characters. Within the dream state, individuals have the power to alter the behaviors, appearances, and interactions of the characters that populate their dreams. This unique capability raises ethical and moral implications as dream characters are essentially projections of the dreamer’s subconscious mind. By manipulating these characters, individuals have the opportunity to explore their own psyche and engage in introspection. However, there is a fine line between harmless experimentation and potential harm or exploitation. It is crucial for lucid dreamers to approach the manipulation of dream characters with respect, taking into consideration the potential consequences and ensuring that the boundaries of consent and ethical treatment are upheld.
Moral Responsibility within Dreams
Moral responsibility within dreams raises thought-provoking questions about the extent to which individuals are accountable for their actions and behavior in the dream world. One argument suggests that since dreams are creations of one’s own mind, where no external consequences exist, individuals bear no moral responsibility for their actions within dreams. Dreams are often surreal, irrational, and disconnected from reality, making it challenging to impose moral judgments on their content or the dreamer’s behavior. However, an opposing viewpoint argues that dreams reflect one’s innermost thoughts, desires, and fears, and may provide insights into a person’s moral character. In this perspective, individuals have a responsibility to critically reflect on their dreams, exploring the beliefs and values that guide their actions during the dream state. Additionally, lucid dreaming introduces another layer of complexity. When individuals become aware that they are dreaming, they may actively choose to engage in behaviors that they would consider immoral or unethical in waking life. This raises further questions about the implications of such actions on an individual’s moral compass and the potential for moral desensitization. It is important to note that moral responsibility within dreams is a philosophical debate, and there is no definitive answer. Exploring this topic prompts contemplation on the nature of morality, consciousness, and the intricacies of the human mind.
Avoiding Harm and Consent
In the realm of lucid dreaming, where dreamers have the ability to manipulate the dream environment and interact with dream characters, the question of avoiding harm and obtaining consent becomes crucial. The power to influence the content of a dream raises ethical considerations about the boundaries of one’s actions within the realm of the unconscious mind. It is essential for lucid dreamers to approach their dream scenarios with a sense of responsibility and respect for the well-being of others, even though the dream characters they encounter may be projections of their own subconscious.
One perspective on this matter emphasizes the importance of obtaining consent from dream characters before attempting to control or manipulate them. Advocates argue that dream characters possess a degree of autonomy and should be approached as individuals with rights, whether they are the reflection of the dreamer’s own psyche or not. By seeking consent, lucid dreamers demonstrate an ethical approach, recognizing the importance of consent and personal agency even in the dream world.
Similarly, avoiding harm is another ethical consideration in lucid dreaming. Dream characters, even if they are mere figments of the dreamer’s imagination, may manifest emotions and experiences that feel genuine. Inflicting harm on dream characters in a lucid dream can have psychological consequences for the dreamer once they wake up. It is essential for lucid dreamers to be mindful of their actions, taking care to preserve the well-being and emotional integrity of the dream characters they encounter.
It is important to note, however, that individuals have different perspectives on the ethical responsibilities within lucid dreaming. Some argue that since lucid dreams are a creation of the dreamer’s mind, there is no obligation to adhere to ethical standards or consider the well-being of dream characters. This viewpoint suggests that the dream world is essentially a playground for exploration and personal desires without the constraints of societal norms.
Ultimately, the ethical considerations of avoiding harm and obtaining consent in lucid dreaming reflect larger ethical and moral debates about the nature of consciousness, personal agency, and the boundaries of our actions. As the field of lucid dreaming continues to be explored, further discussions and research are necessary to navigate these complex ethical dimensions and strike a balance between the freedom of exploration and the respect for the well-being of dream characters.
Usefull links:
- Famous Lucid Dreamers in History
- Lucid Dreaming: Benefits and Challenges
- Lucid Dreaming and Self-Reflection: Exploring the Subconscious Mind
Societal and Cultural Considerations

Societal and cultural considerations play a significant role in shaping our understanding and perception of lucid dreaming. The impact of lucid dreaming on personal values, religious and spiritual views, and even legal implications cannot be overlooked.
Lucid dreaming has the potential to challenge and influence personal values. As individuals navigate and manipulate their dreams, they may encounter situations and scenarios that conflict with their moral beliefs or societal norms. The ability to exert control over dream content raises questions about the extent to which individuals should indulge in fantasies or pursue desires within their dreams, especially if those desires are considered unethical or harmful in waking life.
Religious and spiritual perspectives on lucid dreaming vary across different belief systems. Some interpret lucid dreaming as a form of spiritual enlightenment, a way to access higher realms of consciousness or commune with divine entities. Others may view it as a phenomenon that blurs the boundaries between the physical and spiritual realms. However, certain religious traditions caution against the potential dangers of lucid dreaming, associating it with practices that are deemed as forbidden or disruptive to the natural order of things.
From a legal standpoint, lucid dreaming exists in a murky space. Since the dream world exists solely within an individual’s consciousness, it is challenging to regulate or impose legal frameworks upon it. However, specific actions taken within the dream may have real-world consequences. For example, if a person intentionally harms or violates consent within their lucid dream, it raises ethical and legal concerns about the boundaries of personal responsibility and the potential impact on psychological well-being.
These societal and cultural considerations surrounding lucid dreaming highlight the complex interplay between our dreams and our wakeful lives. They invite us to reflect on the ethical implications of our actions and the far-reaching consequences of our subconscious desires. As lucid dreaming continues to captivate the imaginations of individuals worldwide, navigating these considerations becomes essential in fostering a conscious and responsible approach to this extraordinary phenomenon.
Impact on Personal Values
The impact of lucid dreaming on personal values can be profound and thought-provoking. When individuals have the ability to consciously navigate and manipulate their dreams, they have the opportunity to explore and challenge their own belief systems and values within the confines of the dream world. Lucid dreaming allows individuals to engage in scenarios that may be impossible or impractical in waking life, enabling them to question and reassess their moral and ethical boundaries. For example, someone who values honesty may find themselves in a lucid dream where they are tempted to deceive others. This can prompt deep introspection and reflection on the nature of honesty and its importance in their personal values. By confronting conflicting values and engaging with ethical dilemmas in the dream state, individuals can gain insights into their own character and develop a stronger understanding of their core values. The ability to consciously explore personal values in dreams may also lead to personal growth and the refinement of moral principles in waking life.
Religious and Spiritual Views
Religious and spiritual views on lucid dreaming vary across different cultures and belief systems. Some religious traditions perceive dreams as a means of communication between individuals and higher powers or divine realms. For example, in certain tribal cultures, lucid dreaming is considered a sacred practice that allows individuals to connect with their ancestors and receive guidance from the spiritual realm. In Hinduism, dreams are seen as a reflection of the soul’s journey through different realms, and lucid dreaming is seen as a way to gain insight into one’s spiritual progress. Similarly, in Buddhism, dreams are seen as illusions of the mind, and lucid dreaming is viewed as an opportunity to cultivate mindfulness and awareness.
On the other hand, some religious traditions view lucid dreaming with caution or even skepticism. In some branches of Christianity, lucid dreaming may be seen as an occult practice or a gateway to demonic influence. It is important to note that these perspectives on lucid dreaming within religious and spiritual contexts can vary widely, and individuals within the same tradition may hold different beliefs.
The interpretation of lucid dreams within religious and spiritual frameworks often depends on the individual’s cultural background and personal beliefs. Some individuals may incorporate lucid dreaming into their spiritual practices, using it as a tool for self-exploration, meditation, or connecting with the divine. Others may avoid or discourage lucid dreaming due to concerns about its potential for tampering with the natural order of dreams or spiritual experiences. Ultimately, the stance on lucid dreaming within religious and spiritual frameworks is subjective, and individuals are encouraged to consult their own beliefs and traditions to determine their views on this phenomenon.
Legal Implications
Legal implications play a significant role in the exploration of lucid dreaming. While it is a distinctly personal experience occurring within the realm of one’s mind, certain actions taken during a lucid dream might have legal consequences in the waking world. Understanding these implications is crucial for individuals practicing and experimenting with lucid dreaming.
One aspect that raises legal concerns is the potential for lucid dreaming to intersect with criminal behavior. As individuals gain control over their dreams, the line between imagination and reality can become blurred, potentially leading to unethical or harmful actions within the dream environment. For example, if someone were to harm or violate the rights of a dream character in a lucid dream, it raises questions of moral responsibility and legal accountability.
Another area of legal consideration is the concept of consent. Lucid dreamers have the ability to manipulate dream characters and engage in various activities within their dreams. However, the consent of these dream characters is questionable, as they are constructs of the dreamer’s mind. This raises ethical concerns regarding the extent to which dream characters can be influenced or manipulated without their consent. Although the legal framework in most jurisdictions currently does not directly address these issues, they open up discussions about the potential need for ethical guidelines and frameworks concerning lucid dreaming.
It is worth noting that the legal status of lucid dreaming itself is not a matter of concern in most jurisdictions. Lucid dreaming is a natural phenomenon that occurs during sleep and does not typically involve any illegal activities. However, individuals should be aware that their actions and decisions within a lucid dream may have consequences if they cross legal boundaries or infringe upon the rights of others in the waking world.
While lucid dreaming itself is not typically regulated by the law, the actions and decisions made within a dream can raise ethical and legal questions. The potential for criminal behavior, issues of consent, and the need for ethical guidelines are all important considerations within the legal implications of lucid dreaming.
Benefits and Perceived Dangers
Lucid dreaming offers a range of both benefits and perceived dangers, which contribute to its allure and intrigue. On the positive side, lucid dreaming has been linked to the enhancement of creativity and problem-solving abilities. By actively engaging with and manipulating the dream environment, individuals can explore new ideas, scenarios, and perspectives, potentially leading to innovative solutions in their waking lives. Lucid dreaming also holds promise as a therapeutic tool for addressing nightmares and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Through lucid dreaming, individuals can confront and reframe their fears within the safety of the dream world, promoting healing and reducing the negative impact of traumatic experiences.
However, there are also perceived dangers associated with lucid dreaming. One concern is the blurring of the line between reality and dreams. As individuals gain more control over their dream experiences, there is a risk of becoming detached from the waking world and prioritizing the dream realm over real-life responsibilities and relationships. Some argue that manipulating the content and characters within dreams raises ethical questions. While dreams are typically seen as a private and personal space, exerting influence over dream scenarios and dream characters could be interpreted as a violation of their autonomy and consent.
Despite these concerns, the overall impact of lucid dreaming on an individual’s well-being and psychological state remains subjective and highly personal. Some individuals find empowerment and enrichment through their lucid dreaming experiences, while others may find it disorienting or unsettling. It is essential to approach lucid dreaming with a balanced perspective, considering both the potential benefits and the potential risks. By understanding and navigating the ethical dimensions of lucid dreaming, individuals can make informed choices and harness its potential for personal growth and self-discovery.
Enhancing Creativity and Problem Solving
Enhancing Creativity and Problem Solving:
One of the fascinating benefits associated with lucid dreaming is its potential to enhance creativity and problem-solving skills. When individuals have the ability to consciously manipulate their dreams, they are presented with a limitless canvas on which they can explore and experiment with new ideas and concepts. Lucid dreaming provides a unique environment for creativity to flourish, as individuals have the freedom to create and shape their dream scenarios, indulge in imaginative experiences, and engage with their subconscious mind.
Within the realm of lucid dreams, individuals can encounter vivid and surreal landscapes, interact with fantastical characters, and even travel through time and space. This uninhibited exploration of the dream world can inspire individuals to think outside the box, challenge their preconceived notions, and develop innovative solutions to real-life problems.
Lucid dreaming allows individuals to practice and refine skills in a safe and controlled environment. For example, musicians may use lucid dreams to improvise and compose music, artists can experiment with different artistic styles and techniques, and athletes may visualize and perfect their athletic performance. Research has shown that engaging in these virtual practice sessions within lucid dreams can have a positive impact on skill acquisition and improvement in waking life.
Lucid dreaming offers a valuable platform for cultivating creativity, fostering imaginative thinking, and honing problem-solving abilities. By tapping into the vast realm of the unconscious mind, individuals can unlock their creative potential and embark on a journey of self-discovery and intellectual growth.
| Benefits of Lucid Dreaming: Enhancing Creativity and Problem Solving |
|---|
| 1. Exploration and Experimentation: Lucid dreaming provides a limitless canvas for exploring new ideas and concepts. |
| 2. Inspiring Innovation: Engaging with the dream world can inspire individuals to think outside the box and develop innovative solutions. |
| 3. Safe Skill Development: Lucid dreaming allows for practicing and refining skills in a safe and controlled environment. |
| 4. Virtual Practice Sessions: Musicians, artists, and athletes can utilize lucid dreams to practice and improve their skills. |
| 5. Self-Discovery and Growth: Lucid dreaming unlocks creative potential and fosters personal and intellectual growth. |
Treating Nightmares and PTSD
Studies have shown that lucid dreaming can be a valuable tool in treating nightmares and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Nightmares can be incredibly distressing, causing fear and anxiety that can linger even after waking up. However, being able to recognize and control the dream state in lucid dreaming offers a unique opportunity to confront and overcome these nightmares. By actively participating in the dream narrative, individuals can confront their fears, reframe the dream’s content, and ultimately transform the nightmare into a less threatening or more positive experience.
Lucid dreaming has shown promise in helping individuals with PTSD as well. PTSD often involves recurrent distressing dreams or nightmares related to a traumatic event. Through lucid dreaming, individuals may be able to confront and process their traumatic experiences in a safe and controlled environment. With the ability to manipulate the dream scenario, individuals can choose to confront their fears or modify the dream’s outcome, leading to a reduction in anxiety and an opportunity for emotional healing.
It is important to note that while lucid dreaming can be a potentially effective therapeutic technique, it should be approached with caution and in conjunction with professional guidance. It may not be suitable for everyone, and individuals with certain mental health conditions should consult with a qualified healthcare professional before attempting lucid dreaming as a form of treatment.
Lucid dreaming’s ability to empower individuals to actively engage with and alter the content of their dreams opens up exciting possibilities for therapy and self-improvement. By harnessing this unique state of consciousness, individuals can potentially find relief from nightmares and PTSD, offering a glimmer of hope and transformation in the realm of dream therapy.
Blurring the Line between Reality and Dreams
The concept of lucid dreaming raises thought-provoking questions about the boundary between reality and dreams. When individuals can consciously control and manipulate their dreams, it can blur the line between what is imagined and what is considered real. This blurring of boundaries can have both profound and fascinating implications.
On one hand, lucid dreaming can provide an opportunity for individuals to explore and experience scenarios that may not be possible or feasible in waking life. It allows people to engage in creative endeavors, visit exotic locations, or even interact with their favorite fictional characters. This aspect of lucid dreaming can be seen as a form of escapism or a way to fulfill unattainable desires.
However, the blurring of reality and dreams can also have potential drawbacks. A person who frequently engages in lucid dreaming may find it difficult to distinguish between dream experiences and waking life. This can lead to confusion, disorientation, and difficulty in distinguishing between what is real and what is imagined. In some cases, individuals may start questioning their own memories, wondering if certain events actually happened or if they were part of a dream.
The blurring of boundaries between reality and dreams can have implications on decision-making and personal identity. When individuals have the power to control their dreams, they may start questioning the boundaries of their own autonomy. They may wonder whether they should be held accountable for their actions within dreams, especially if those actions would be considered immoral or unethical in waking life.
Lucid dreaming has the potential to blur the line between reality and dreams, offering both exciting opportunities and thought-provoking challenges. It allows individuals to explore their creativity and fulfill fantasies but also raises questions about personal identity and decision-making. The line between the conscious mind and the dreaming mind becomes increasingly hazy as individuals navigate the realm of lucid dreaming.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lucid dreaming is a fascinating and complex phenomenon that raises numerous ethical and moral implications. By understanding the definition and characteristics of lucid dreaming, we can appreciate the scientific research that has shed light on this extraordinary state of consciousness. Exploring the ethical dimensions of lucid dreaming reveals the potential for influencing dream content, manipulating dream characters, and the moral responsibility that arises within the dream realm. Additionally, societal and cultural considerations highlight the impact of lucid dreaming on personal values, religious and spiritual views, and even legal implications. While there are both benefits and perceived dangers associated with lucid dreaming, from enhancing creativity and problem-solving to treating nightmares and blurring the line between reality and dreams, it is crucial to approach this phenomenon with mindfulness and caution. Lucid dreaming provides us with a unique opportunity to delve into the depths of our minds and explore the vast potential of our consciousness, but it is essential to navigate the ethical landscape and consider the consequences of our actions in this dream realm. As we continue to unravel the mysteries of lucid dreaming, may we do so with a sense of wonder, curiosity, and respect for both ourselves and the fabric of our dreams.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What exactly is lucid dreaming?
Lucid dreaming is a state in which a person becomes aware that they are dreaming while still asleep. It allows individuals to consciously navigate and manipulate their dreams, blurring the line between imagination and reality.
2. Is lucid dreaming a common experience?
While exact statistics are challenging to determine, research suggests that approximately 55% of people have experienced at least one lucid dream in their lifetime. However, the frequency of lucid dreaming varies widely among individuals.
3. Can anyone learn to have lucid dreams?
Yes, with practice and various techniques, most people can learn to have lucid dreams. Methods like reality checks, dream journaling, and mnemonic induction can increase the likelihood of experiencing lucid dreams.
4. Are there any potential risks associated with lucid dreaming?
For the majority of individuals, lucid dreaming is considered safe. However, it’s essential to maintain a healthy sleep routine and prioritize mental well-being. Some people may experience sleep disruptions or struggle with differentiating between dreams and reality, which can affect overall sleep quality and daily functioning.
5. Can lucid dreaming have therapeutic benefits?
Yes, lucid dreaming has shown potential therapeutic benefits. It can be used to treat nightmares, phobias, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Lucid dreaming can also aid in creative problem-solving, self-reflection, and personal growth.
6. Are there any cultural or religious beliefs associated with lucid dreaming?
Yes, various cultural and religious traditions have recognized and explored lucid dreaming throughout history. Practices like Tibetan dream yoga and Aboriginal dreamtime spirituality incorporate lucid dreaming as a means of spiritual exploration and personal transformation.
7. Can lucid dreaming be used to enhance creativity?
Absolutely. Lucid dreaming provides a unique platform for engaging with the creative elements of the subconscious mind. Many artists, writers, and musicians have drawn inspiration from their lucid dreams, finding new ideas and perspectives that enrich their creative endeavors.
8. Is lucid dreaming similar to astral projection?
Lucid dreaming and astral projection are often confused, but they are distinct experiences. Lucid dreams occur within the dreamer’s mind, while astral projection involves an out-of-body experience where the individual perceives themselves as separate from their physical body.
9. Can lucid dreaming be controlled to manipulate dream scenarios or outcomes?
Yes, one of the intriguing aspects of lucid dreaming is the ability to exert control over dream content. Lucid dreamers can manipulate dream scenarios, interact with dream characters, and even alter the dream environment according to their conscious intentions.
10. Do people experience lucid dreaming during specific phases of sleep?
Lucid dreaming can occur during any stage of sleep, but it is most commonly reported during Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep. REM sleep is associated with vivid dreams, and it is the stage where lucidity is more easily achieved.